Shapefile
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
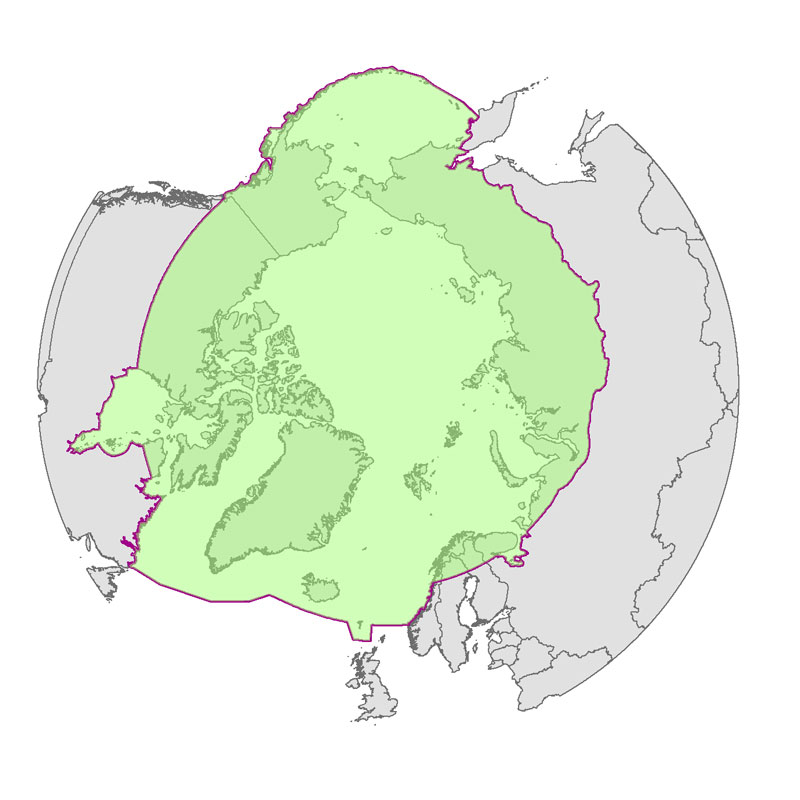
Defines the area covered by the the Arctic Assessment and Monitoring Programme (AMAP www.amap.no) working group of the Arctic Council.
-
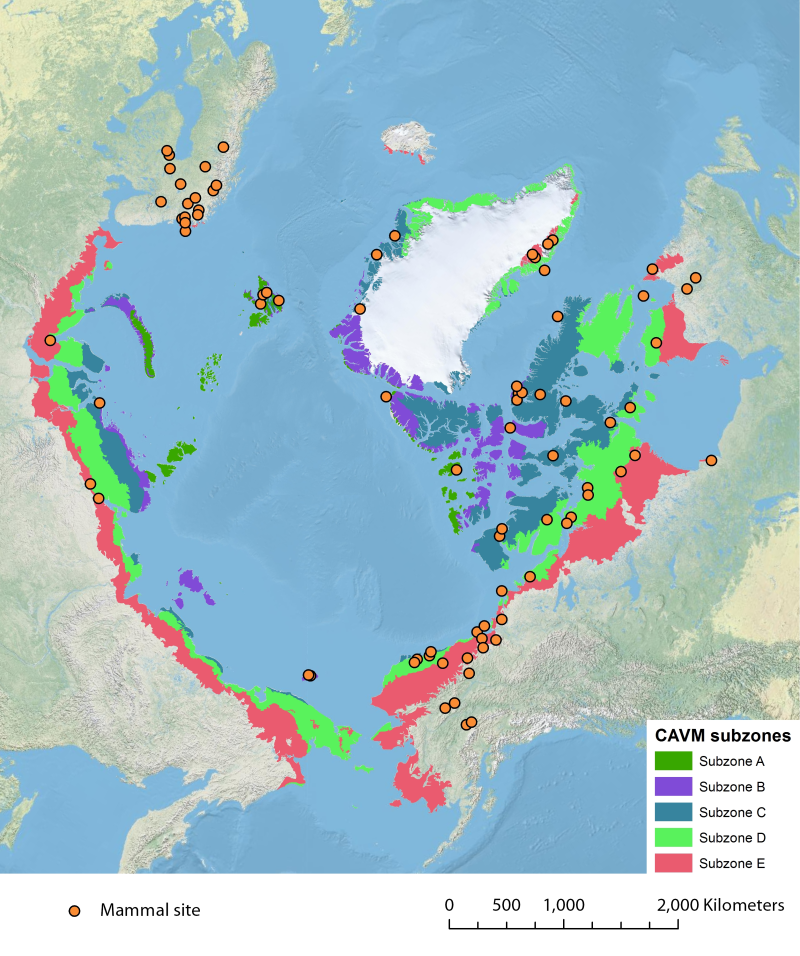
Location of long-term mammal monitoring sites and programs. Comes from the Arctic Terrestrial Biodiversity Monitoring Plan is developed to improve the collective ability of Arctic traditional knowledge holders, northern communities and scientists to detect, understand and report on long-term change in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity..
