inlandWaters
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
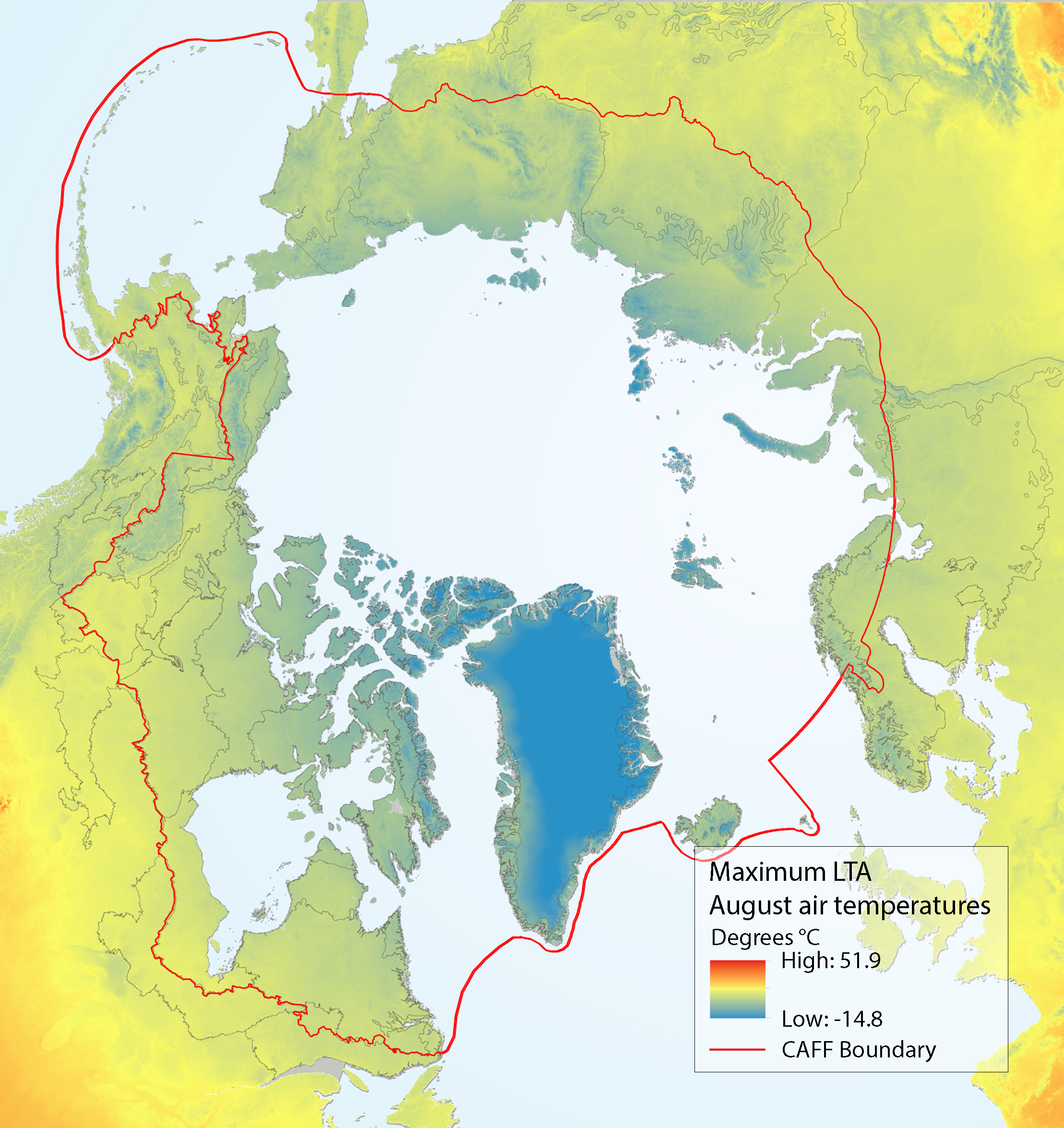
Maximum LTA (long-term average) August air temperatures for the circumpolar region, with ecoregions used in the analysis of the SAFBR outlined in black. Source for temperature layer: Fick and Hijmans (2017). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 5 - Page 89 - Figure 5-5
-
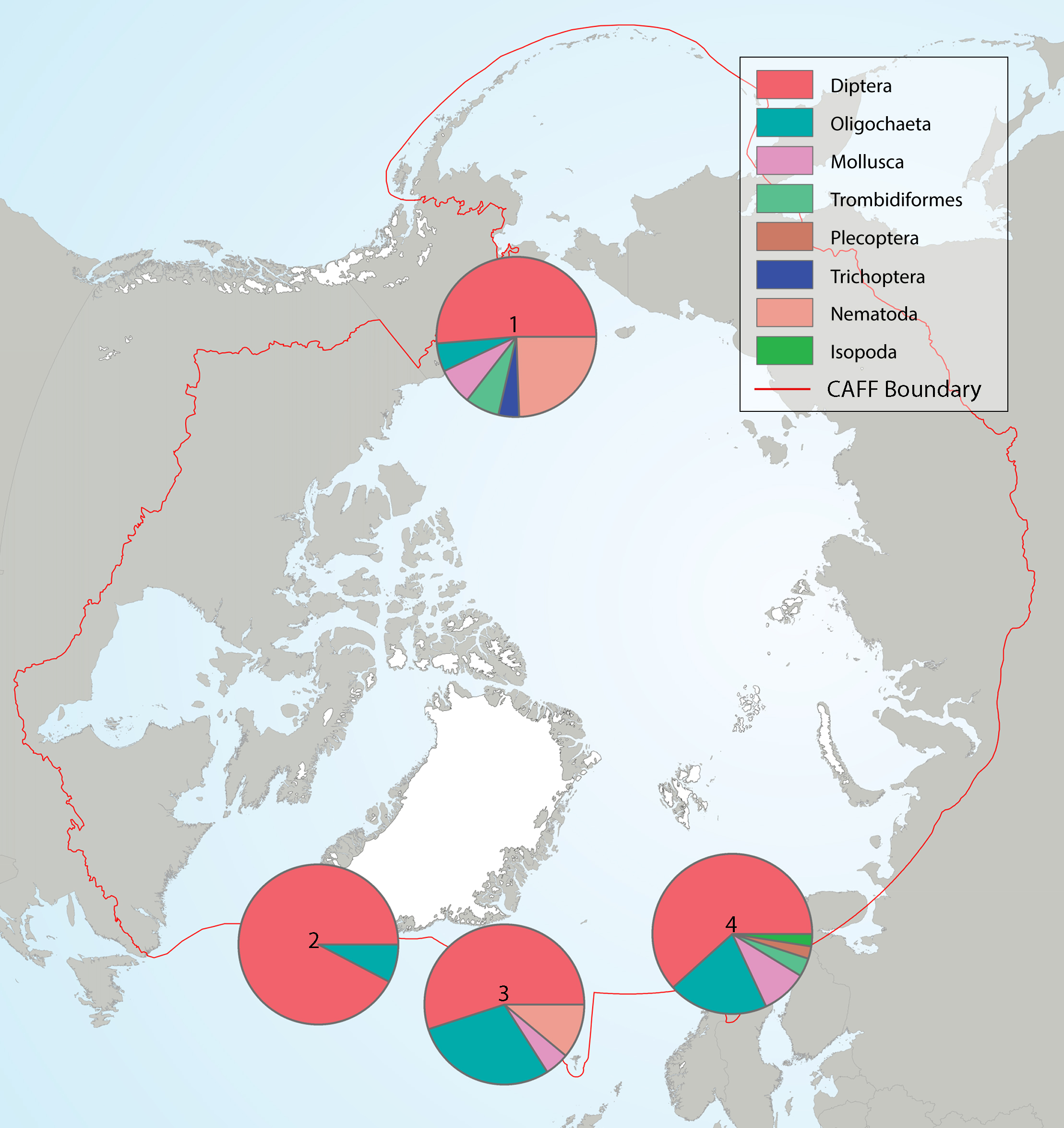
Summary of the taxa accounting for 85% of the lake littoral benthic macroinvertebrates collected in each of several highly-sampled geographic areas, with taxa grouped