Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna (CAFF)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
-
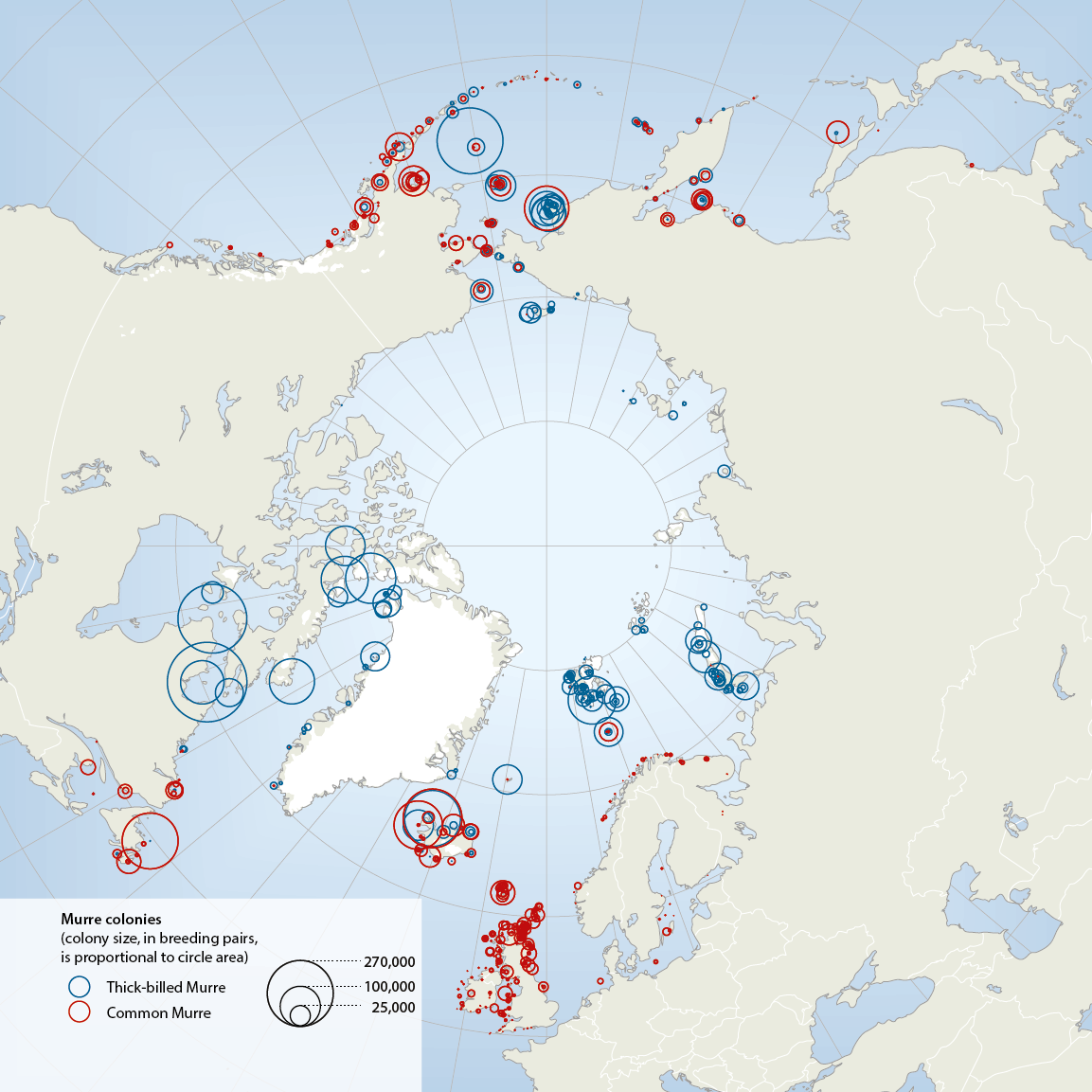
The two species of murres, thick-billed Uria lomvia and common U. aalge, both have circumpolar distributions, breeding in Arctic, sub-Arctic and temperate seas from alifornia and N Spain to N Greenland, high Arctic Canada, Svalbard, Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya (Box 4.3 Fig. 1). Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Birds(Chapter 4) page 163
-
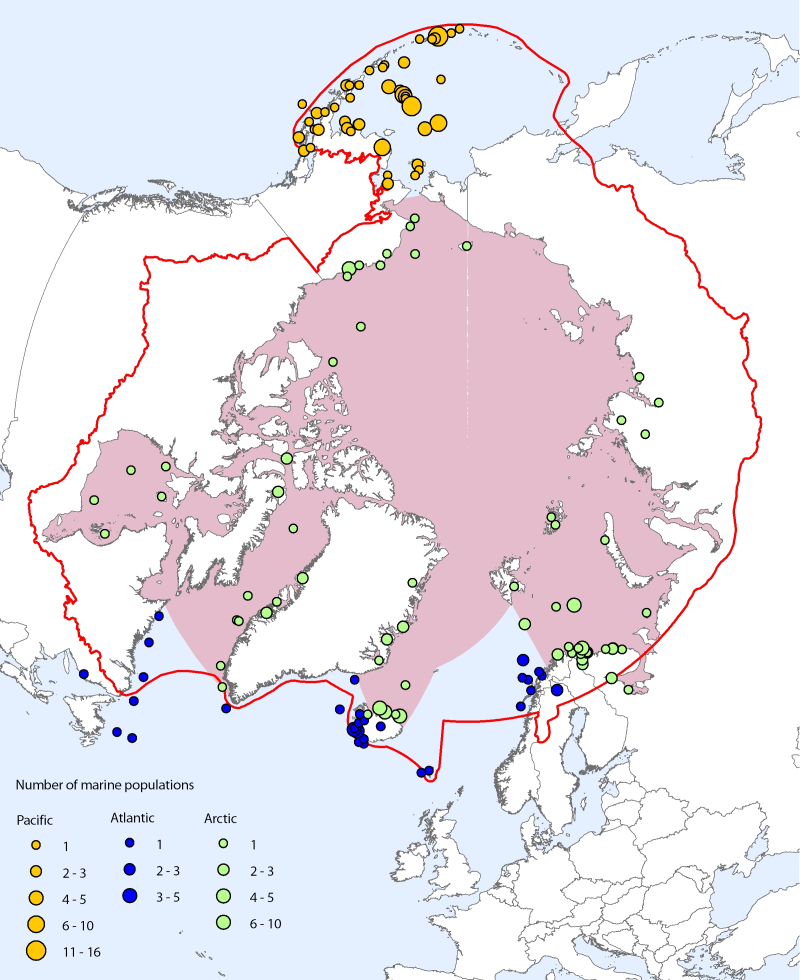
<img src="http://geo.abds.is/geonetwork/srv/eng//resources.get?uuid=59d822e4-56ce-453c-b98d-40207a2e9eec&fname=cbmp_small.png" alt="logo" height="67px" align="left" hspace="10px"> The Arctic marine data set contains a total of 111 species and 310 population time series from 170 locations. Species coverage is about 34% of Arctic marine vertebrate species (100% of mammals, 53% of birds, and 27% of fishes) (Bluhm et al. 2011). At the species level, even though the representation of Arctic fish species is lower than that of mammals and birds, the data are dominated by fishes, primarily from the Pacific Ocean (especially the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands). However, there are more