Land cover
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
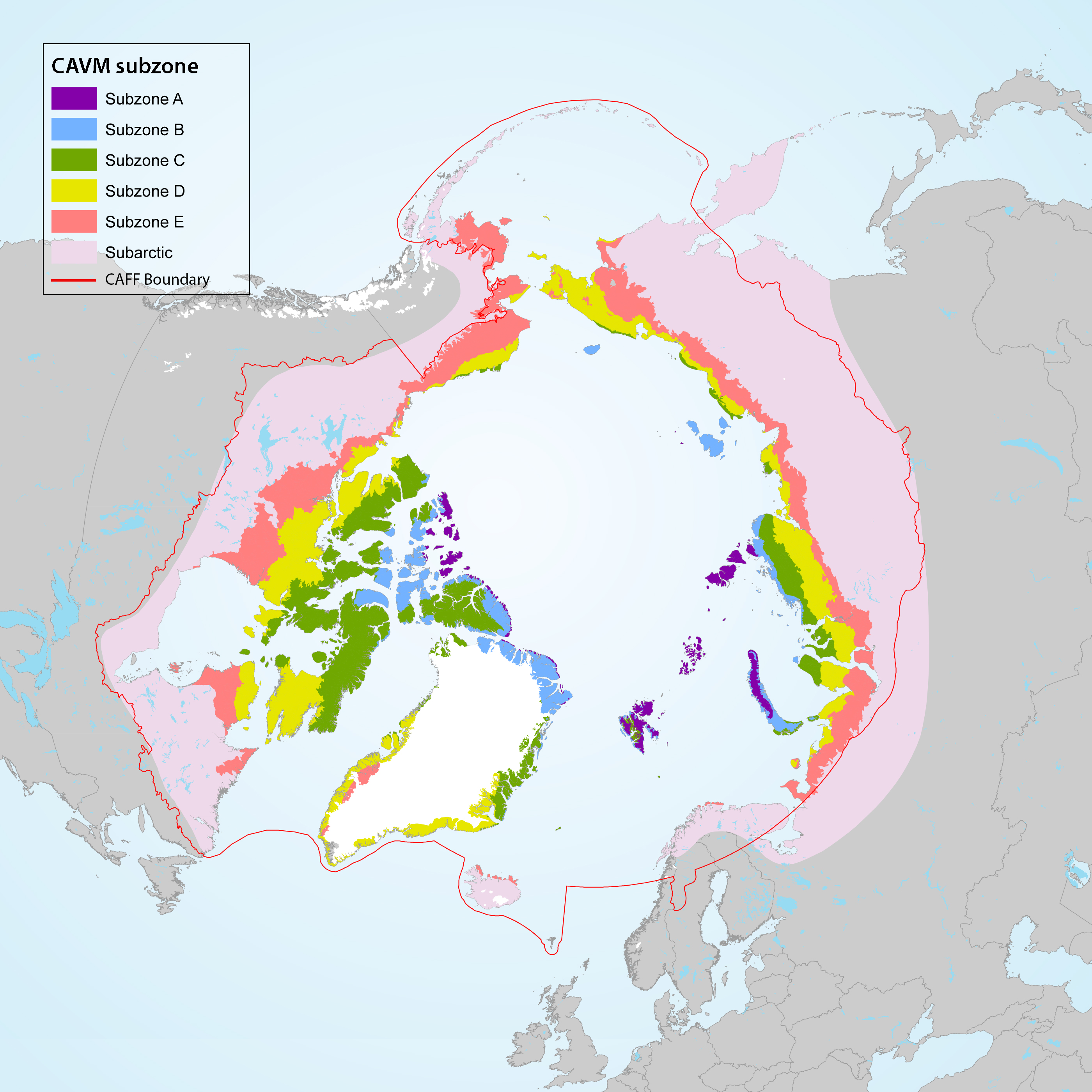
Geographic area covered by the Arctic Biodiversity Assessment and the CBMP–Terrestrial Plan. Subzones A to E are depicted as defined in the Circumpolar Arctic Vegetation Map (CAVM Team 2003). Subzones A, B and C are the high Arctic while subzones D and E are the low Arctic. Definition of high Arctic, low Arctic, and sub-Arctic follow Hohn & Jaakkola 2010. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 1 - Page 14 - Figure 1.2
-
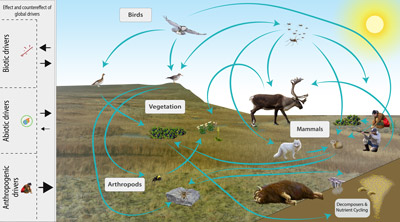
The Arctic terrestrial food web includes the exchange of energy and nutrients. Arrows to and from the driver boxes indicate the relative effect and counter effect of different types of drivers on the ecosystem. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 26- Figure 2.4
