dataset
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
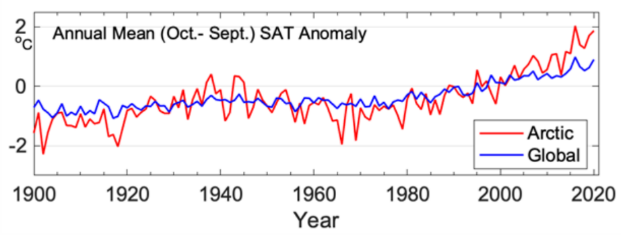
Warming in the Arctic has been significantly faster than anywhere else on Earth (Ballinger et al. 2020). Trends in land surface temperature are shown on Figure 2-2. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 23 - Figure 2.2
-

Interannual differences in taxonomic composition of phytoplankton during summer in a) Kongsfjorden and b) Rijpfjorden (Source: MOSJ, Norwegian Polar Institute). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/plankton" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 74 - Figure 3.2.5
-

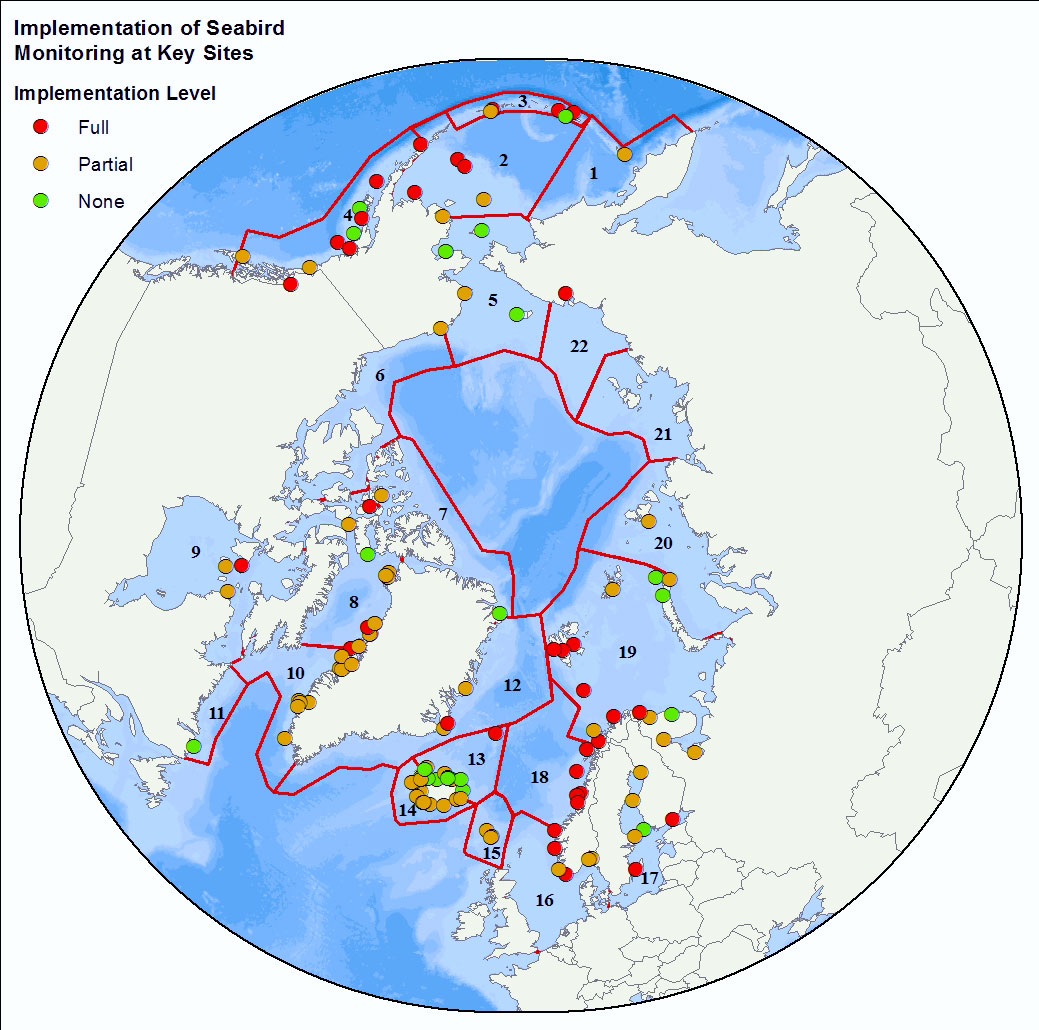
The Seabird Information Network (SIN) developed by the Circumpolar Seabird expert group (<a href="http://caff.is/seabirds-cbird" target="_blank">CBird</a>) of the Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna (<a href="http://caff.is" target="_blank">CAFF</a>) working group of the Arctic Council focuses on the development of a data entry and analysis portal system allowing for circumpolar seabird colony information to be contributed, mapped, and shared by scientists and monitoring programs around the Arctic. - <a href="http://axiom.seabirds.net/maps/js/seabirds.php?app=circumpolar#z=2&ll=NaN,0.00000" target="_blank"> Circumpolar Seabird portal</a>
-
Appendix 17.3. Phylogeographic and population genetics studies of selected Arctic species.