population time series in total for bird species, which is reflective of this group being both better studied historically and also monitored at many small study sites compared to fish and marine mammal species, which are regularly monitored at a much larger scale through stock management. Note that the time span selected for marine analyses is 1970 to 2005 (compared with 1970 to 2007 for the ASTI for all species). CAFF Assessment Series No. 7 April 2012 - <a href=http://caff.is/asti/asti-publications/28-arctic-species-trend-index-tracking-trends-in-arctic-marine-populations" target="_blank"> The Arctic Species Trend Index - Tracking trends in Arctic marine populations </a>
-
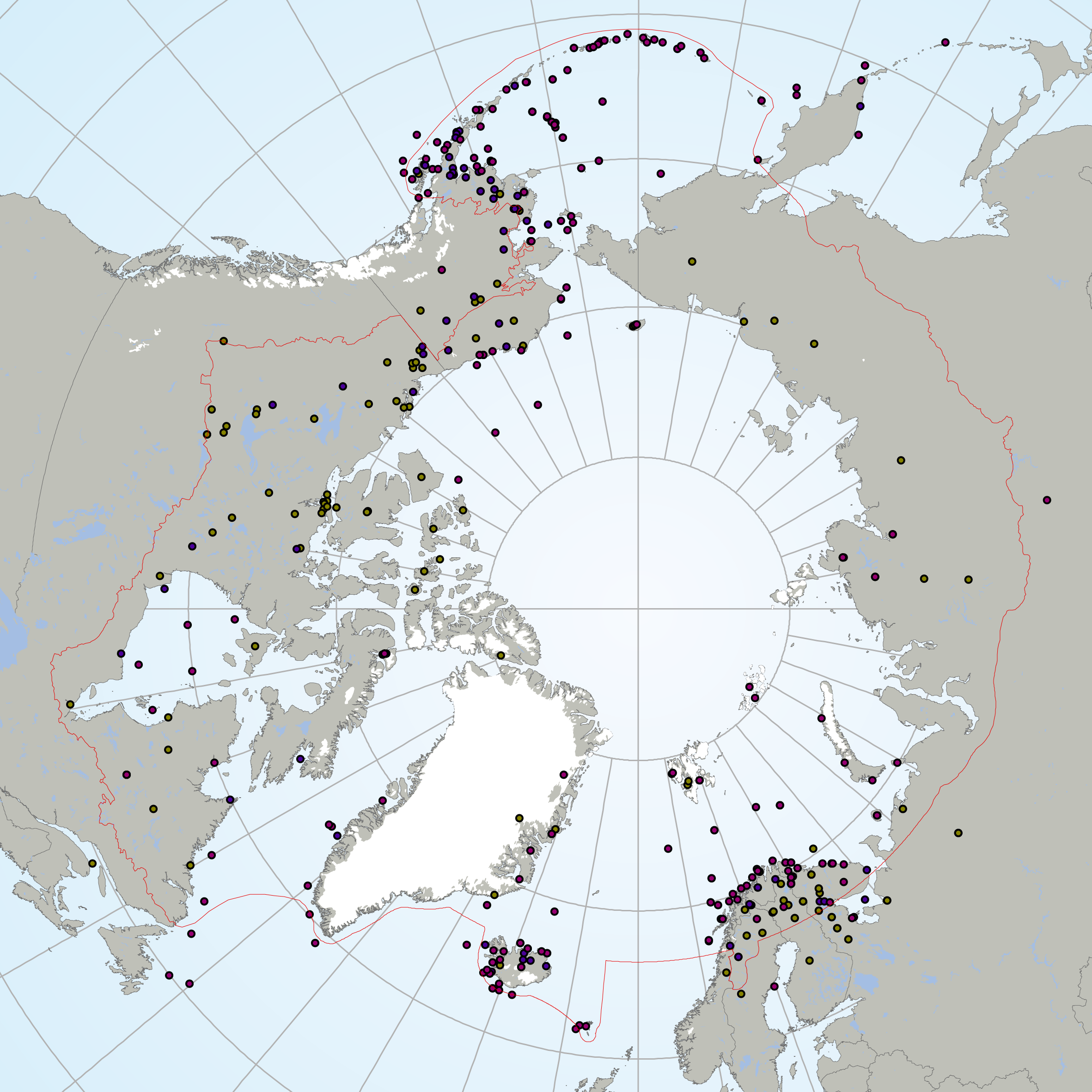
The Circumpolar Biodiversity Monitoring Program, a cornerstone programme of the Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna (CAFF), Arctic Council working Group is an international network of scientists, government agencies, Indigenous organizations and conservation groups working together to harmonize and integrate efforts to monitor the Arctic's living resources.CBMP experts are developing four coordinated and integrated Arctic Biodiversity Monitoring Plans to help guide circumpolar monitoring efforts. Results will be channeled into effective conservation, mitigation and adaptation policies supporting the Arctic. These plans represent the Arctic's major ecosystems(Marine, Freshwater, Coastal, Terrestrial). It is important that monitoring programs develop the most effective reporting strategies if they are to inform decision making. To facilitate effective and consistent reporting, the CBMP has chosen a suite of indices and indicators that provide a comprehensive picture of the state of Arctic biodiversity – from species to habitats to ecosystem processes to ecological services. These indices and indicators are developed in a hierarchical manner, allowing users to drill down into the data from the higher-order indices to more detailed indicators. These are being developed through an expert consultation process. The Arctic Species Trend Index (ASTI) is part of this suite of indicators and indices developed by CAFFs CBMP. It tracks trends in over 300 Arctic vertebrate species and comprises the Arctic component of the Living Planet Index. It is important to identify how wildlife and ecosystems are changing in order to develop effective conservation and adaptation strategies in the Arctic, an environment undergoing dramatic changes. The ASTI describes overall trends across species, taxonomy, ecosystems, regions and other categories.