-
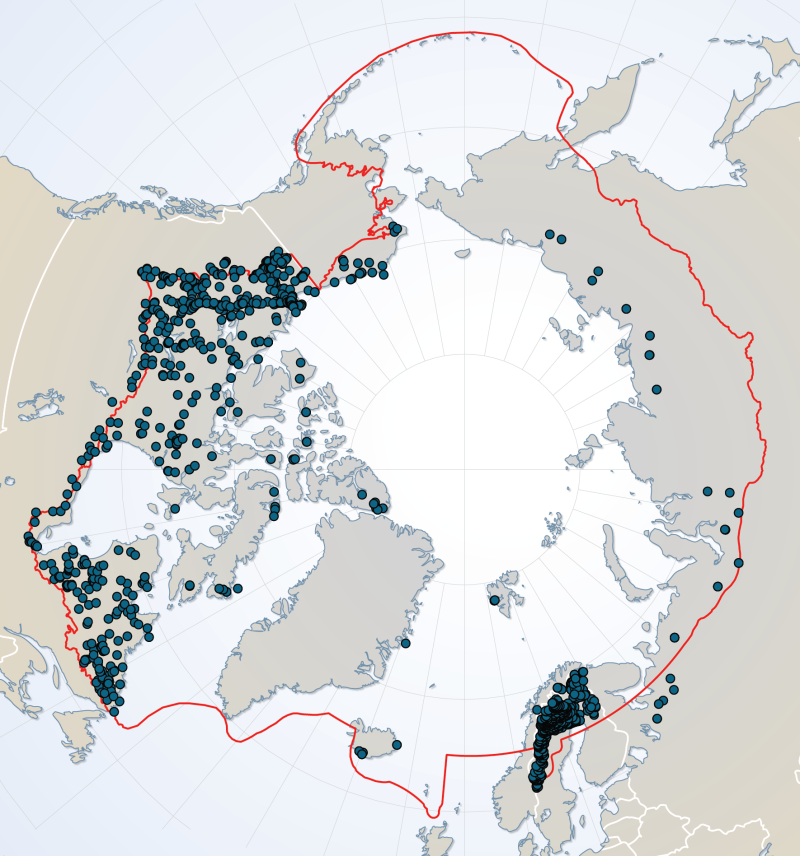
River dataset showing location of study sites in rivers for the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Monitoring Plan. Published in the Arctic Freshwater Monitoring Plan Brochure released in 2013 http://www.caff.is/monitoring-series/view_document/277-arctic-freshwater-biodiversity-monitoring-plan-brochure
-
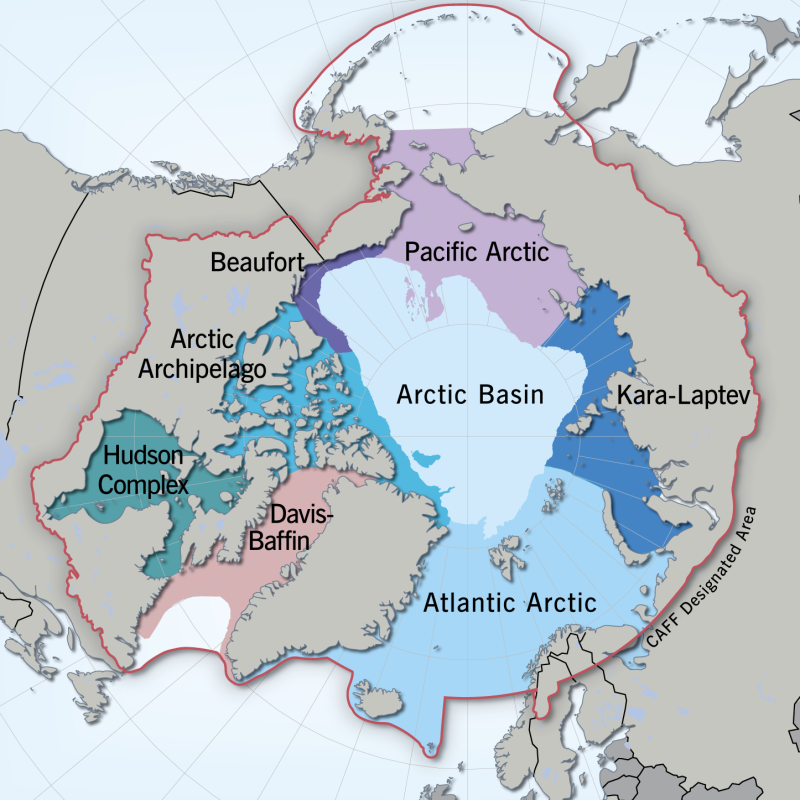
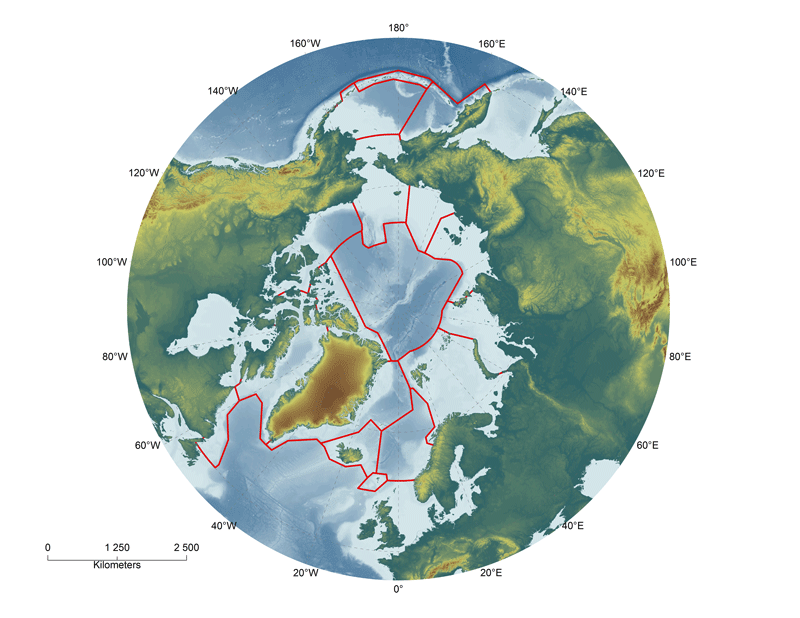
Regional divisions of the marine Arctic, as determined by the Marine Expert Monitoring Group of the Circumpolar Biodiversity Monitoring Programme (CBMP). The Circumpolar Marine Biodiversity Monitoring plan identifies eight Arctic Marine Areas where a suite of common parameters, sampling approaches and indicators will be used. Regionally specific parameters may also be applied. Exact boundaries may change over time to reflect changing bio-physical conditions. <a href="http://caff.is/marine/marine-monitoring-publications/3-arctic-marine-biodiversity-monitoring-plan" target="_blank"> Published in the Arctic Marine Biodiversity Monitoring Plan, Chapter 2, page20 - released in 2011 </a>
-
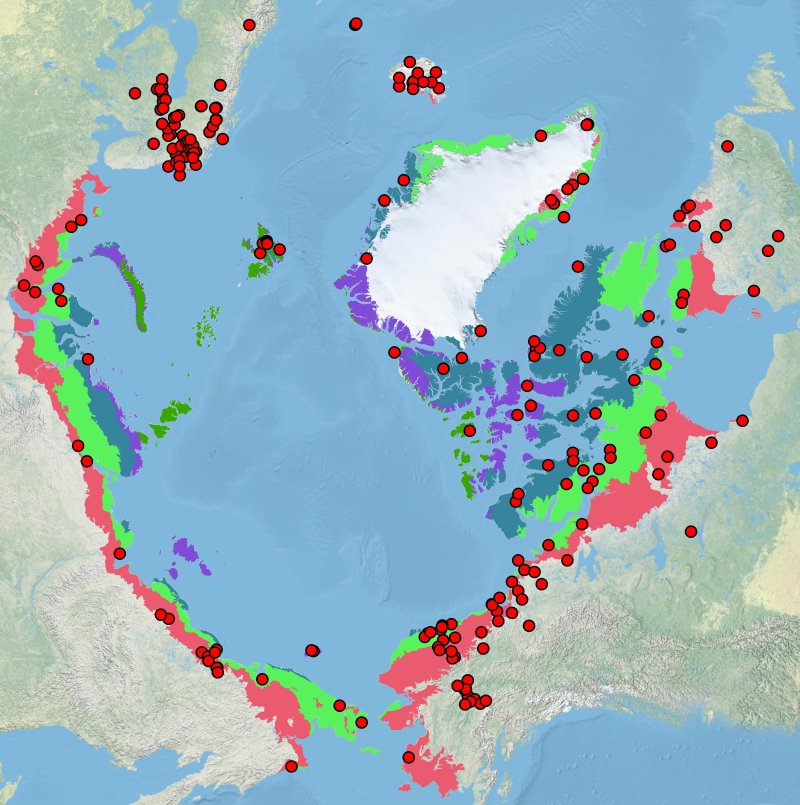
Sites of existing lake biotic and abiotic data as compiled by the Freshwater Expert Monitoring Group (FEMG) of the Circumpolar Biodiversity Monitoring Group (CBMP) Published in the CBMP Freshwater Brochure 2013 https://oaarchive.arctic-council.org/items/e76cce2c-4c87-4eb4-89d3-c88c3ae955d6