-
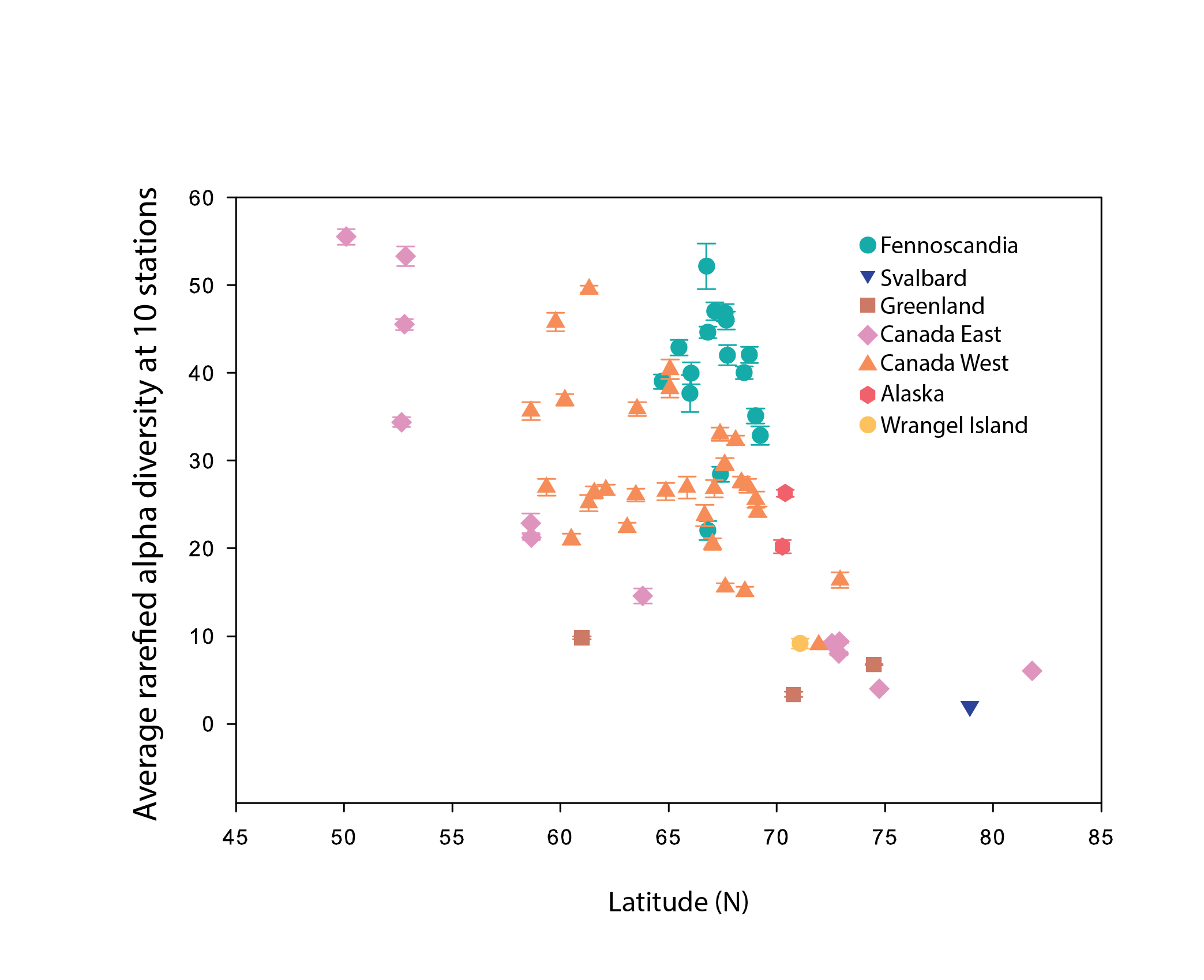
Alpha diversity (rarefied to 10 stations, with error bars indicating standard error) of river benthic macroinvertebrates plotted as a function of the average latitude of stations in each hydrobasin. Hydrobasins are coloured based on country/region State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 68 - Figure 4-32
-
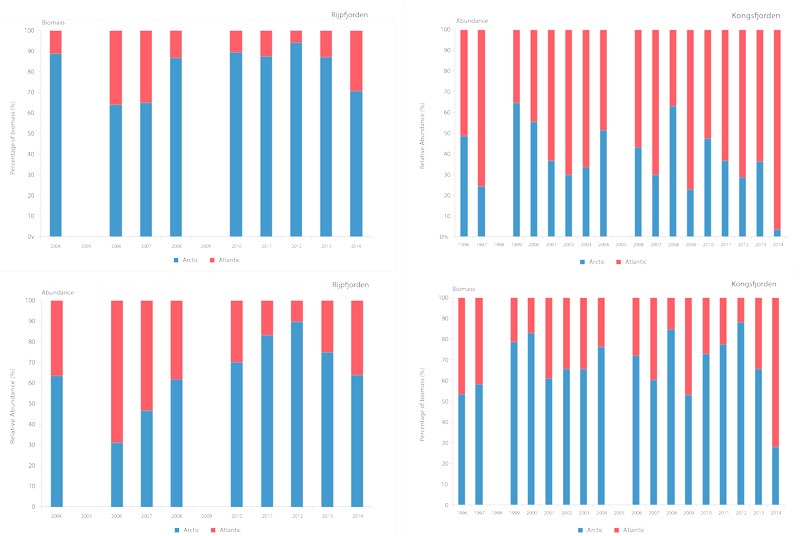
Time series of relative proportions of Arctic and Atlantic Calanus species in Kongsfjorden (top) and Rijpfjorden (bottom) (Source: MOSJ, Norwegian Polar Institute). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/plankton" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 77 - Figure 3.2.8
-