-
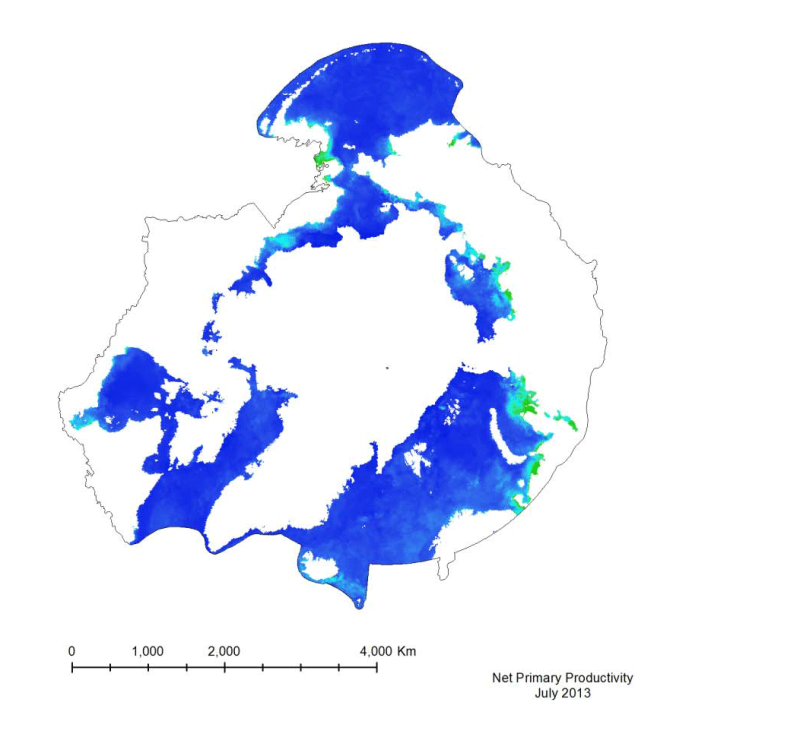
Marine primary productivity is not available from the NASA Ocean Color website. Currently the best product available for marine primary productivity is available through Oregon State University’s Ocean Productivity Project. A monthly global Net Primary Productivity product at 9 km spatial resolution has been selected for this analysis. The algorithm used to create the primary productivity is a Vertically Generalized Production Model (VGPM) created by Behrenfeld and Falkowski (1997). It is a “chlorophyll-based” model that estimates net primary production from chlorophyll using a temperature-dependent description of chlorophyll photosynthetic efficiency (O’Malley 2010). Inputs to the function are chlorophyll, available light, and photosynthetic efficiency.