-
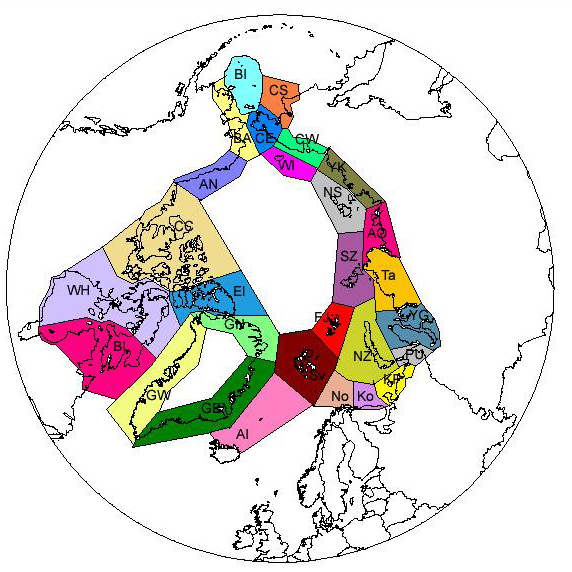
Subdivision of the Arctic into 28 sectors follows mainly the division used in the Pan Arctic Flora (PAF) project. In a few cases some islands are separated from their mainland in the beginning, thus representing very small sectors. Some of them have now been united like in the PAF project, for example Jan Mayen with Arctic Iceland and Bear Island with Svalbard. Others, like the Beringian Islands are still kept separate from the mainland on both sides. - <a href="http://www.caff.is/assessment-series/32-pan-arctic-checklist-of-lichens-and-lichenicolous-fungi" target="_blank"> Pan-Arctic Checklist of Lichens and Lichenicolous Fungi (2011)</a>
-
The Arctic Terrestrial Biodiversity Monitoring Plan is developed to improve the collective ability of Arctic traditional knowledge holders, northern communities and scientists to detect, understand and report on long-term change in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity.
-
A total of 95 areas of heightened ecological significance have been identified within the Arctic LMEs. The areas were identified primarily on the basis of their ecological importance to fish, birds and/or mammals, as these species are the most widely studied Arctic groups. The majority of areas identified are used by birds (85) and marine mammals (81), with a lower number used by fish (40, most of them spawning areas). About 70 areas are used both by birds and mammals, and only two of the areas identified are used only by fish.The areas of heightened ecological significance comprise a total area of about 12 million km2, or more than half the total area of the ice-covered part of the marine Arctic. The areas are generally not homogenous but comprise subareas used by fish, birds or mammals. Based on the approach used, subareas were identified separately for fish, birds, and mammals, or information on the use of the larger areas by these groupswas summarized. The subareas often overlap and are also often used by two or more species of birds or mammals, such as for breeding in seabird colonies or for staging by waterfowl and shorebirds. Information on species present and the times and purposes of use are given in summary tables for each LME. Thus, while the areas identified as being of heightened ecological significance cover a large total area, this is the aggregate area used over all seasons throughout the year. The area used at any one time is lower due to the strong seasonal pattern in the annual migratory cycles of fish, birds and mammals.
