inlandWaters
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
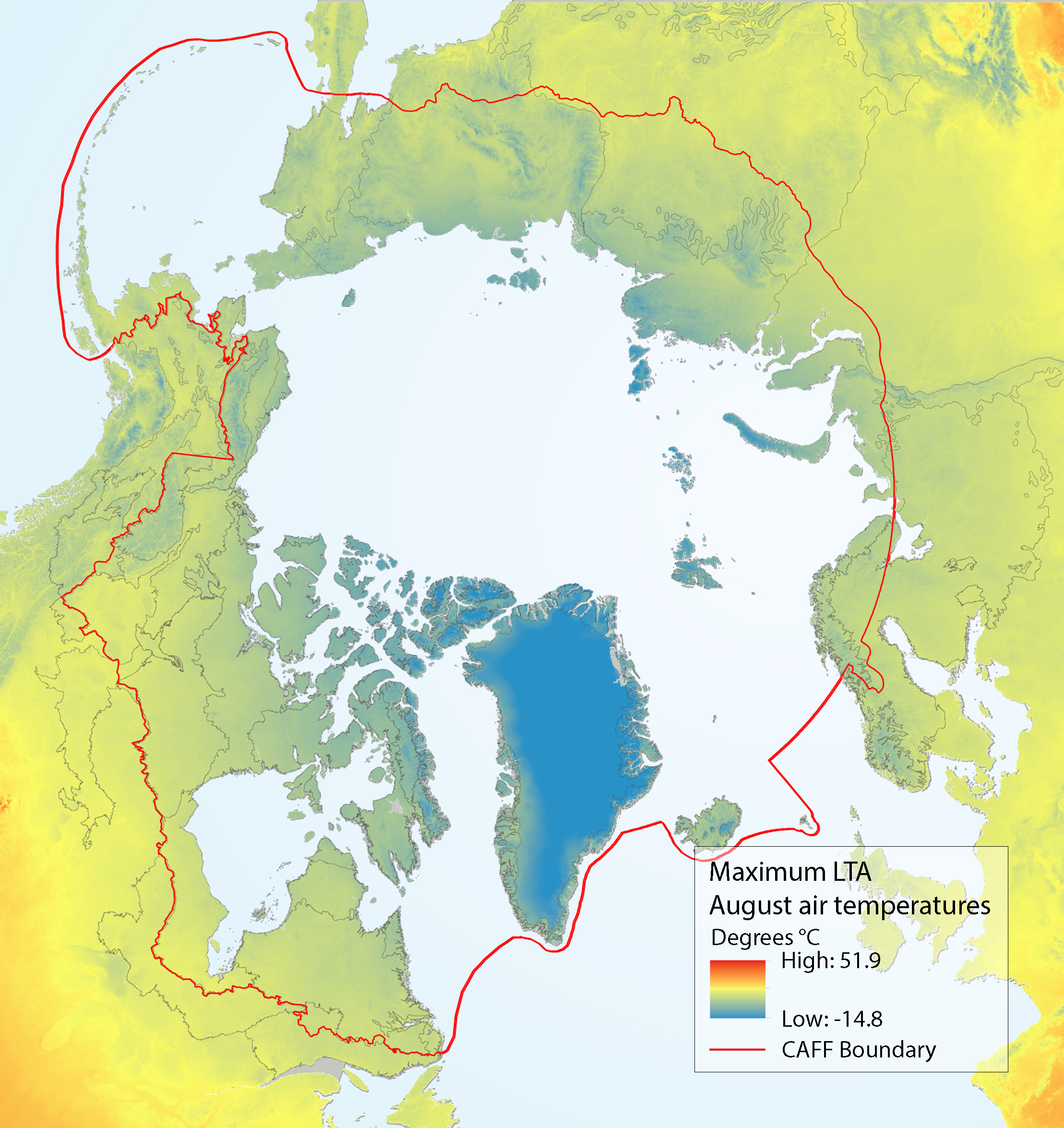
Maximum LTA (long-term average) August air temperatures for the circumpolar region, with ecoregions used in the analysis of the SAFBR outlined in black. Source for temperature layer: Fick and Hijmans (2017). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 5 - Page 89 - Figure 5-5
-
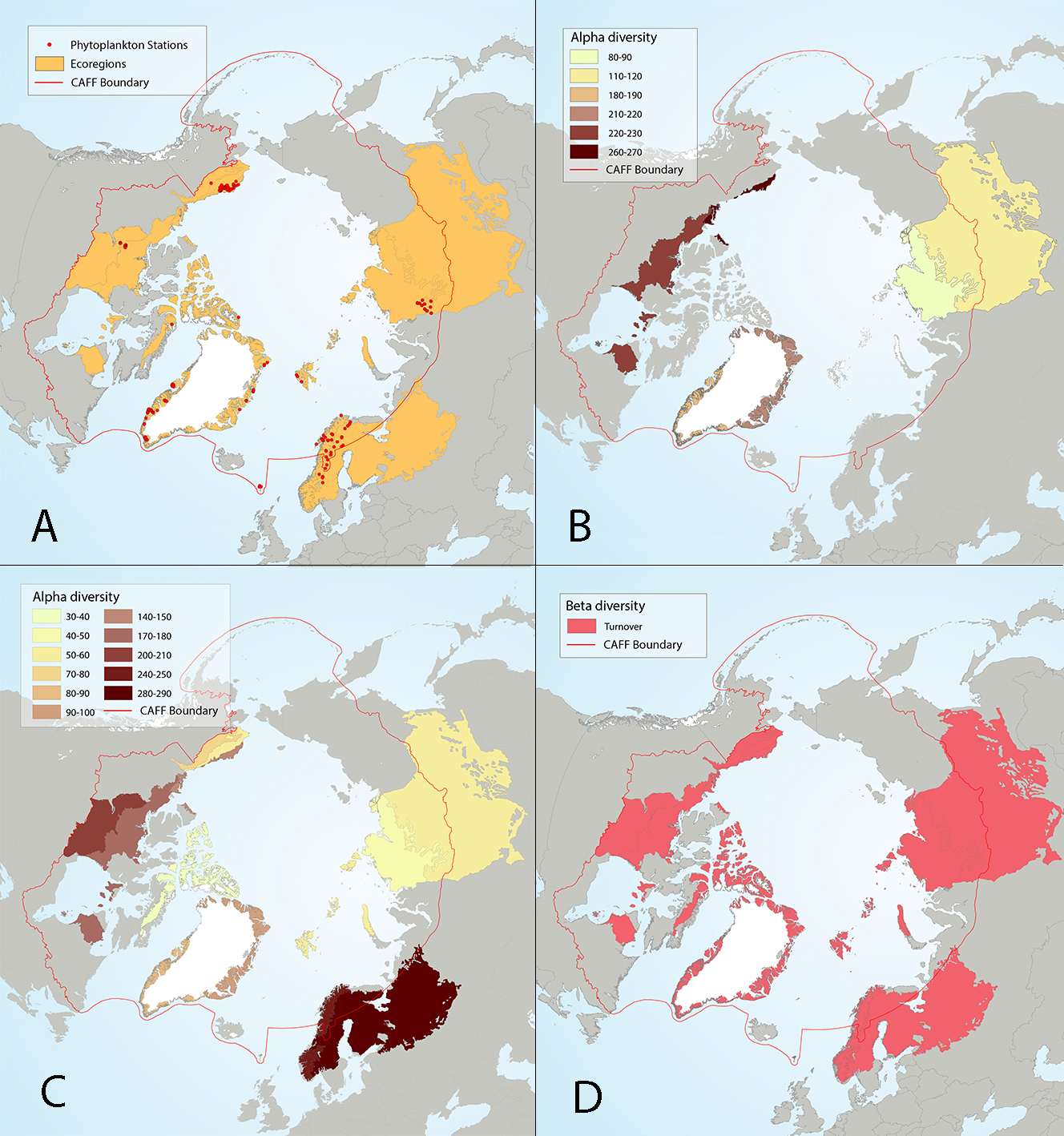
Figure 4 17 Results of circumpolar assessment of lake phytoplankton,(a) the location of phytoplankton stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 35 stations; (c) all