vegetation
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
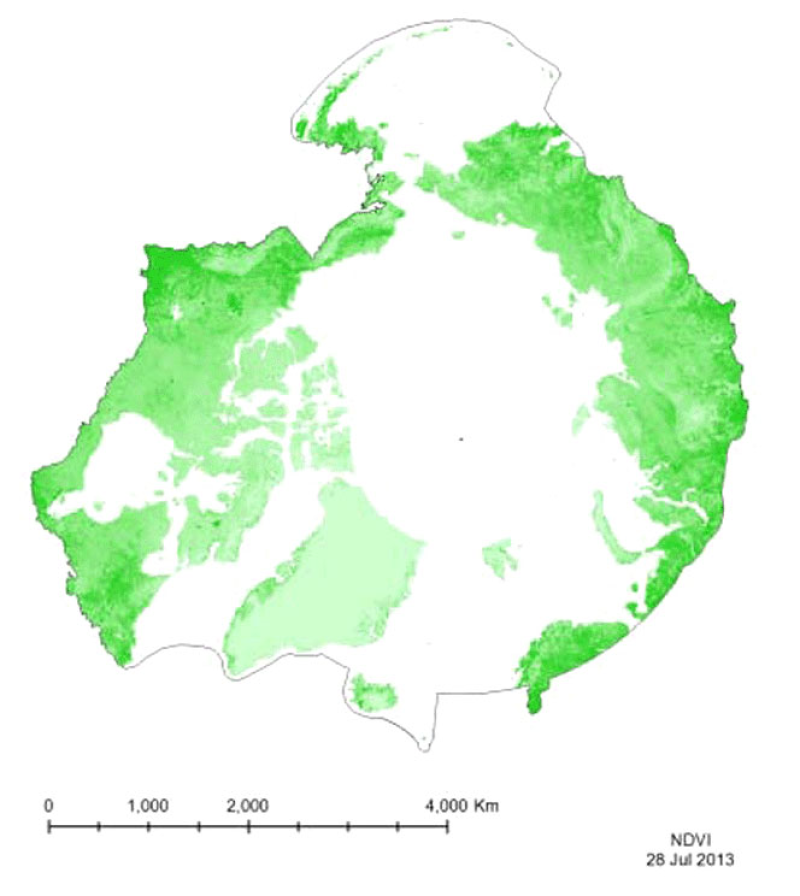
Vegetation indices quantify the concentrations of green leaf vegetation (chlorophyll)around the globe, in an attempt to monitor and correlate vegetation health and stress. The MODIS vegetation products include the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)and an Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI). Included in the MOD13C1 product is both NDVIand EVI, so both have been provided for the CAFF Dedicated Pan-Arctic Satellite RemoteSensing Products and Distribution System. These indices come in a variety of resolutions,but MTRI has provided a monthly global composite on a 0.05° Climate Model GRID(CMG).
-
The Land Cover Dynamics MODIS product is a yearly product that represents thetiming of vegetation phenology globally. Sub-datasets include vegetation growth, maturity,senescence, and dormancy. This product also includes the NBAR-(Nadir Bidirectionalreflectance distribution function (BRDF) adjusted Reflectance) based EVI, in part becausethe EVI is used to create the Land Cover Dynamics. The Land Cover Dynamics product uses both Terra and Aqua MODIS data. Version005 (provided) has a 500 m spatial resolution, which is an improvement from the 1,000 mversion 004 product. This product is only available in MODIS tiles, so the tiles needed tocover the CAFF pan-Arctic region has been downloaded but not clipped to the pan-Arcticextent at this time.