-
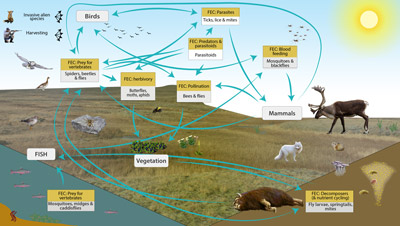
Conceptual model of the FECs and processes mediated by more than 2,500 species of Arctic arthropods known from Greenland, Iceland, Svalbard, and Jan Mayen. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 37- Figure 3.7
-
Trend quality categories are: (1) data are lacking such that trends are unknown, (2) regional and site-specific monitoring allow for assumptions of trend, (3) international monitoring allows estimation of trend direction, and (4) rigorously designed international monitoring programmes yield estimates of precision. Modified from Smith et al. 2020. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapte31 - Page 59 - Figure 3.26
-
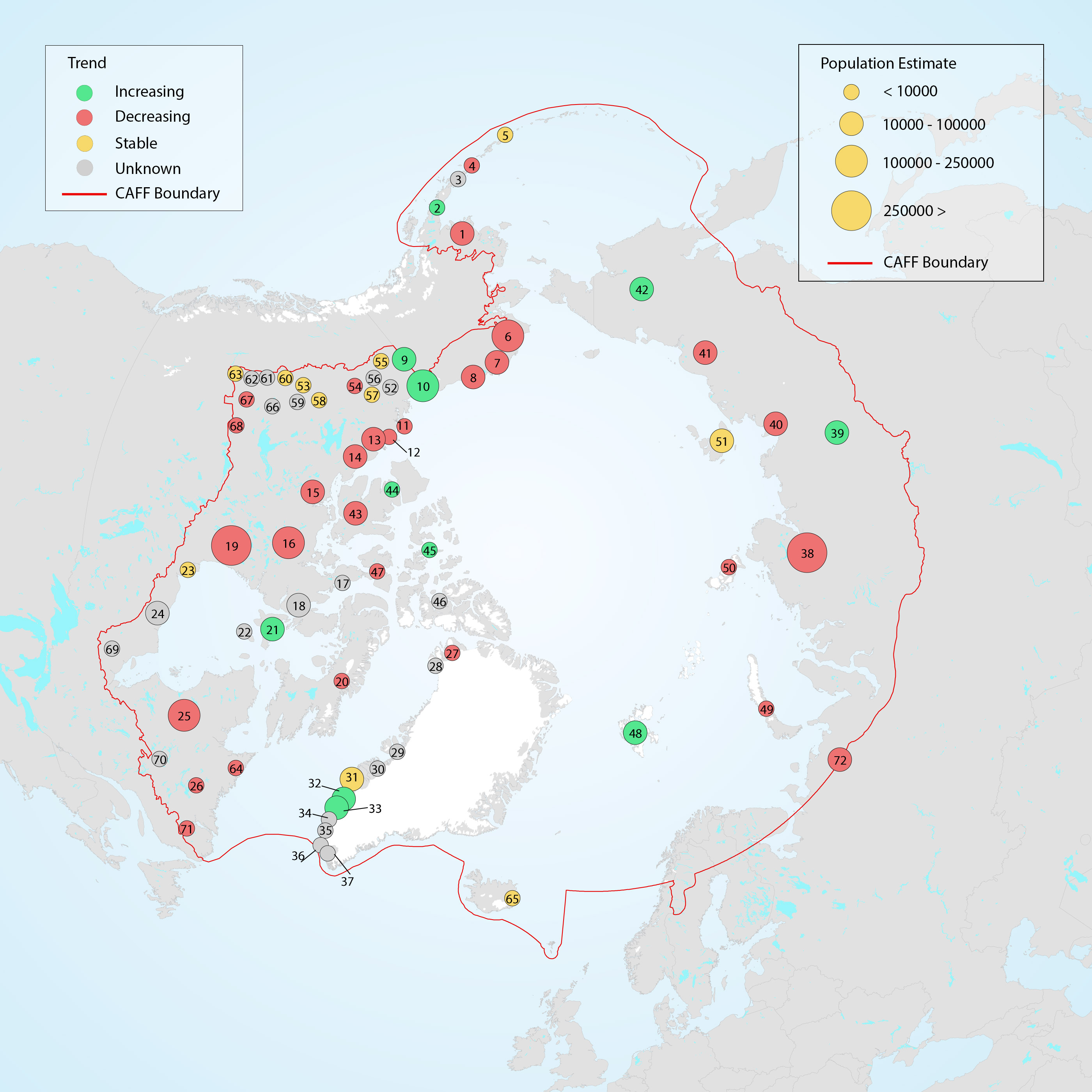