by order level or higher in pie charts placed spatially to indicate sampling area. Pie charts correspond to (1) Alaska, (2) Greenland low Arctic, (3) Iceland, and (4) Fennoscandia. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 69 - Figure 4-33
-
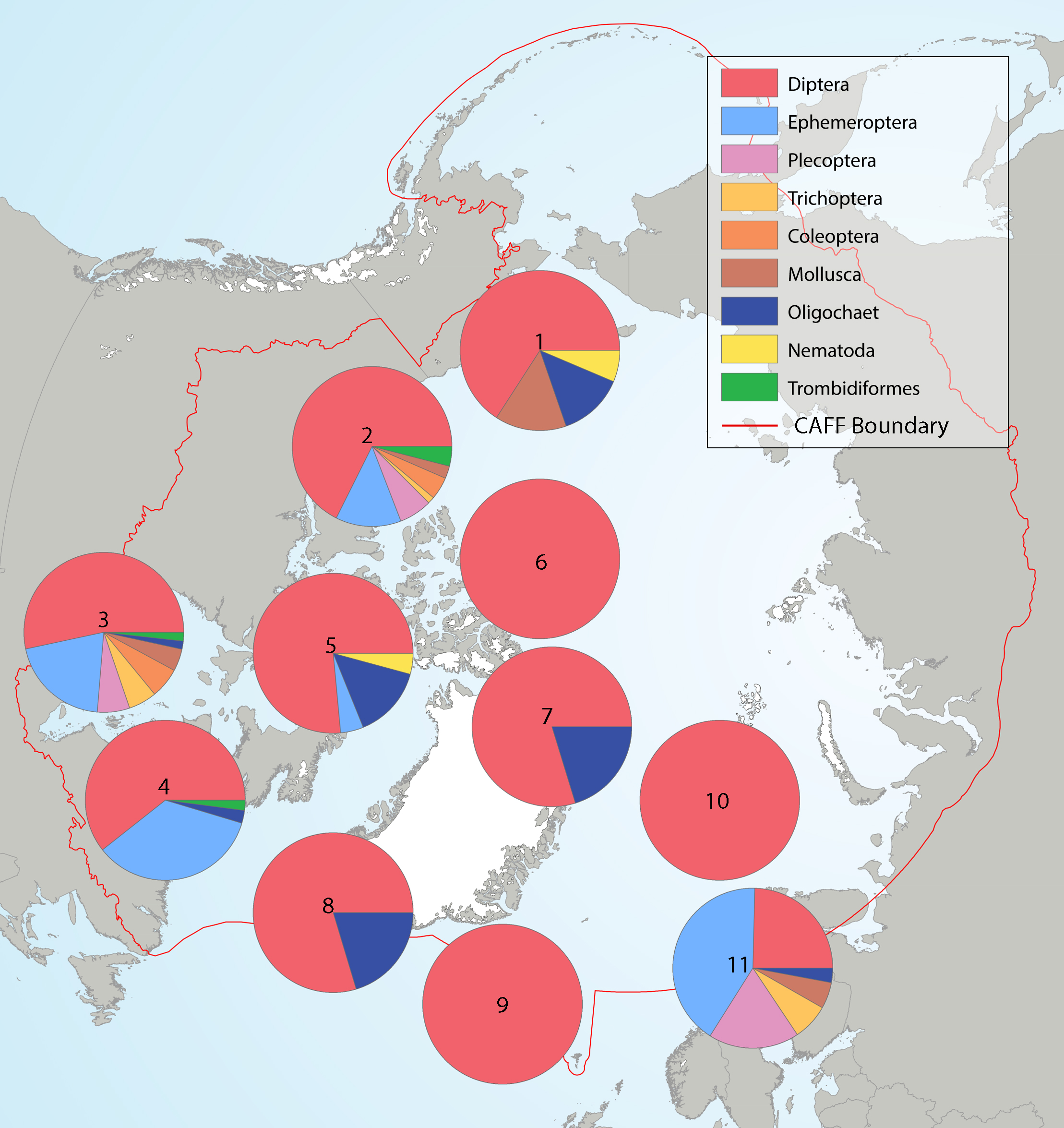
Summary of the taxa accounting for 85% of the river benthic macroinvertebrates collected in each of several highly-sampled geographic areas, with taxa grouped by order level or higher in pie charts placed spatially to indicate sampling area. Pie charts correspond to (1) Alaska, (2) western Canada, (3) southern