<img width="80px" height="67px" alt="logo" align="left" hspace="10px" src="http://geo.abds.is/geonetwork/srv/eng//resources.get?uuid=7d8986b1-fbd1-4e1a-a7c8-a4cef13e8eca&fname=cbird.png">The Circumpolar Seabird Monitoring Plan is designed to 1) monitor populations of selected Arctic seabird species, in one or more Arctic countries; 2) monitor, as appropriate, survival, diets, breeding phenology, and productivity of seabirds in a manner that allows changes to be detected; 3) provide circumpolar information on the status of seabirds to the management agencies of Arctic countries, in order to broaden their knowledge beyond the boundaries of their country thereby allowing management decisions to be made based on the best available information; 4) inform the public through outreach mechanisms as appropriate; 5) provide information on changes in the marine ecosystem by using seabirds as indicators; and 6) quickly identify areas or issue in the Arctic ecosystem such as declining biodiversity or environmental pressures to target further research and plan management and conservation measures. - <a href="http://caff.is" target="_blank"> Circumpolar Seabird Monitoring plan </a>
-
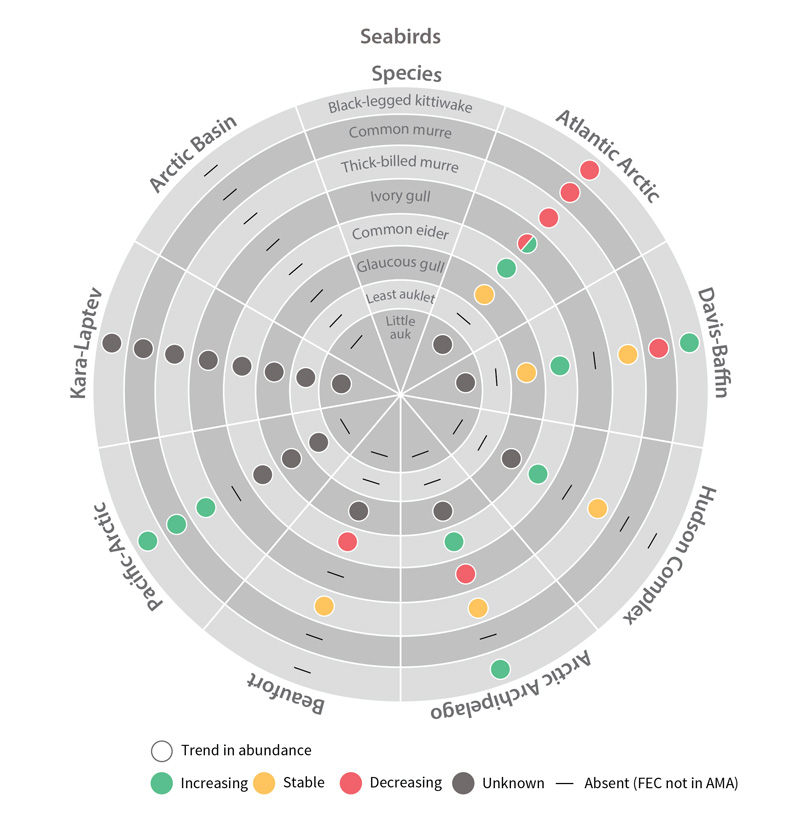
Trends in abundance of seabird Focal Ecosystem Components across each Arctic Marine Area. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 4 - Page 181 - Figure 4.5
-
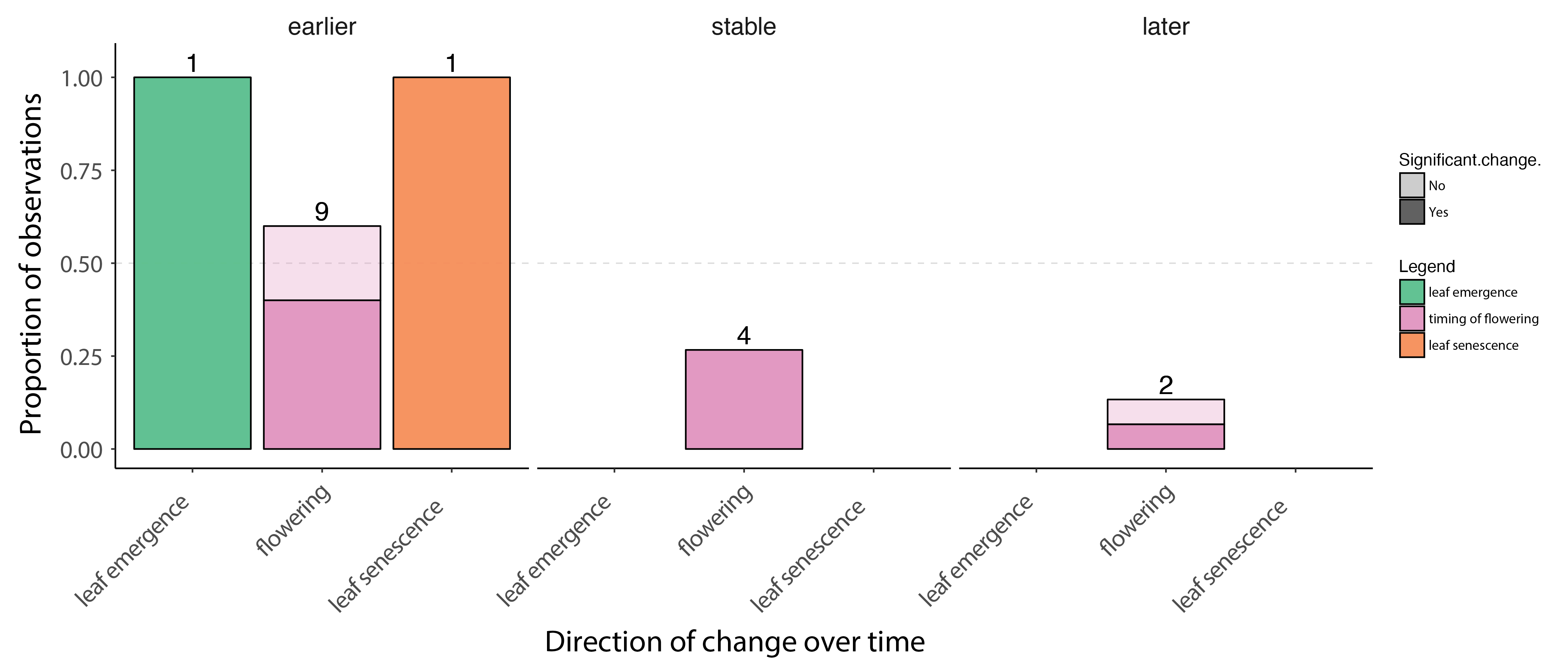
Change in plant phenology over time based on published studies, ranging from 9 to 21 years of duration. The bars show the proportion of observations where timing of phenological events