Several smaller populations of caribou inhabit sub-Arctic portions of Alaska, including five populations along the Aleutian Archipelago and west coast. These populations are considered part of the migratory tundra ecotype based on genetics, although in some instances their ecology and habitat are similar to the mountain caribou ecotype found in western Canada. Population dynamics and trends for these populations are variable (Figure 3-29). They are managed by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game through hunting quotas. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 72 - Figure 3.29
-
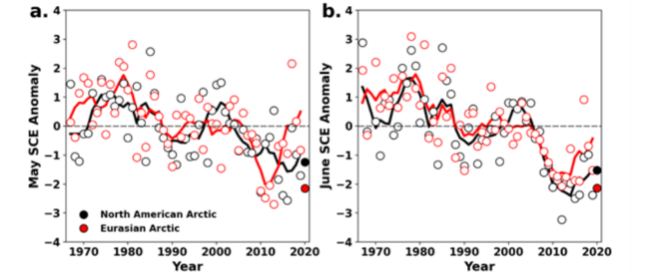
Monthly snow cover extent (SCE) for Arctic land areas (>60° N) for (a) May and (b) June 1967–2020, a 54-year record. Anomalies are relative to the 1981–2010 average and standardised (each observation was differenced from the mean and divided by the standard deviation, and thus unitless). Solid black and red lines depict 5-year running means for North America and Eurasia, respectively. Filled circles are used to highlight 2020 anomalies. (Mudryk et al. 2020). STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 23 - Figure 2.3
-
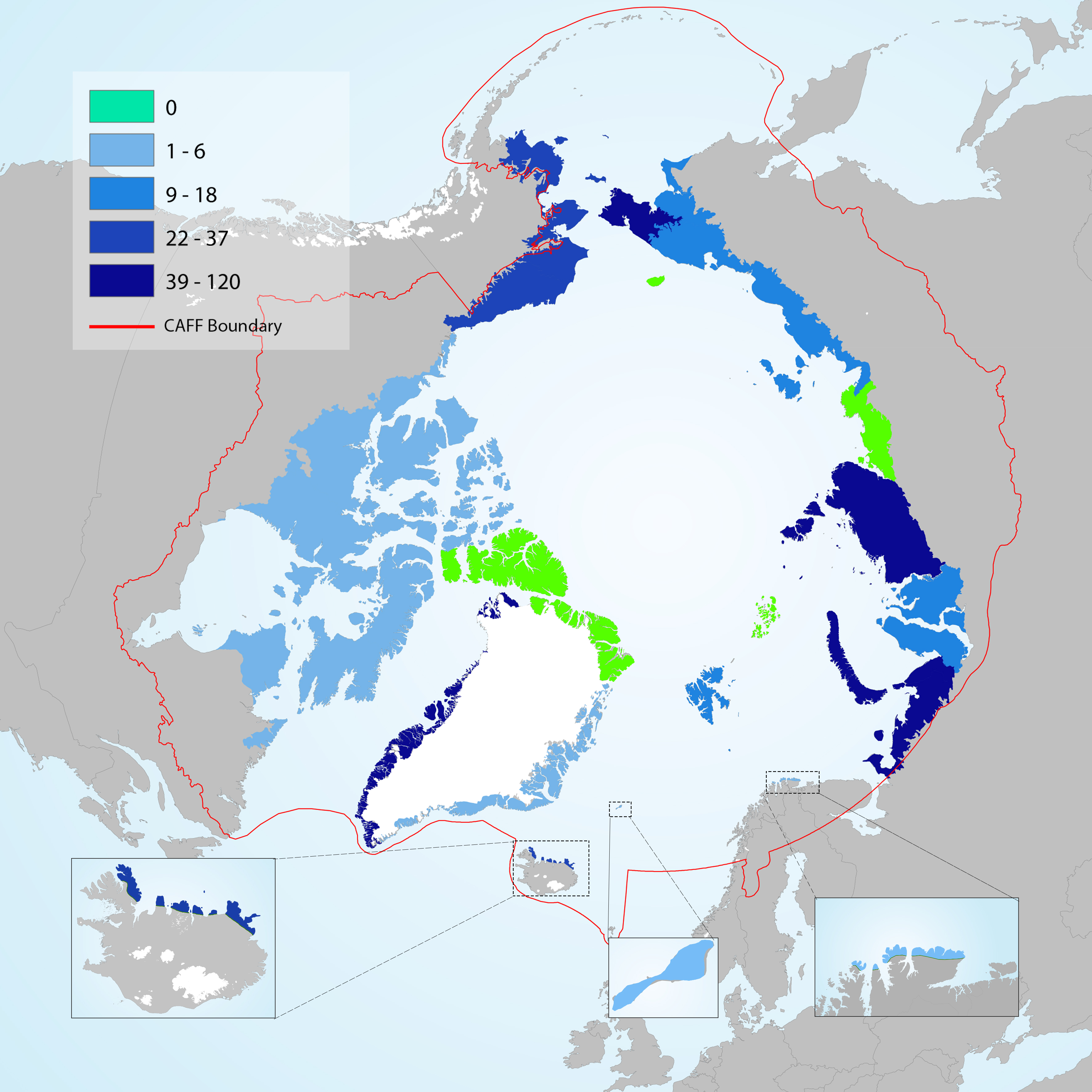
Number of non-native plant taxa that have become naturalised across the Arctic. No naturalised non-native taxa are recorded from Wrangel Island, Ellesmere Land – northern Greenland, Anabar-Olenyok and Frans Josef Land. Modified from Wasowicz et al. 2020 STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 32 - Figure 3.4
-
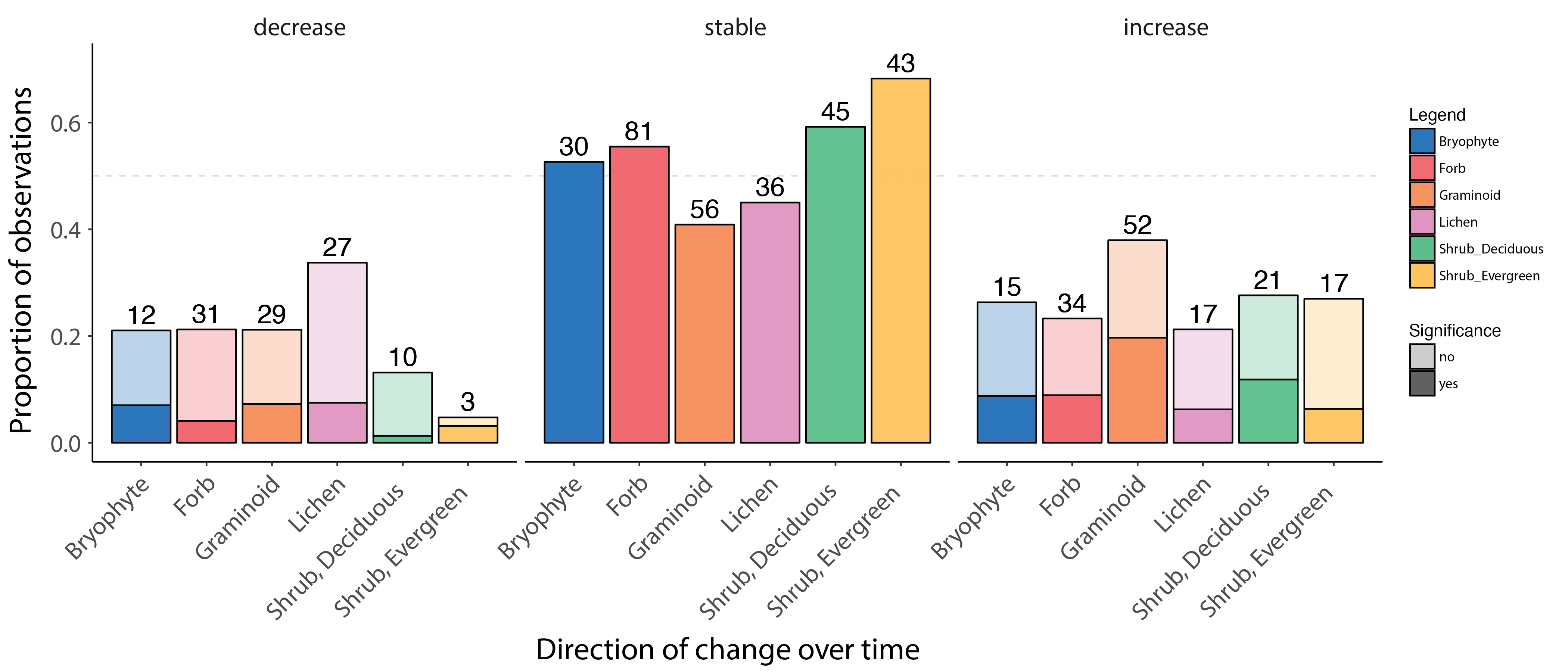