Canada, south of Hudson Bay, (4) northern Labrador, (5) Baffin Island, (6) Ellesmere Island, (7) Greenland high Arctic, (8) Greenland low Arctic, (9) Iceland, (10) Svalbard, and (11) Fennoscandia. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 70 - Figure 4-34
-
Figure 4 12 Diatom groups from Self Organizing Maps (SOMs) in lake top sediments, showing the geographical distribution of each group (with colors representing different SOM groups). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 39 - Figure 4-12
-
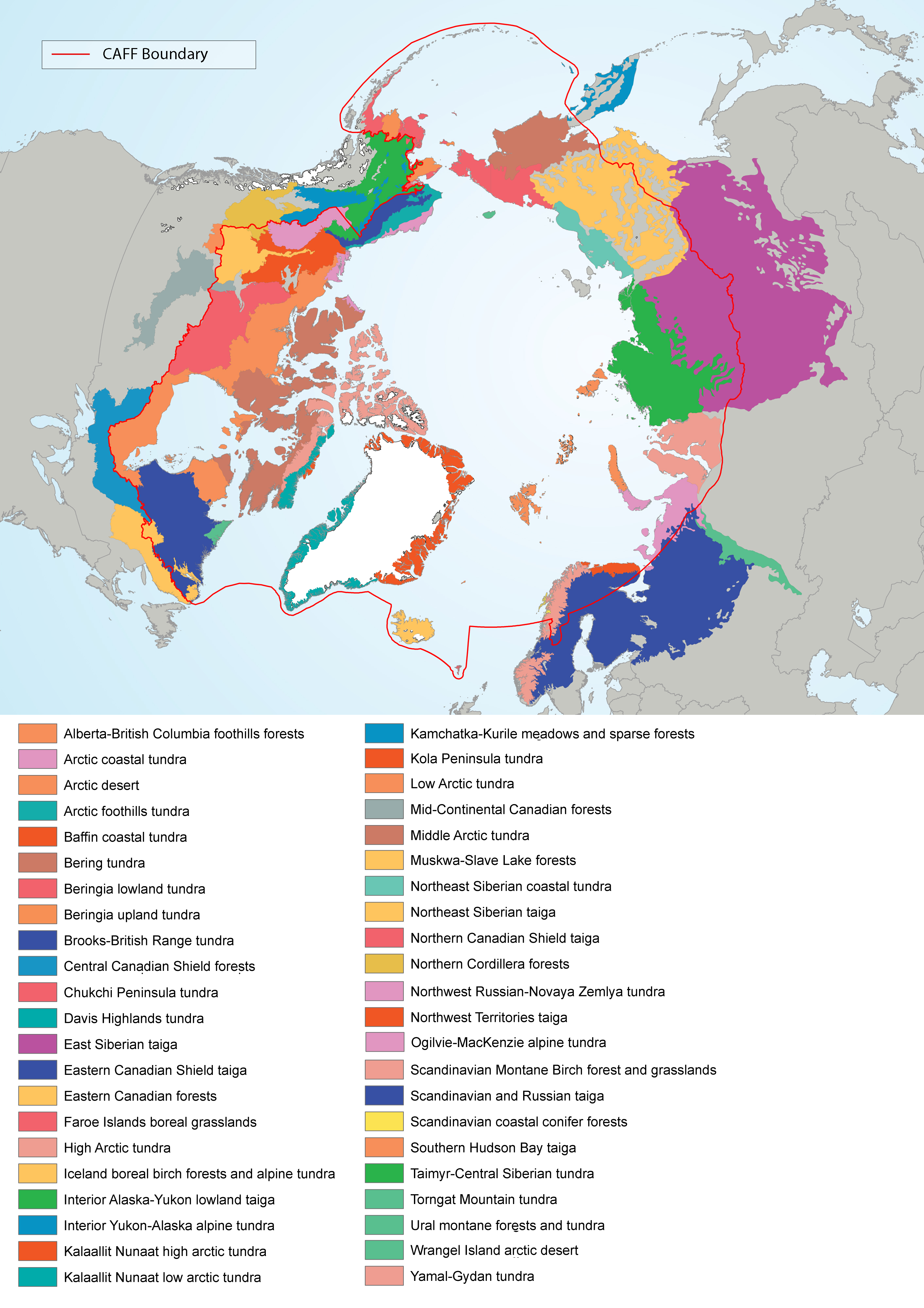