-
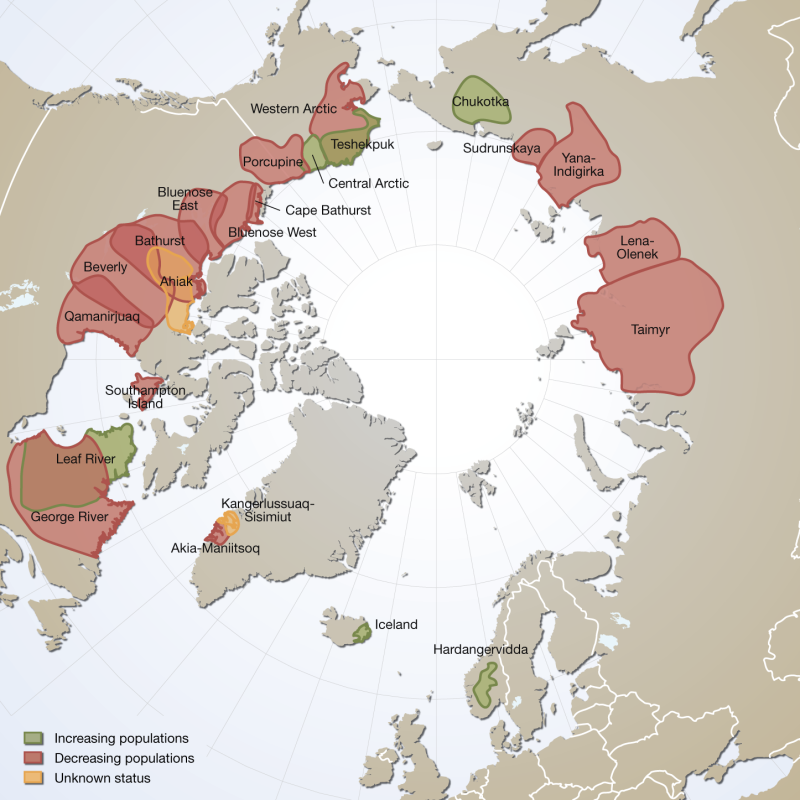
Distribution and observed trends of wild Rangifer populations throughout the circumpolar Arctic (from The Circum Arctic Rangifer Monitoring and Assessment Network, CARMA). Note: Wild boreal forest reindeer have not been mapped by CARMA and thus are not represented here. Published in the Arctic Biodiversity Trends 