-
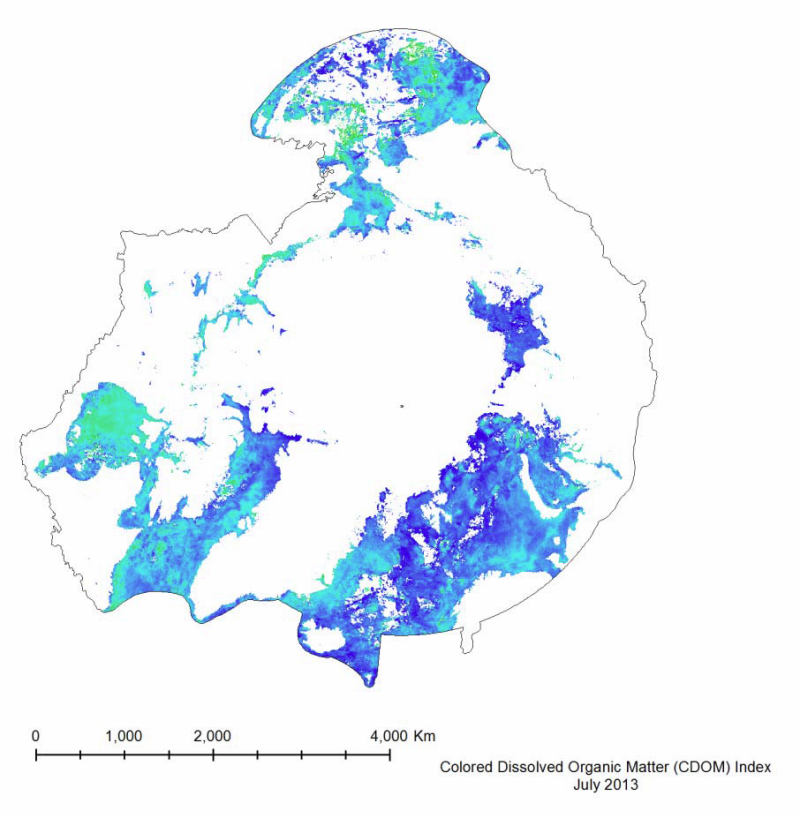
Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) is a measurement of the absorption of light in the UV and visible spectrum by the colored components of dissolved organic carbon. It is essentially the yellow substance in water as a result of decaying detritus. It is important to measure because it limits the amount of sunlight penetration, and thus restricts the growth of plankton populations. It is measured in a unit-less CDOM index. Data generated as part of CAFFs Circumpolar Biodiversity Monitoring Program (CAFF) and its Land Cover Change Initiative (LCC) Trends visible in the MODIS dataset show an overall decrease in the mean CDOM from 2003 to 2012, with a percent change of -31.7%. This trend can be seen in Figure 40. This decrease corresponds to the increase in total yearly primary productivity (Figure 30), as a decrease in the CDOM allows for sunlight to penetrate deeper into the water, boosting chlorophyll concentrations and thus primary productivity.