ecoregions with phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 56 - Figure 4-17
-
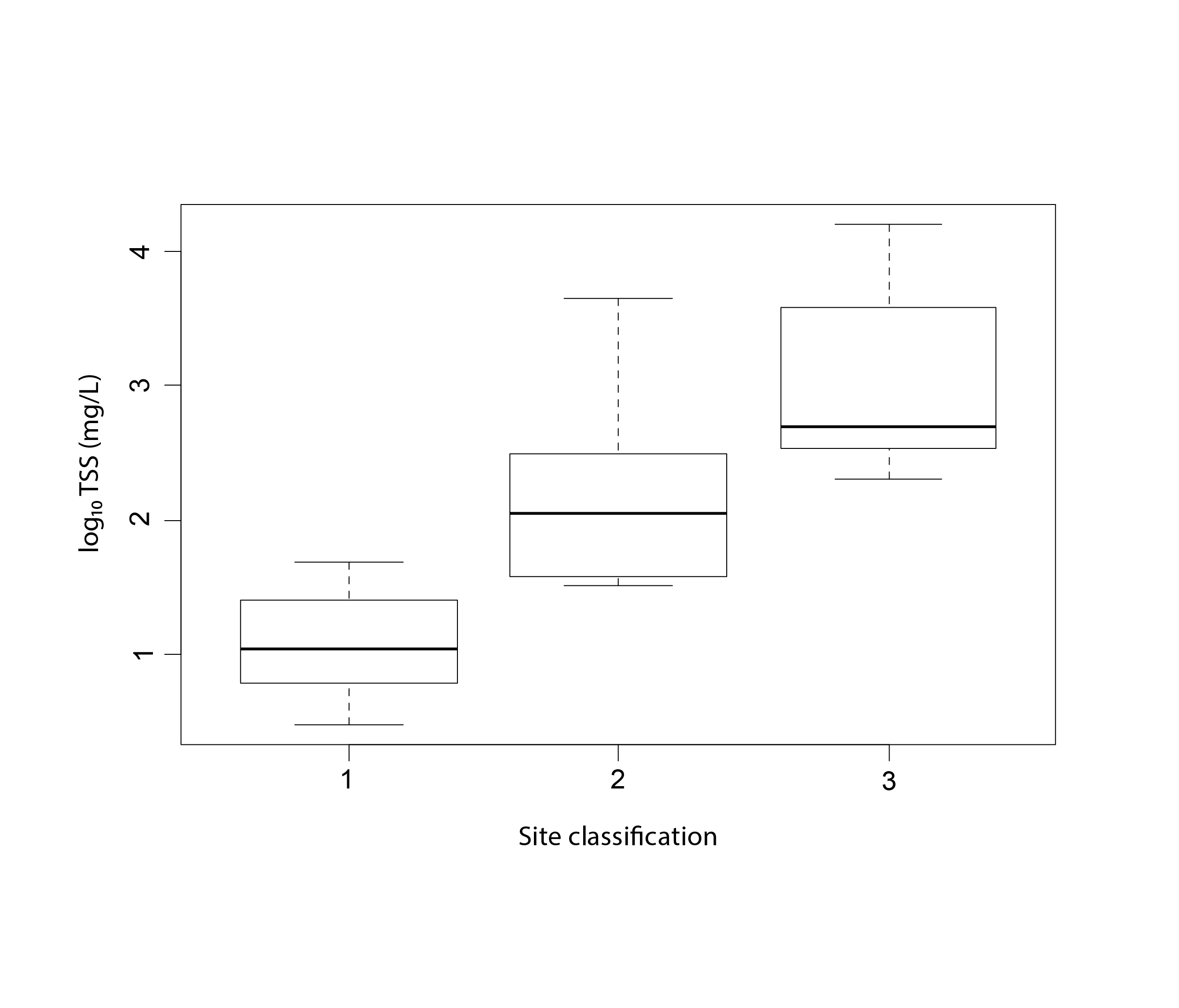
Figure 3-4 Effects of permafrost thaw slumping on Arctic rivers, including (upper) a photo of thaw slump outflow entering a stream on the Peel Plateau, Northwest Territories, Canada, and (lower) log10-transformed total suspended solids (TSS) in (1) undisturbed, (2) 1-2 disturbance, and (3) > 2 disturbance stream sites, with letters indicating significant differences in mean TSS among disturbance classifications Plot reproduced from Chin et al. (2016). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter3 - Page 21 - Figure 3-4