2010 - Selected indicators of change, INDICATOR #02 - released in 2010
-
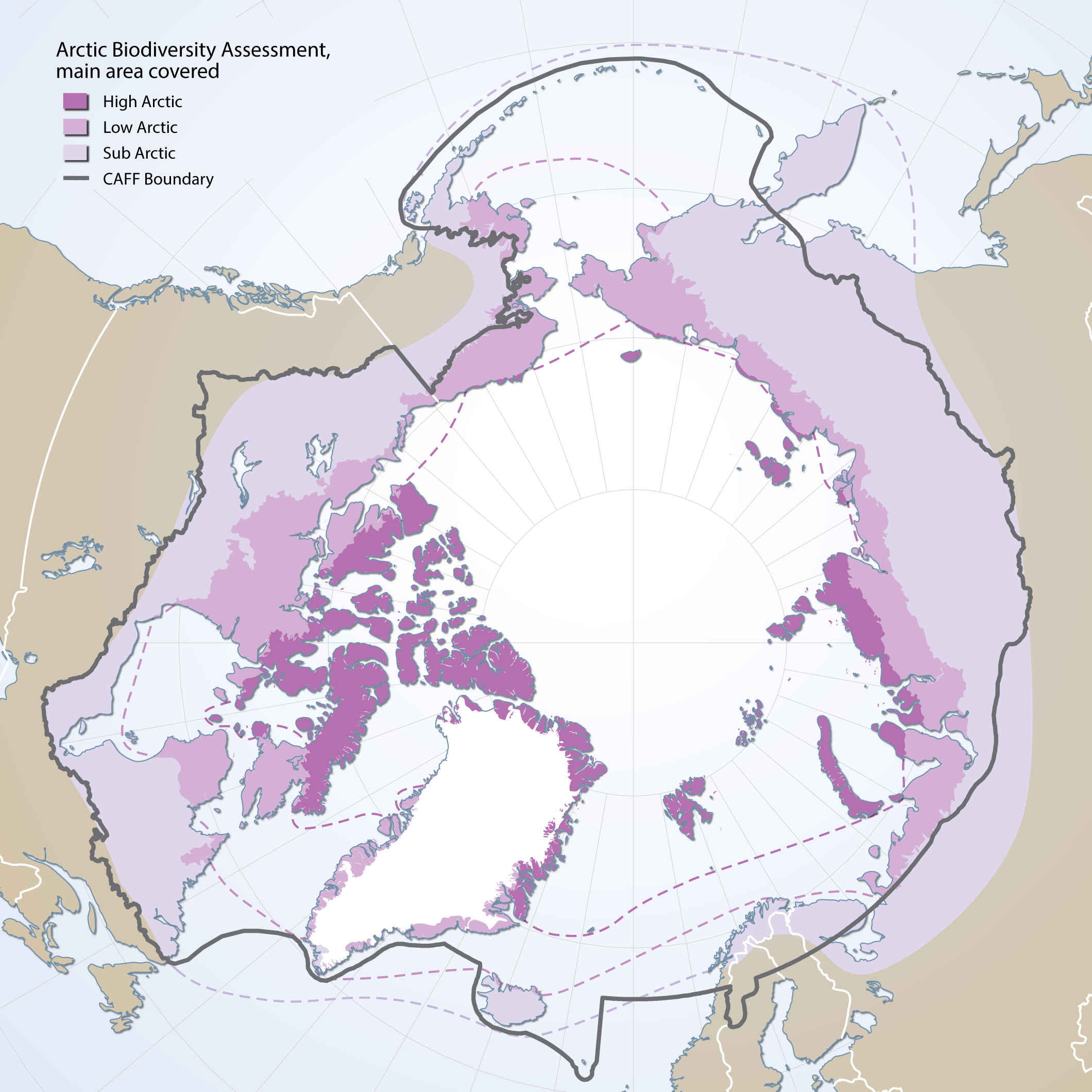
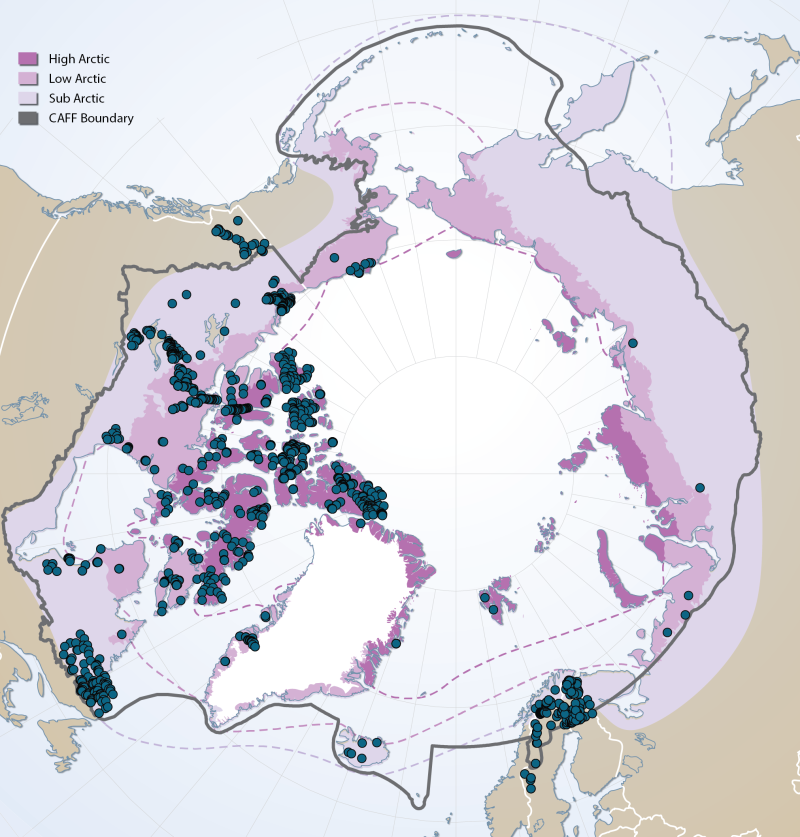
Boundaries of the geographic area covered by the Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Includes sub, low and high Arctic bounbaries
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)