-
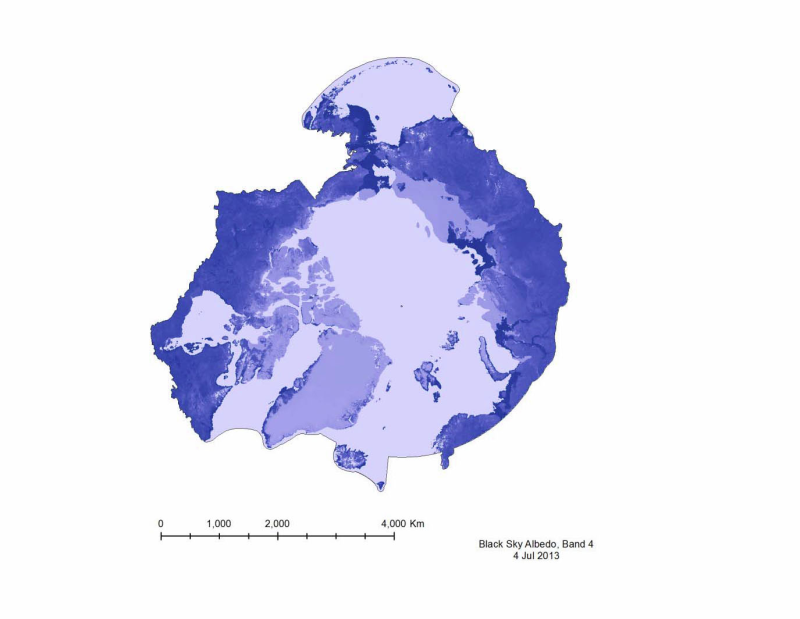
Albedo is a reflection coefficient that describes the reflecting power of a surface. Data compiled for CAFFs Land Cover Change Initiative with dataset for the firs of very month during 2001- 20112. - <a href="http://www.caff.is/indices-and-indicators/land-cover-change-index" target="_blank"> Land Cover Change Initiative (LCC)</a>
-
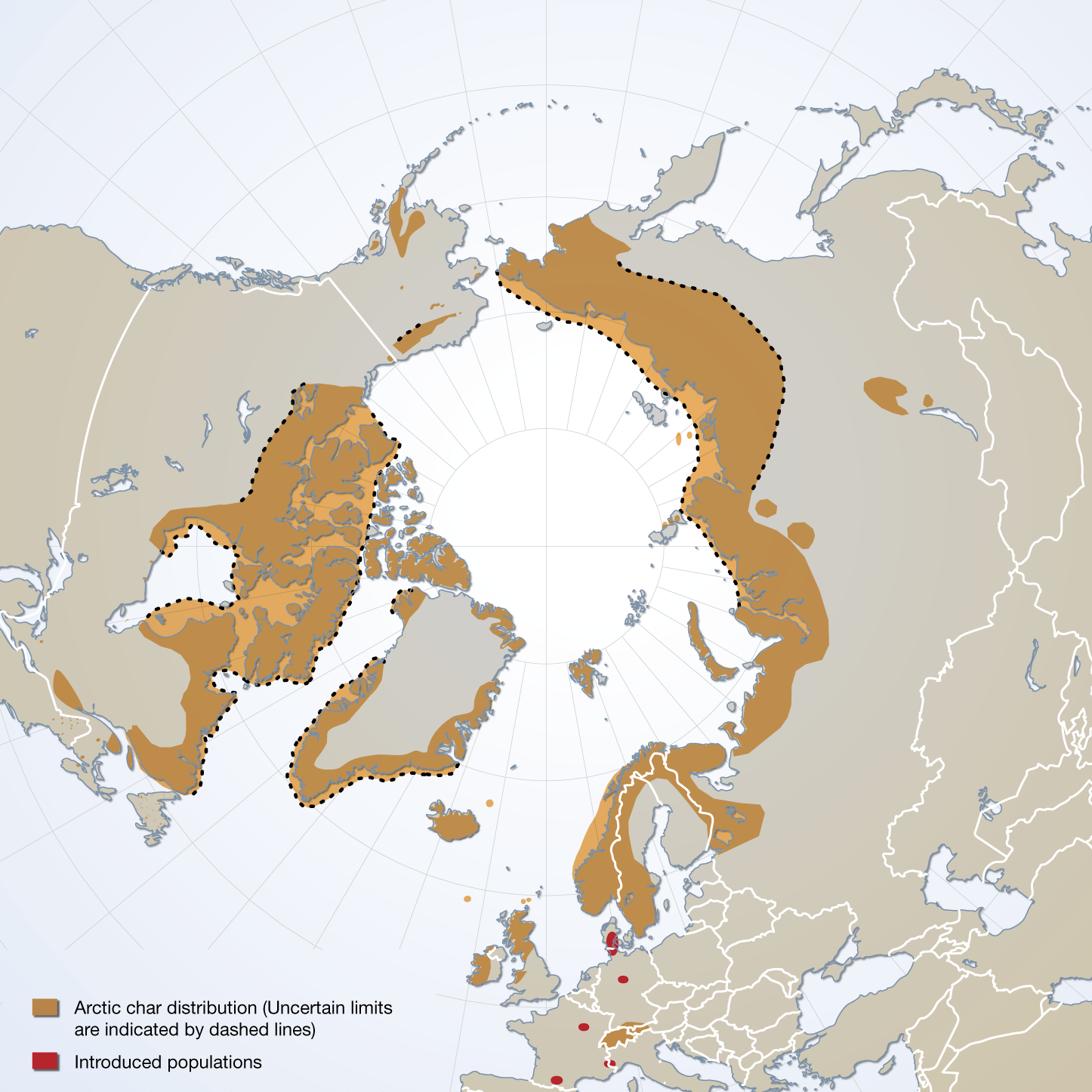
The distribution of Arctic char species complex, sensu stricto, and the location of introduced populations. Published in the Arctic Biodiversity trends 2010, Indicator #06 Arctic char, page 41 - released in May 2010