-
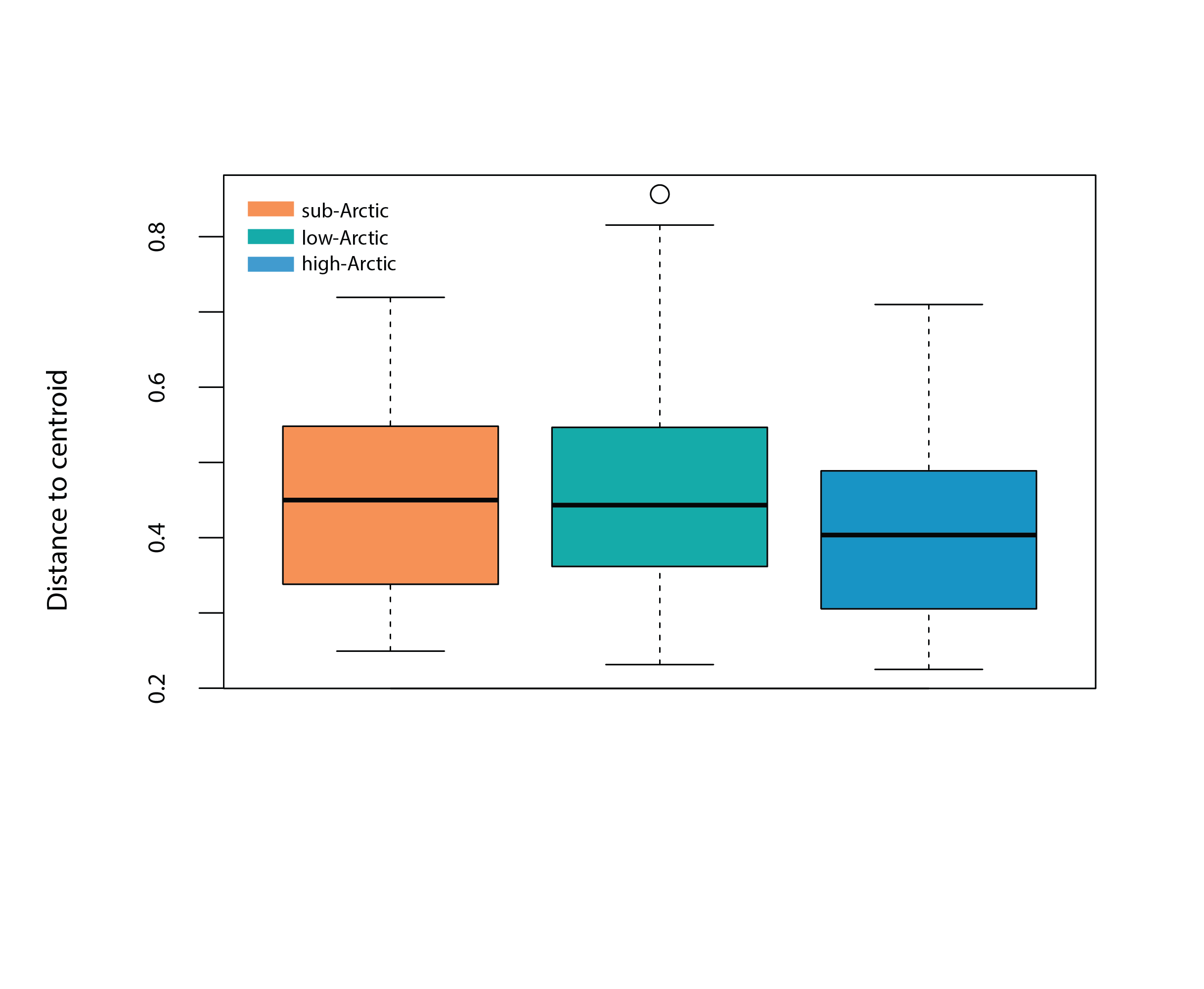
Box plot represents the homogeneity of assemblages in high Arctic (n=190), low Arctic (n=370) and sub-Arctic lakes (n=1151), i.e., the distance of individual lake phytoplankton assemblages to the group centroid in multivariate space. The mean distance to the centroid for each of the regions can be seen as an estimated of beta diversity, with increasing distance equating to greater differences among assemblages. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 48 - Figure 4-18
-
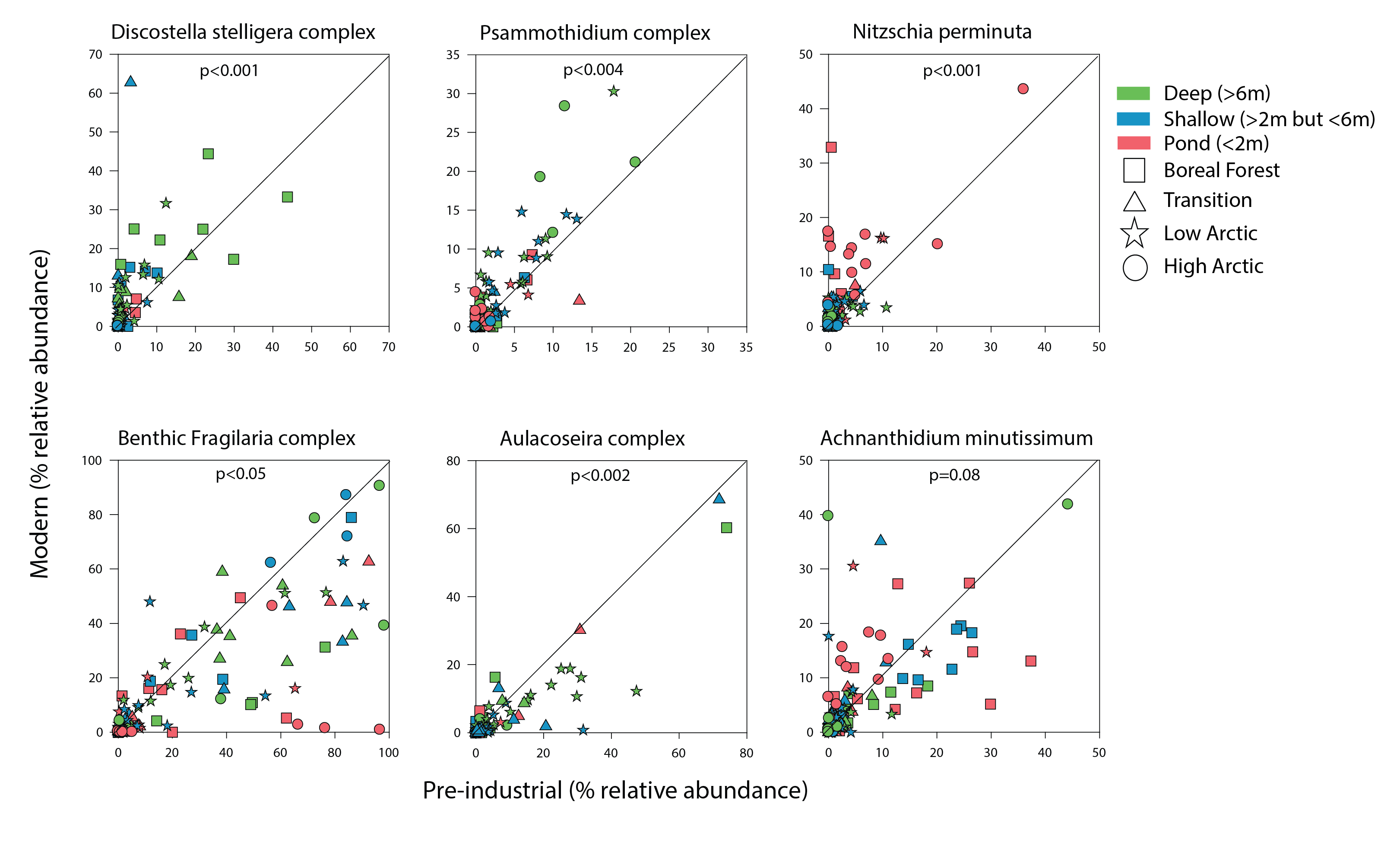