-

Bird and distance transect biodiversity GRID data from Barrow, Alaska-
-
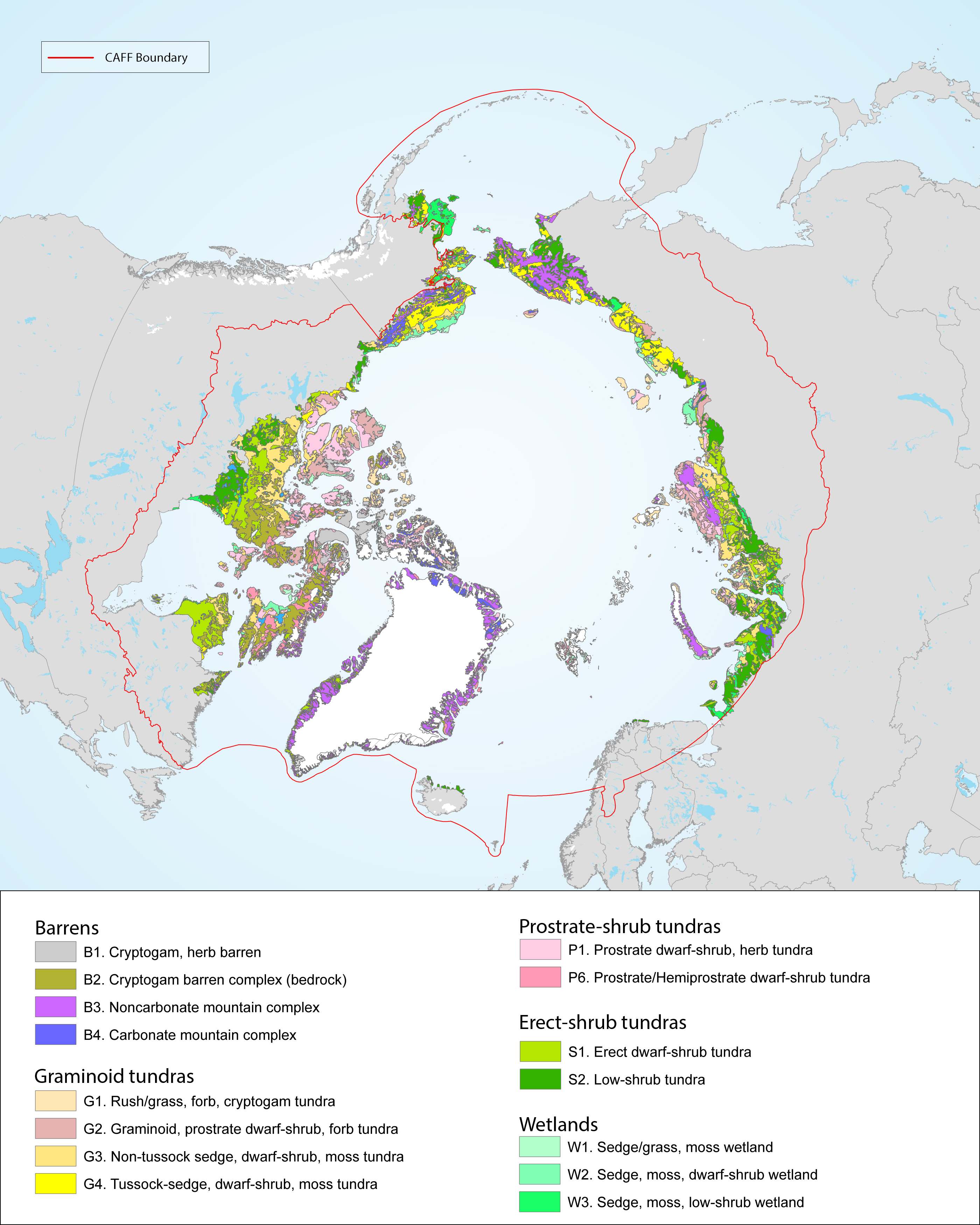
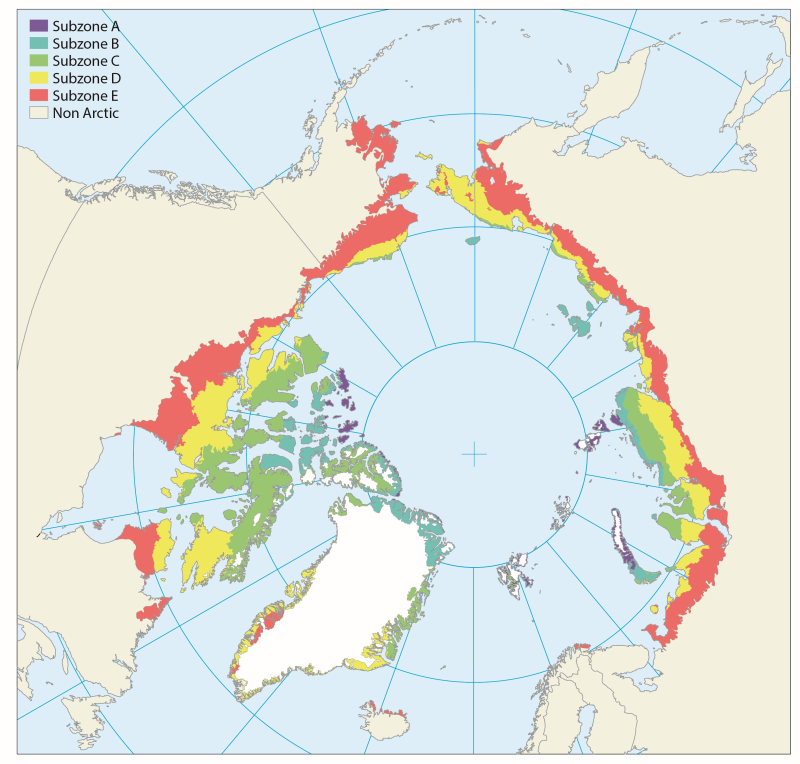
There is a great variation and heterogeneity among terrestrial Arctic ecosystems. This is further described as biogeographical areas in the Annotated Checklist of the Pan-Arctic Flora (Elven et al. 2020), as vegetation zones (Walker et al. 2005, Raynolds et al 2019) or as ecoregions recognised by Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World (Olson et al. 2001). The START focuses on high and low Arctic regions consistent with the CAVM’s subzones A to E, as shown in Figure 1-2 and Figure 2-1 STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 19 - Figure 2.1
-
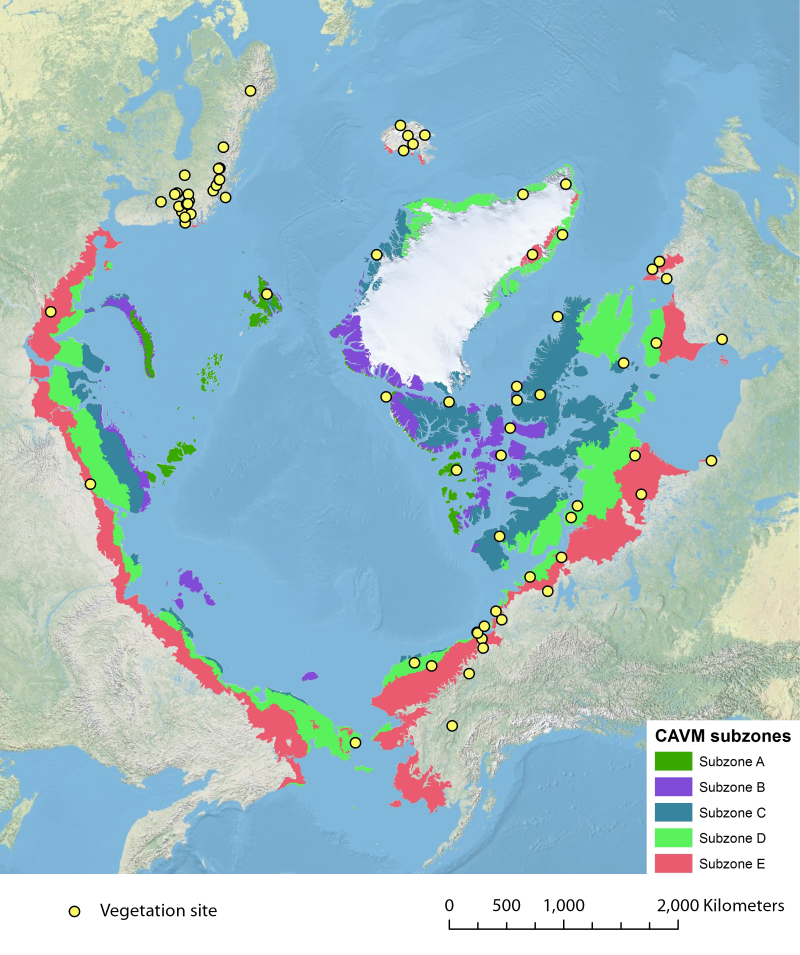
Location of long-term vegetation (including fungi, non-vascular and vascular plants) monitoring sites and programs. Comes from the Arctic Terrestrial Biodiversity Monitoring Plan is developed to improve the collective ability of Arctic traditional knowledge holders, northern communities and scientists to detect, understand and report on long-term change in Arctic terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. The report can be seen here http://www.caff.is/publications/view_document/256-arctic-terrestrial-biodiversity-monitoring-plan