-
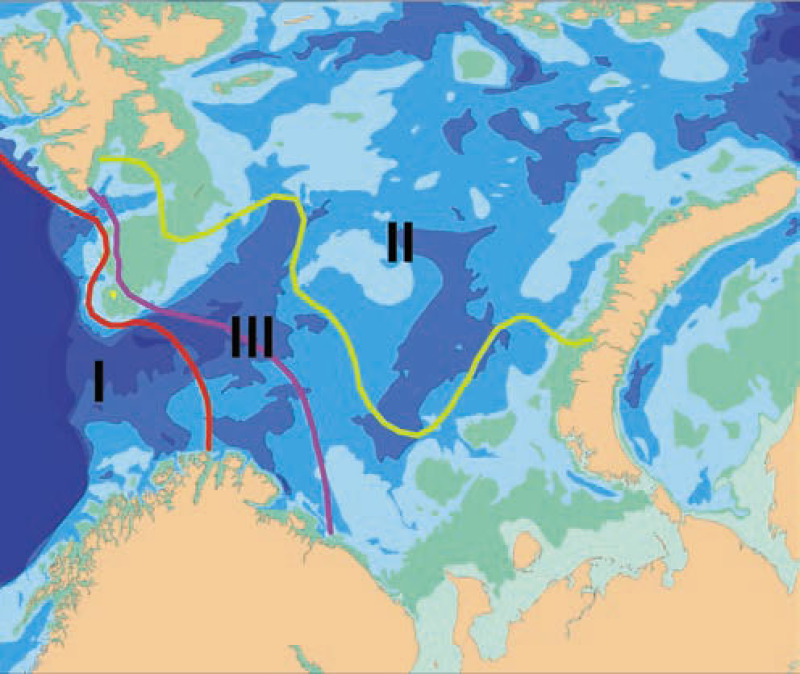
Biogeographic borders in the Barents Sea based on species distributions of bryozoans. Average position of the border with 50:50% of Atlantic boreal and Arctic species numbers is indicated by the pink line, and the red and green lines indicate the extreme positions of the border in cold and warm periods respectively. Area III between them is the transitional zone between the Atlantic boreal and the Arctic regions. Thus, area I always has > 50% Atlantic boreal species, and area II always > 50% Arctic species (after Denisenko 1990).