Figure 4 15 Comparison of the relative abundance of select diatom taxonomic groups between core bottoms (pre-industrial sediments; x- axis) and core tops (modern sediments; y-axis) with a 1:1 line to indicate whether there were higher abundances in fossil samples (below red line) or modern samples (above red line). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 2 - Page 15 - Figure 2-1
-
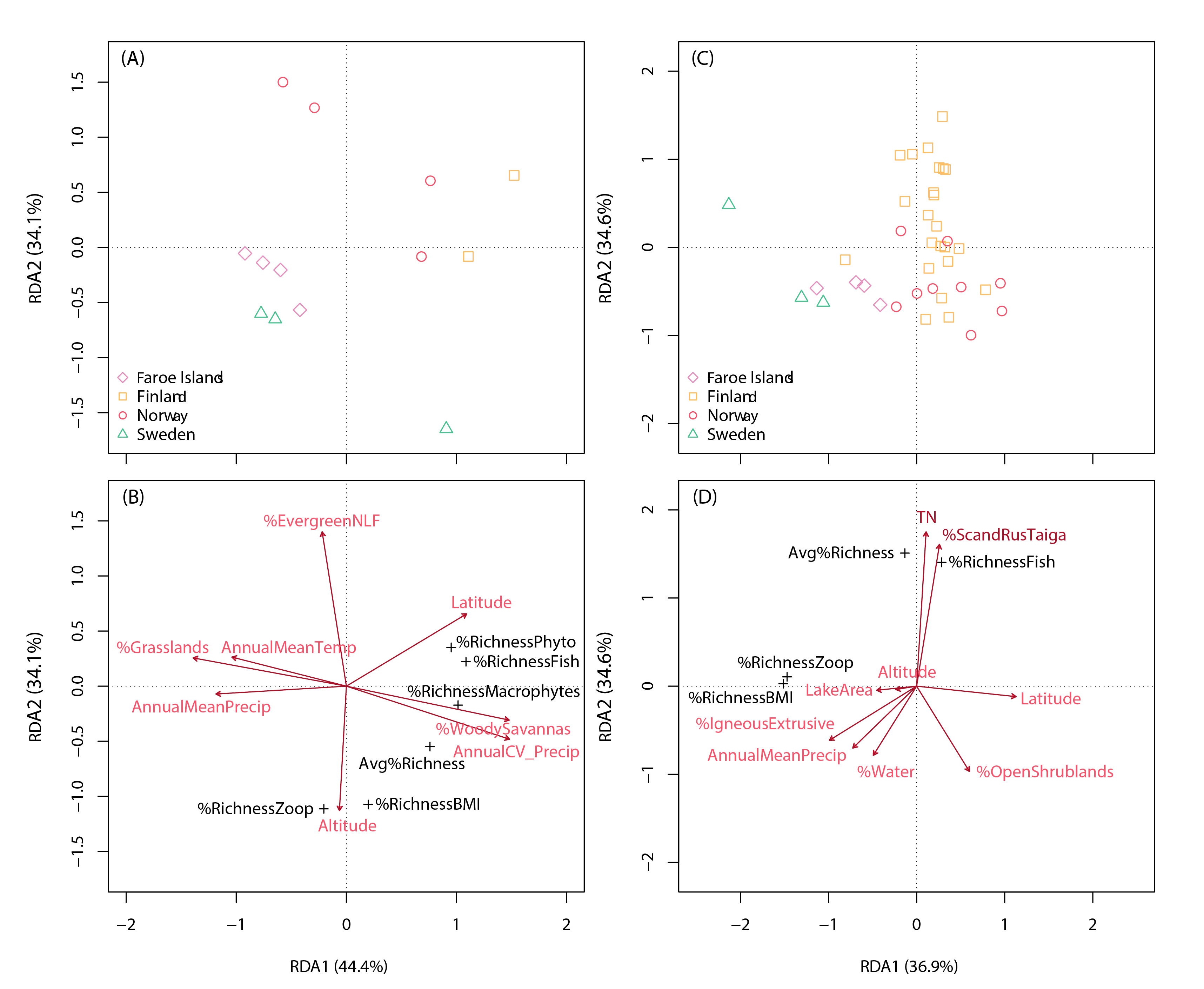
Redundancy analysis of percentage species taxa share (taxa richness relative to richness of all taxa) among 5 FECs (phytoplankton, macrophytes, zooplankton, benthic