The monitoring locations are place over the Circumpolar Arctic bioclimate subzones (CAVM Team 2003) http://www.caff.is/flora-cfg/circumpolar-arctic-vegetation-map
-
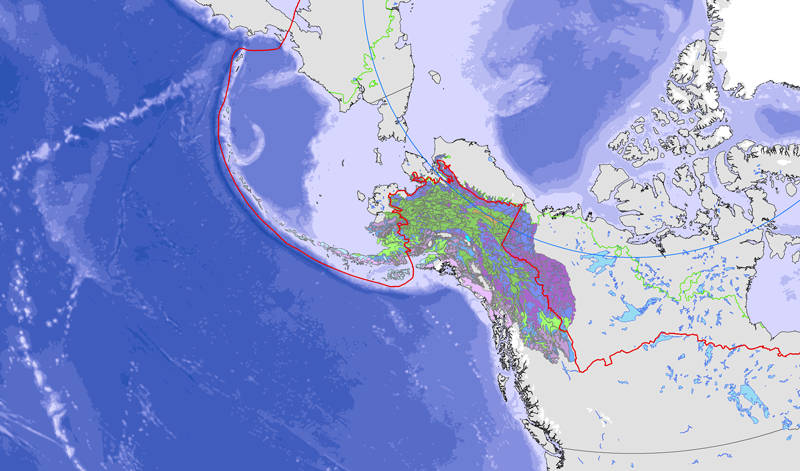
<a href="http://caff.is/strategies-series/359-the-alaska-yukon-region-of-the-circumboreal-vegetation-map-cbvm" target="_blank"> <img width="150px" height="150px" alt="logo" align="left" hspace="10px" src="http://geo.abds.is/geonetwork/images/flora_logo.png"> </a>A map of boreal vegetation for the Alaska-Yukon region was developed to contribute to the circumboreal vegetation mapping (CBVM) project. The effort included developing a map of bioclimates with 12 bioclimate zones, a map of biogeographic provinces with Alaska-Yukon and Aleutian provinces, and a map of geographic sectors with six sectors that provided the basis for classification of boreal vegetation. Vegetation mapping was done at 1:7.5 million scale using the mapping protocols of the CBVM team. Mapping used MODIS imagery as the basis for manual image interpretation and an integrated-terrain-unit approach, which included classifications for bioclimate, physiography, generalized geology, permafrost, disturbance, growth from, geographic sector, and vegetation. Vegetation was mapped at two hierarchical levels: (1) formation group differentiating zonal and azonal systems; and (2) geographic sectors based on bioclimatic zonation and dominant species that characterize broad longitudinal regions or biogeographic provinces. Each of the 19 map units was described by identifying the dominant and characteristic species and its climatic and landscape characteristics, as well as references that relate to the unit.
-
Based on published scientific literature, the diversity of plants in the Arctic is reviewed. The plants are divided into three main groups according to essential differences in anatomy, morphology and reproduction. These are vascular plants, bryophytes (mosses and liverworts) and algae (micro- and macroalgae). As a whole, these three plant groups have the ability to perform photosynthesis. As primary producers they play a key role in the environment, since photosynthesis provides resources for all other organisms. Vascular plants and bryophytes (together with the lichenized fungi, the lichens) are the main structural components of terrestrial vegetation and ecosystems, while algae are more abundant in fresh water and marine ecosystems. Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Plants (Chapter 9)
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)