-
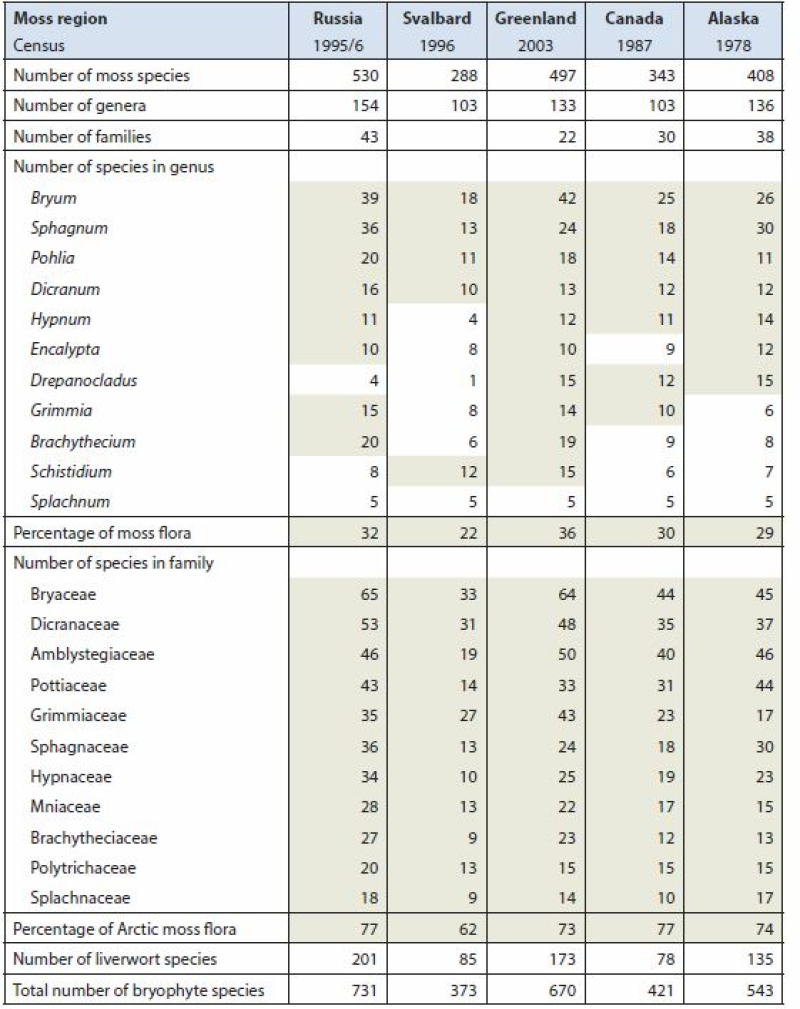
Arctic Biodiversity Assessment (ABA) 2013. Table 9.5. Species numbers of species-rich moss genera and families. Numbers highlighted in grey fields are used in calculating the percentage of the total moss flora. Listed are Splachnum, genera with at least 10 species and families with at least nine species. Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Plants(Chapter 9) page 333
-
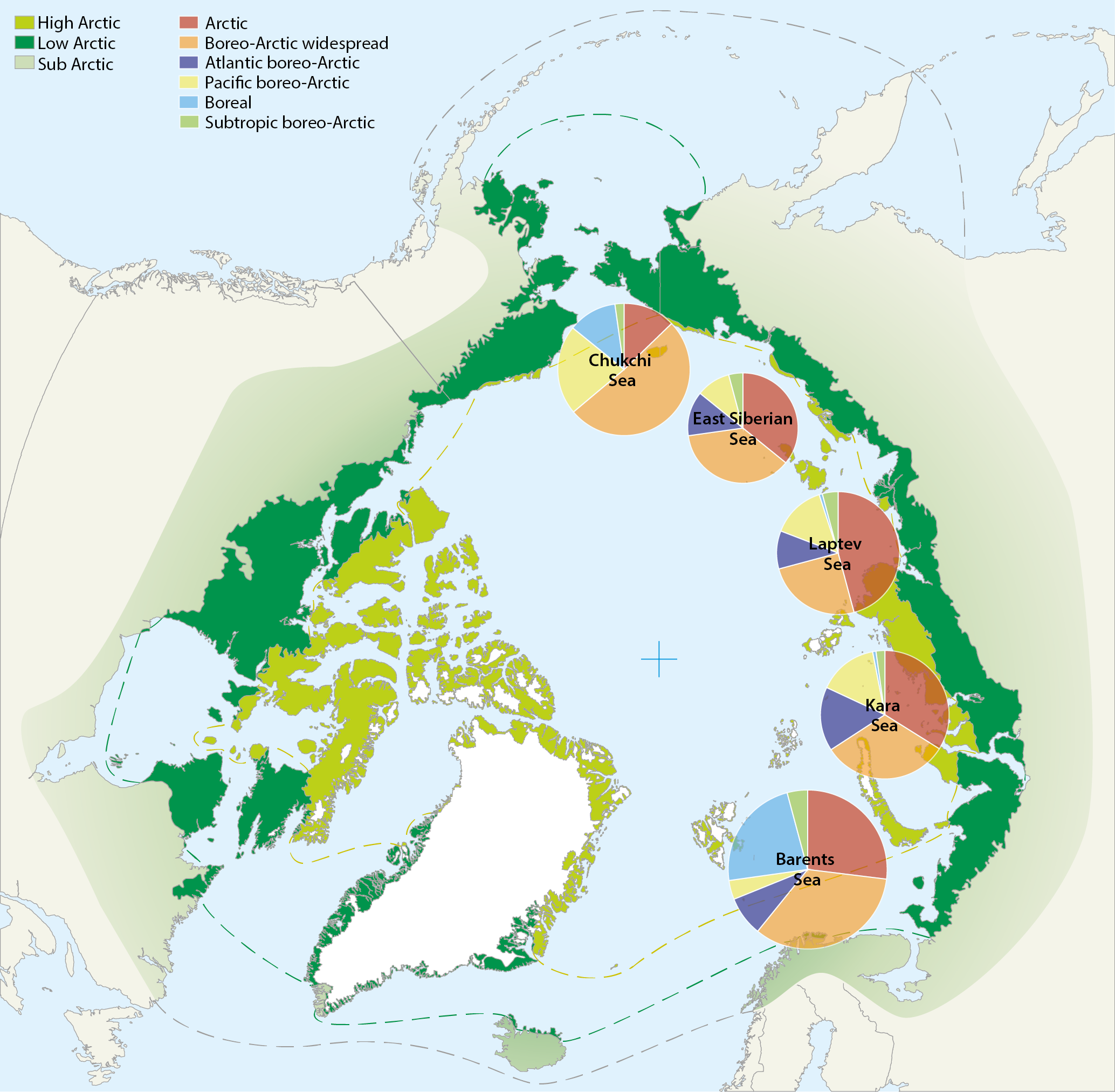
Map of the Arctic Ocean showing the distribution of species richness of Bryozoa for different shelf seas along the Eurasian continental shelf. Diameters of circles are proportional to the number of bryozoan species given in Tab. 8.3. Species numbers partitioned into six