macroinvertebrates and fish) in 13 Fennoscandian lakes (panels A and B) and among 3 FECs in 39 Fennoscandian lakes (panels C and D).The upper panels show lake ordinations, while the bottom panels show explanatory environmental variables (red arrows), as indicated by permutation tests (p < 0.05). Avg%Richness: average species taxa richness as a percentage of richness of all FECs (i.e., including benthic algae if present); %Richness BMI: relative taxa share in benthic macroinvertebrates; %EvergreenNLF: percentage cover of evergreen needle-leaf forests. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 5 - Page 87 - Figure 5-4
-
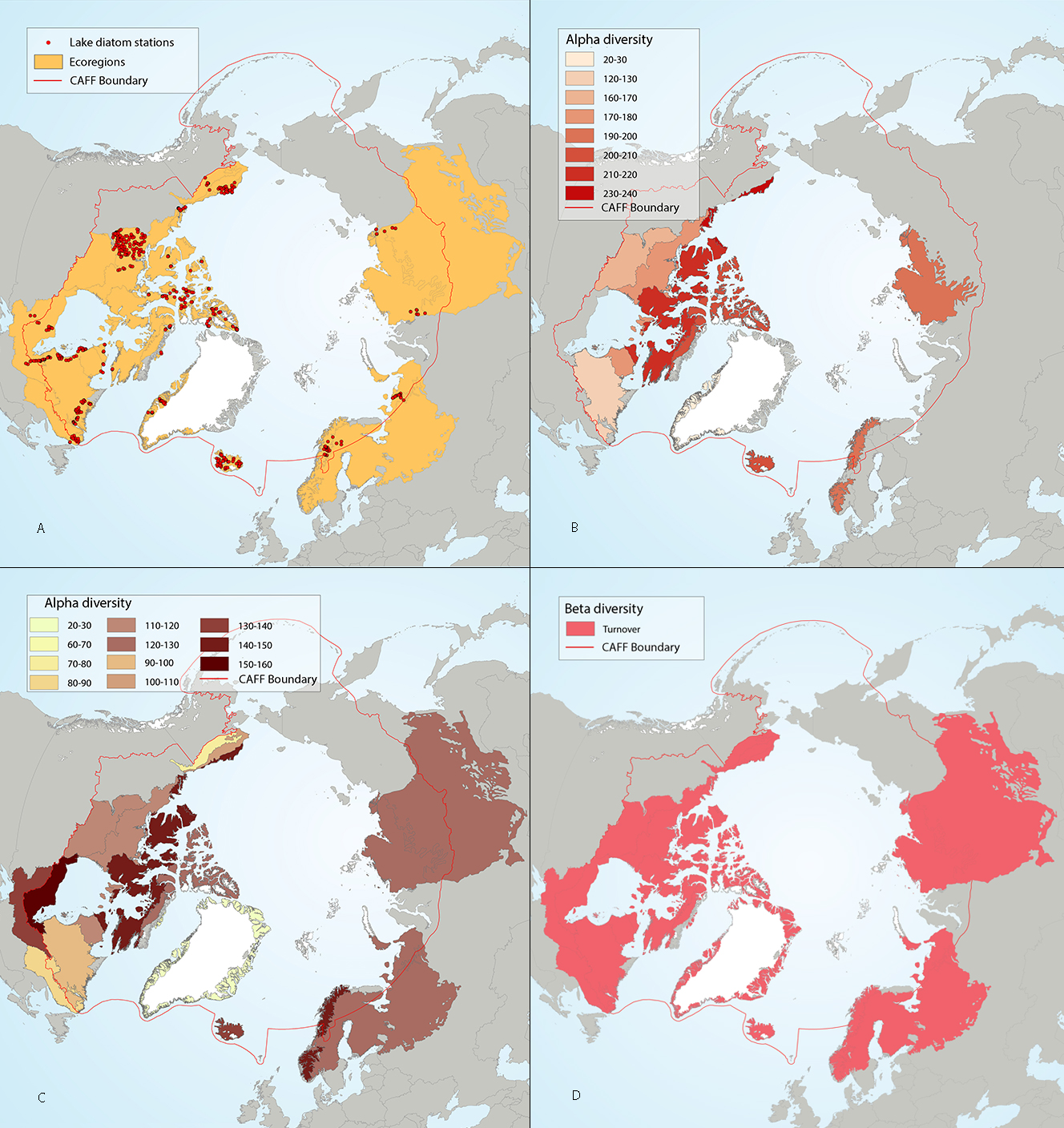
Figure 4-7 Circumpolar assessment of lake diatoms, indicating (a) the location of lake diatom stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many lake diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 40 stations; (c) all ecoregions with lake diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (i.e. species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregio. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 35 - Figure 4-7
-
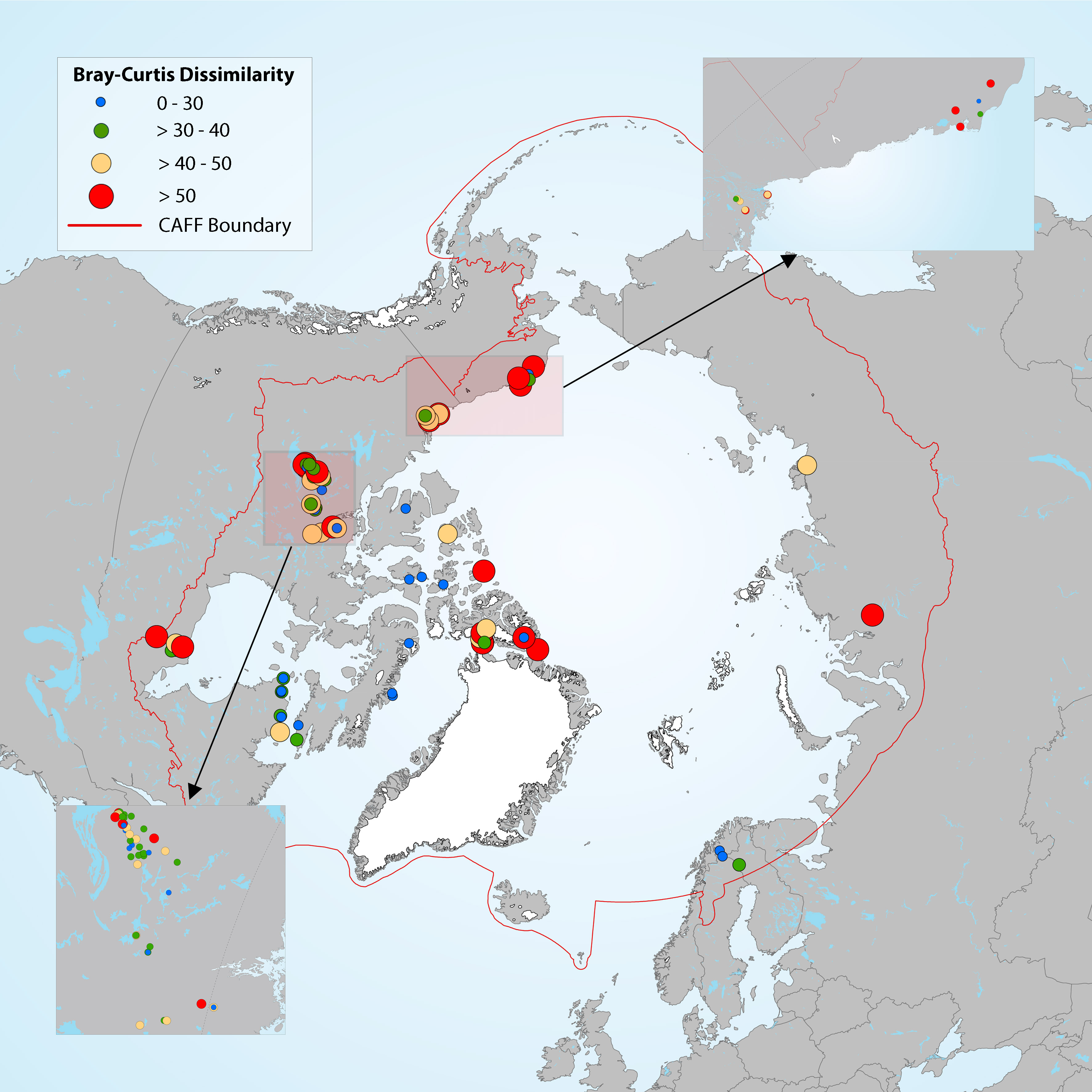