Change in forb, graminoid and shrub abundance by species or functional group over time based on local field studies across the Arctic, ranging from 5 to 43 years of duration. The bars show the proportion of observed decreasing, stable and increasing change in abundance, based on published studies. The darker portions of each bar represent a significant decrease, stable state, or increase, and lighter shading represents marginally significant change. The numbers above each bar indicate the number of observations in that group. Modified from Bjorkman et al. 2020. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 31- Figure 3.2
-
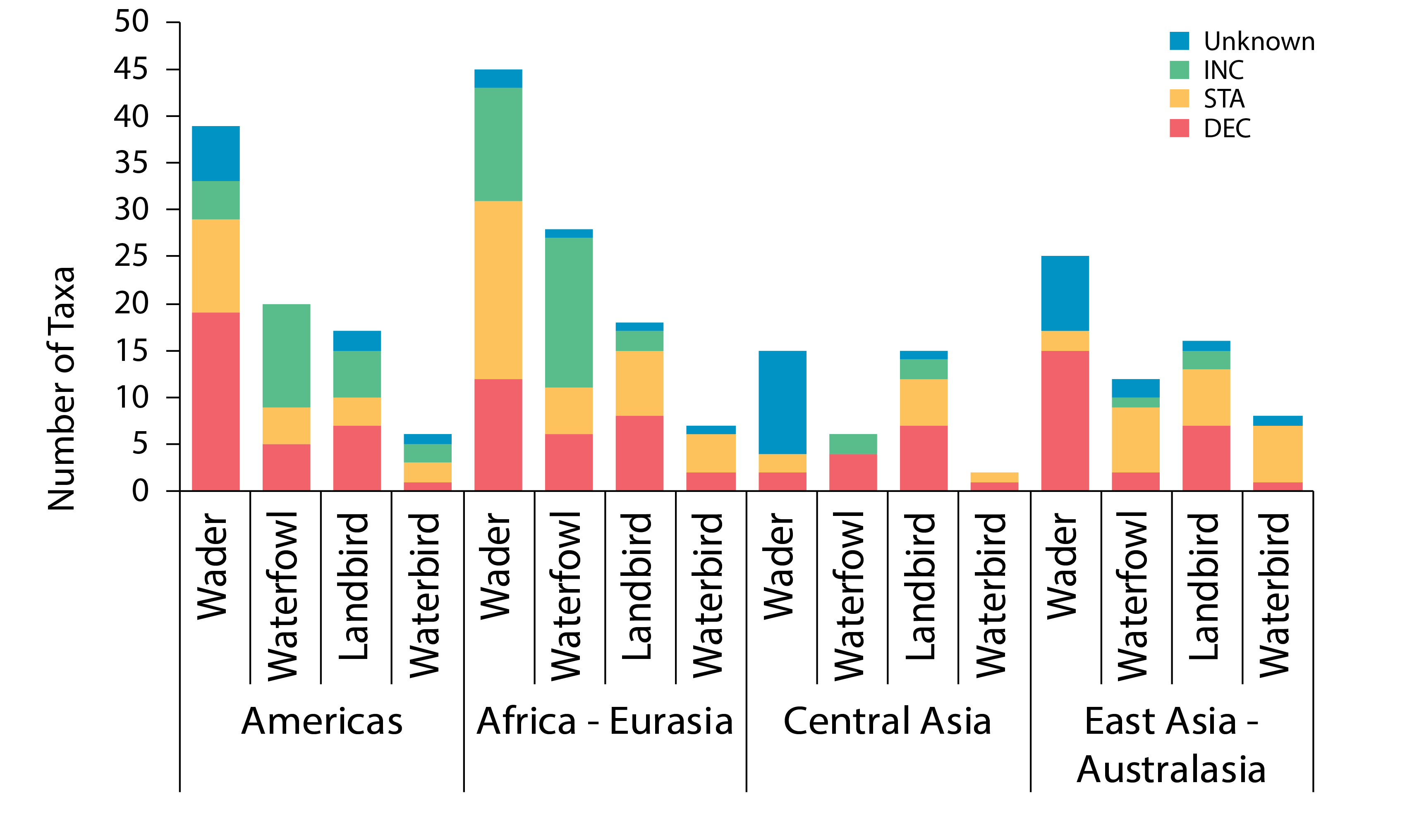
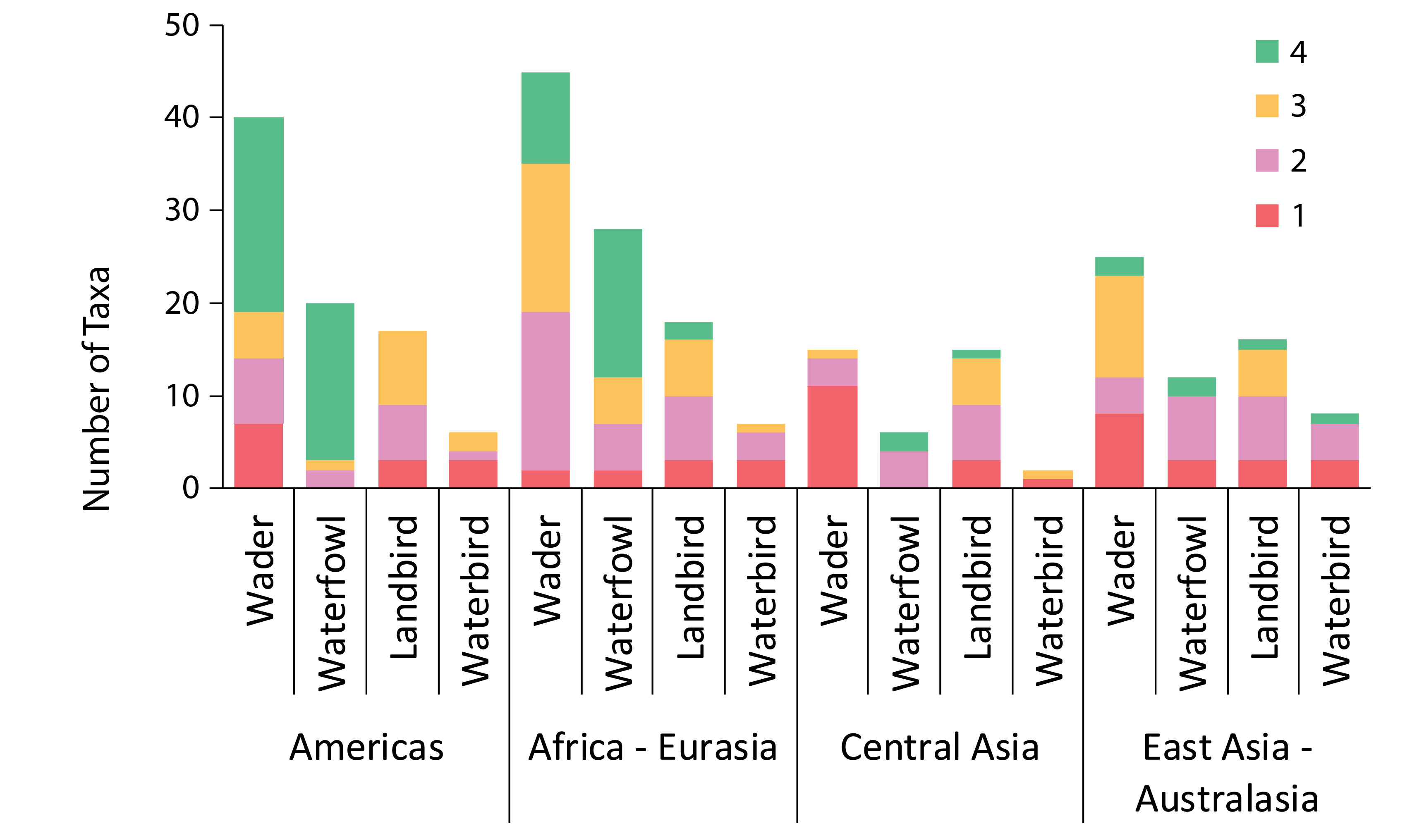
Trends in Arctic terrestrial bird population abundance for four taxonomic groupings in four global flyways. Data are presented as total number of taxa (species, subspecies). Modified from Smith et al. 2020. These broad patterns were generally consistent across flyways, with some exceptions. Fewer waterfowl populations increased in the Central Asian and East Asian–Australasian Flyways. The largest proportion of declining species was among the waders in all but the Central Asian Flyway where the trends of a large majority of waders are unknown. Although declines were more prevalent among waders than other taxonomic groups in both the African–Eurasian and Americas Flyways, the former had a substantially larger number of stable and increasing species than the latter (Figure 3-23). STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 55 - Figure 3.23
 Arctic Biodiversity Data Service - ABDS Catalog
Arctic Biodiversity Data Service - ABDS Catalog