zoogeographical affinities are shown from the: Barents Sea (Denisenko 1990), Kara Sea (Gontar & Denisenko 1989); Laptev Sea (Gontar 2004), East Siberian Sea (Denisenko 2010), Chukchi Sea (Denisenko 2008). Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Marine Invertebrates(Chapter 8) page 282
-
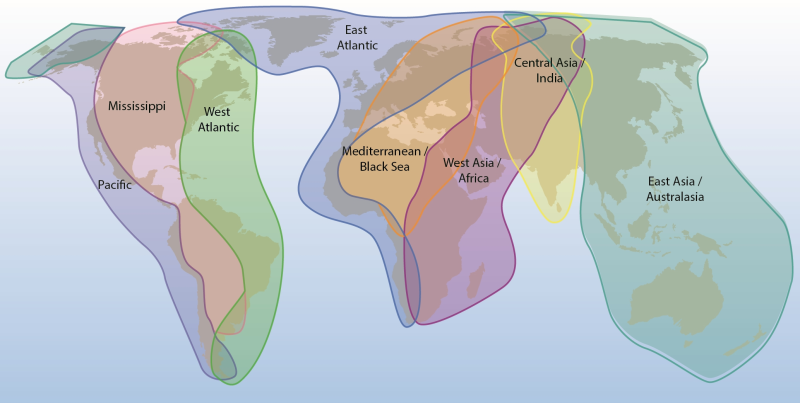
Arctic Biodiversity Assessment (ABA) 2013. Figure 4.2. Major flyways of Arctic birds. Bird migration links Arctic breeding areas to all other parts of the globe (adapted from ACIA 2005). Conservation of Arctic Flora and Fauna, CAFF 2013 - Akureyri . Arctic Biodiversity Assessment. Status and Trends in Arctic biodiversity. - Birds(Chapter 4) page 146
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)