Estimation of diatom assemblage changes over a period of about 200 years (top versus bottom sediment cores). Figure 4-14 Map showing the magnitude of change in diatom assemblages between bottom (pre-industrial) and top (modern) section of the cores, estimated by Bray-Curtis (B-C) dissimilarity. Boundaries for the B-C dissimilarity categories are based on distribution quartiles (0-30%, 30-40%, 40- 50% and >50%), where the lowest values (blue dots) represent the lowest degree of change in diatom assemblage composition between top and bottom sediment core samples in each lake. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 41 - Figure 4-14
-
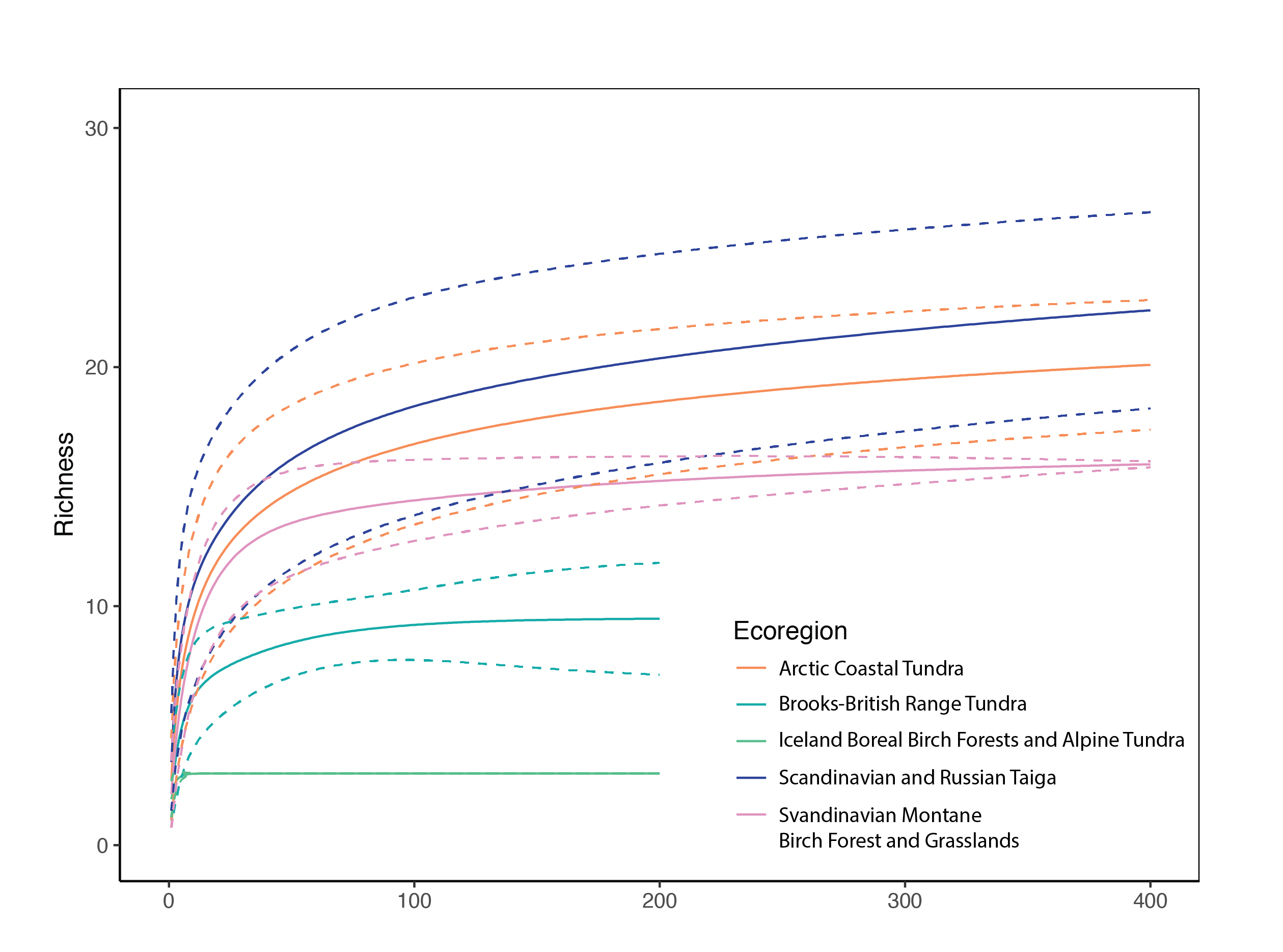
Provides richness estimates and 95% confidence bounds for five ecoregions. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 77 - Figure 4-38
-
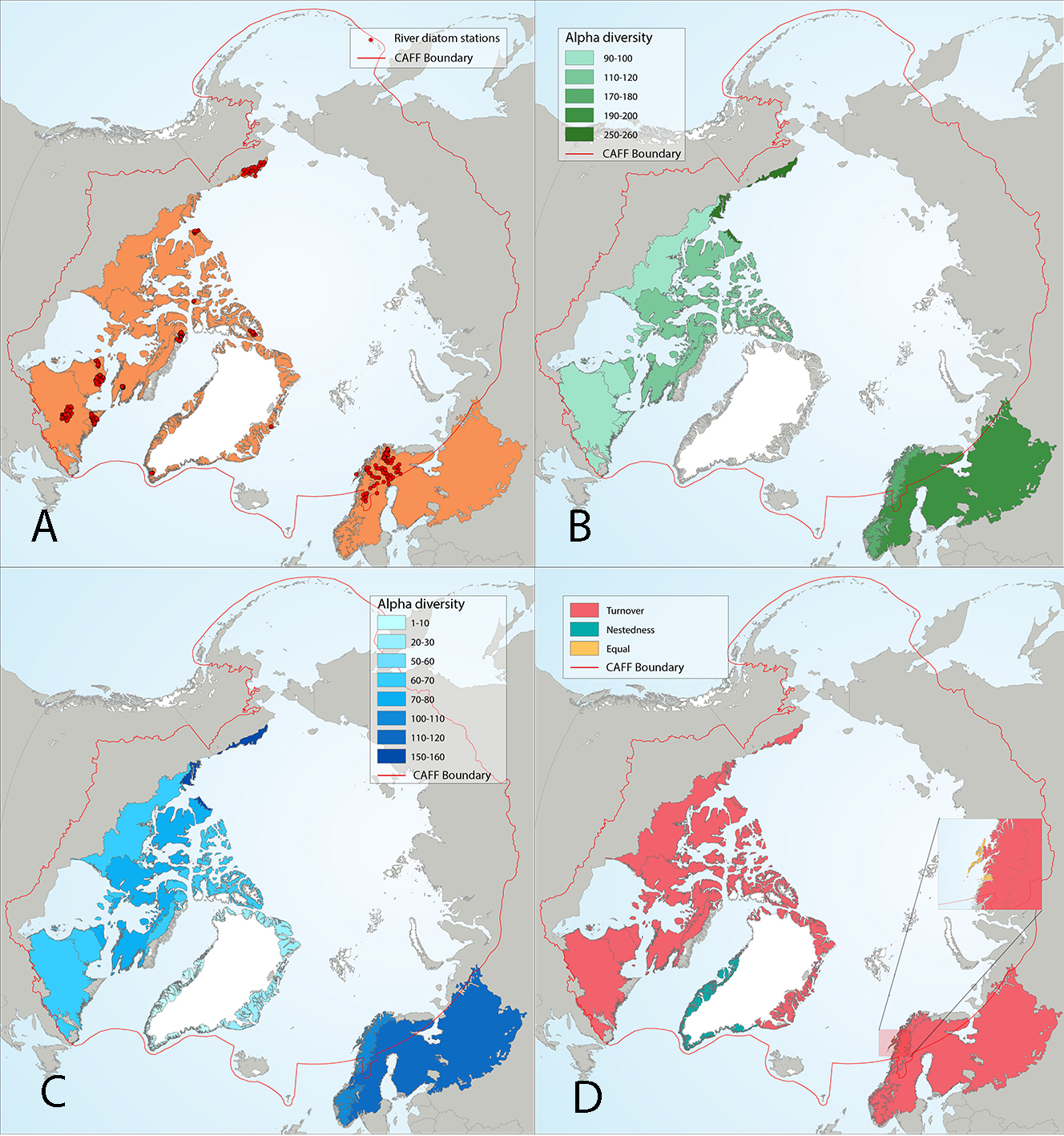
Results of circumpolar assessment of river diatoms, indicating (a) the location of river diatom stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many river diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 40 stations; (c) all ecoregions with river diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 36 - Figure 4-8
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)