advanced (earlier) was stable or were delayed (later) over time. The darker portions of each bar represent visible decrease, stable state, or increase results, and lighter portions represent marginally significant change. The numbers above each bar indicate the number of observations in that group. Figure from Bjorkman et al. 2020. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 31- Figure 3.3
-
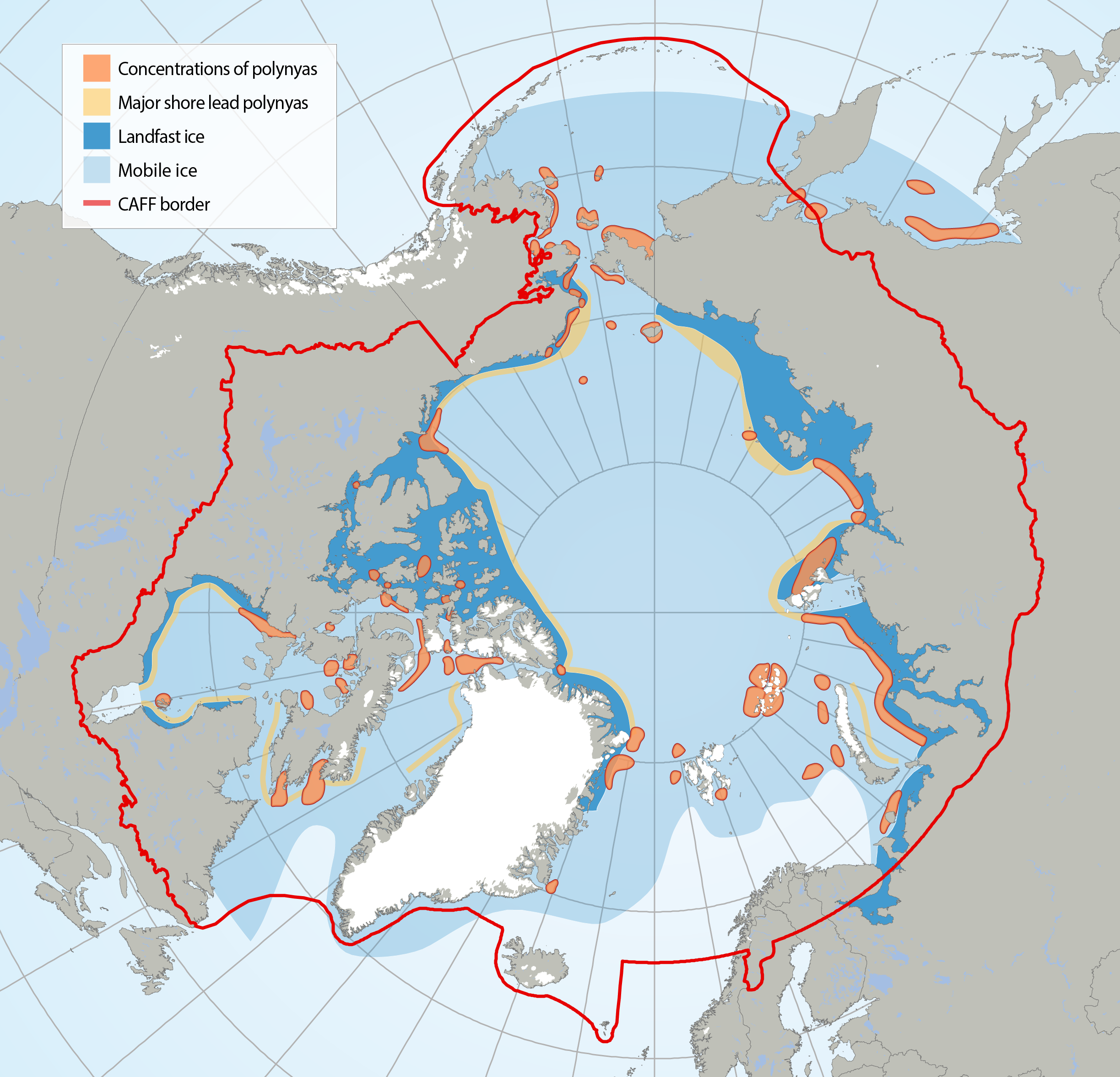
Circumpolar map of known polynyas. Note that polynyas are dynamic systems and some may no longer exist in the form known from their recent history. Adapted from Meltofte (2013) and based on Barber and Massom (2007). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 28 - Figure 2.5
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)