flora
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
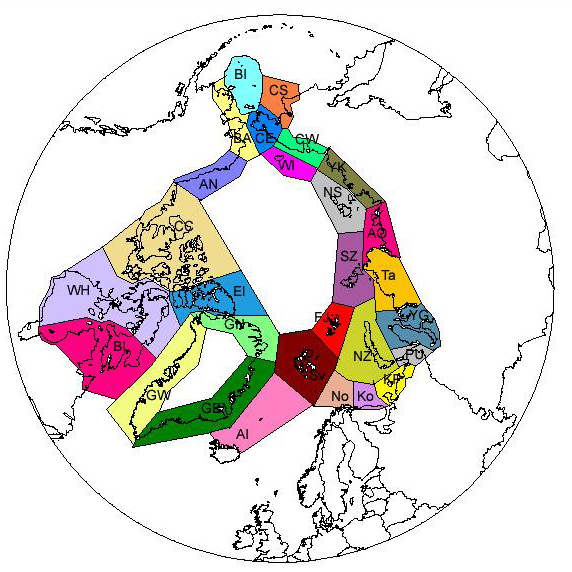
Subdivision of the Arctic into 28 sectors follows mainly the division used in the Pan Arctic Flora (PAF) project. In a few cases some islands are separated from their mainland in the beginning, thus representing very small sectors. Some of them have now been united like in the PAF project, for example Jan Mayen with Arctic Iceland and Bear Island with Svalbard. Others, like the Beringian Islands are still kept separate from the mainland on both sides. - <a href="http://www.caff.is/assessment-series/32-pan-arctic-checklist-of-lichens-and-lichenicolous-fungi" target="_blank"> Pan-Arctic Checklist of Lichens and Lichenicolous Fungi (2011)</a>
-
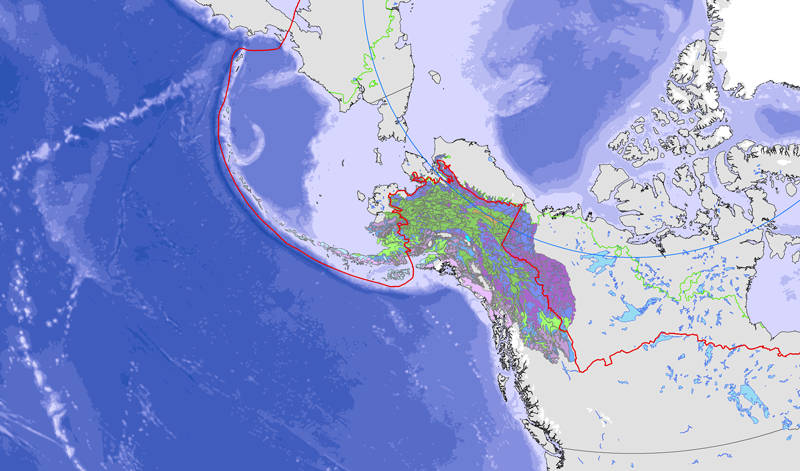
<a href="http://caff.is/strategies-series/359-the-alaska-yukon-region-of-the-circumboreal-vegetation-map-cbvm" target="_blank"> <img width="150px" height="150px" alt="logo" align="left" hspace="10px" src="http://geo.abds.is/geonetwork/images/flora_logo.png"> </a>A map of boreal vegetation for the Alaska-Yukon region was developed to contribute to the circumboreal vegetation mapping (CBVM) project. The effort included developing a map of bioclimates with 12 bioclimate zones, a map of biogeographic provinces with Alaska-Yukon and Aleutian provinces, and a map of geographic sectors with six sectors that provided the basis for classification of boreal vegetation. Vegetation mapping was done at 1:7.5 million scale using the mapping protocols of the CBVM team. Mapping used MODIS imagery as the basis for manual image interpretation and an integrated-terrain-unit approach, which included classifications for bioclimate, physiography, generalized geology, permafrost, disturbance, growth from, geographic sector, and vegetation. Vegetation was mapped at two hierarchical levels: (1) formation group differentiating zonal and azonal systems; and (2) geographic sectors based on bioclimatic zonation and dominant species that characterize broad longitudinal regions or biogeographic provinces. Each of the 19 map units was described by identifying the dominant and characteristic species and its climatic and landscape characteristics, as well as references that relate to the unit.
-
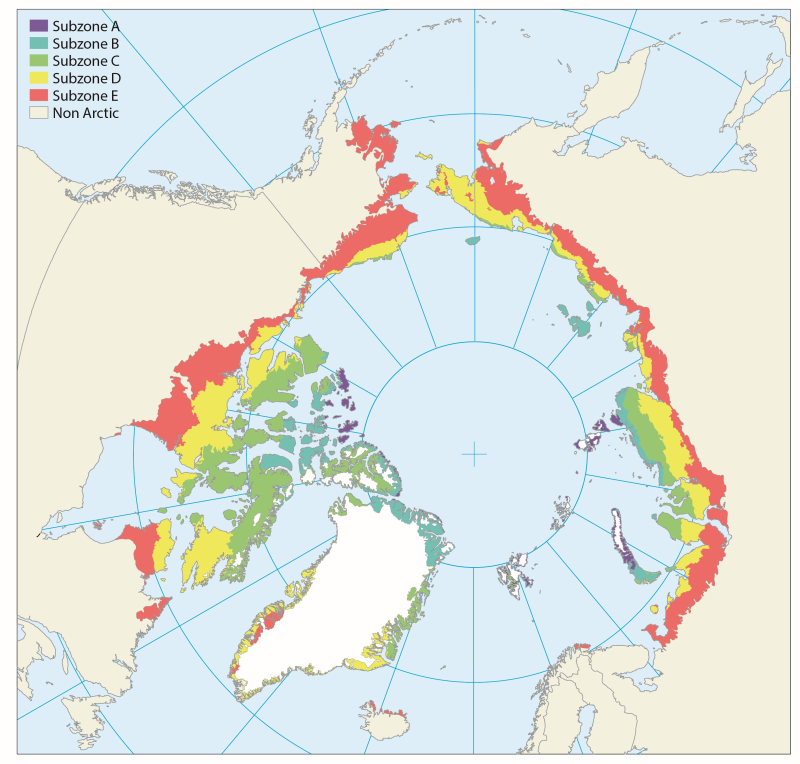
Based on published scientific literature, the diversity of plants in the Arctic is reviewed. The plants are divided into three main groups according to essential differences in anatomy, morphology and reproduction. These are vascular plants, bryophytes (mosses and liverworts) and algae (micro- and macroalgae). As a whole, these three plant groups have the ability to perform photosynthesis. As primary producers they play a key role in the environment, since photosynthesis provides resources for all other organisms. Vascular plants and bryophytes (together with the lichenized fungi, the lichens) are the main structural components of terrestrial vegetation and ecosystems, while algae are more abundant in fresh water and marine ecosystems. Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Plants (Chapter 9)
 Arctic Biodiversity Data Service - ABDS Catalog
Arctic Biodiversity Data Service - ABDS Catalog