Figure 4-5 Terrestrial ecoregions that are included within the circumpolar region within the CAFF boundary and/or the ABA boundaries. Source: Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World (TEOW; Olson et al. 2001). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 28 - Figure 4-5
-
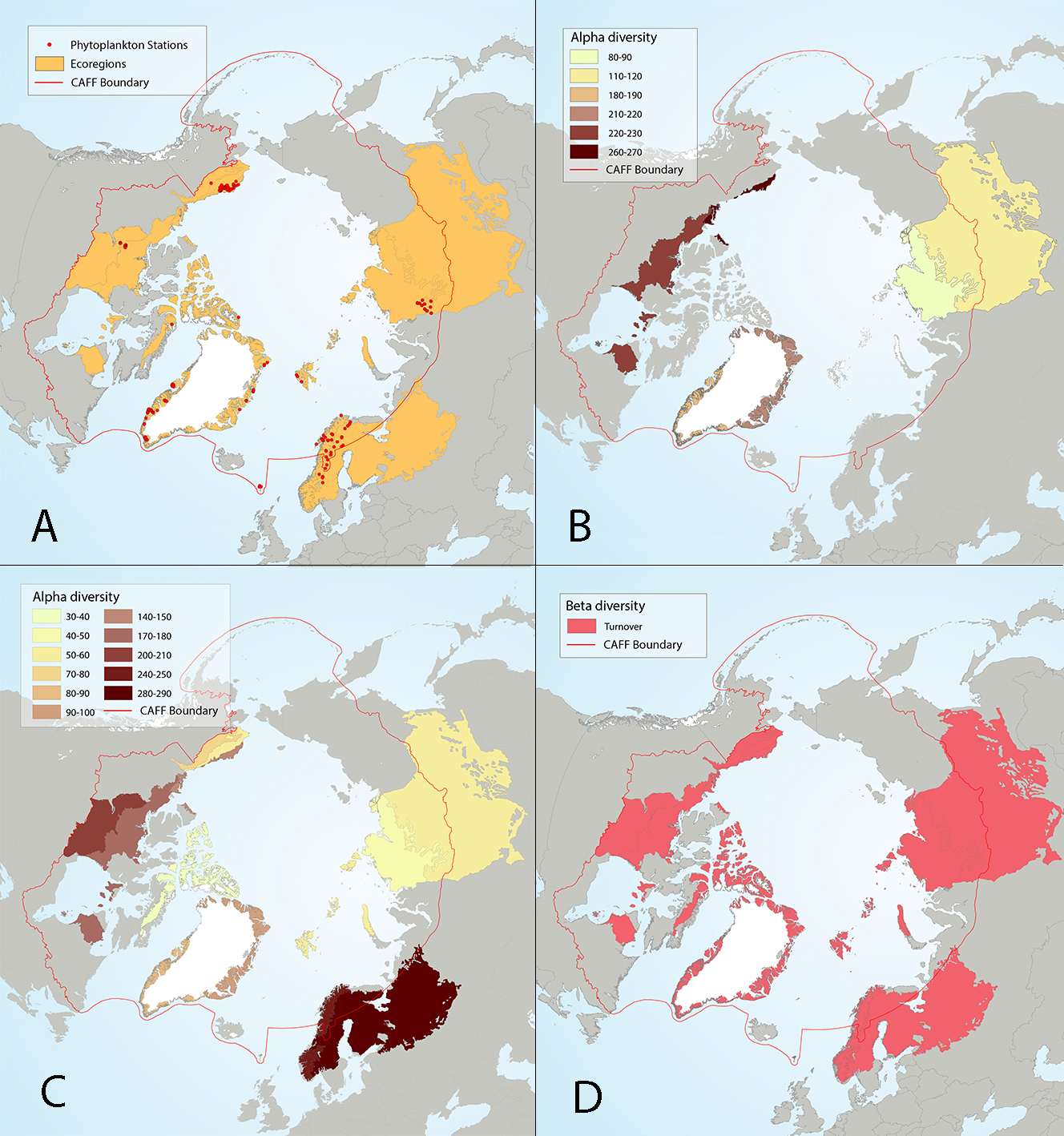
Figure 4 17 Results of circumpolar assessment of lake phytoplankton,(a) the location of phytoplankton stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 35 stations; (c) all ecoregions with phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 56 - Figure 4-17
-

Although the circumpolar countries endeavor to support monitoring programs that provide good coverage of Arctic and subarctic regions, this ideal is constrained by the high costs associated with repeated sampling of a large set of lakes and rivers in areas that often are very remote. Consequently, freshwater monitoring has sparse, spatial coverage in large parts of the Arctic, with only Fennoscandia and Iceland having extensive monitoring coverage of lakes and streams Figure 6-2 Current state of monitoring for river FECs in each Arctic country State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 6 - Page 94 - Figure 6-2
-
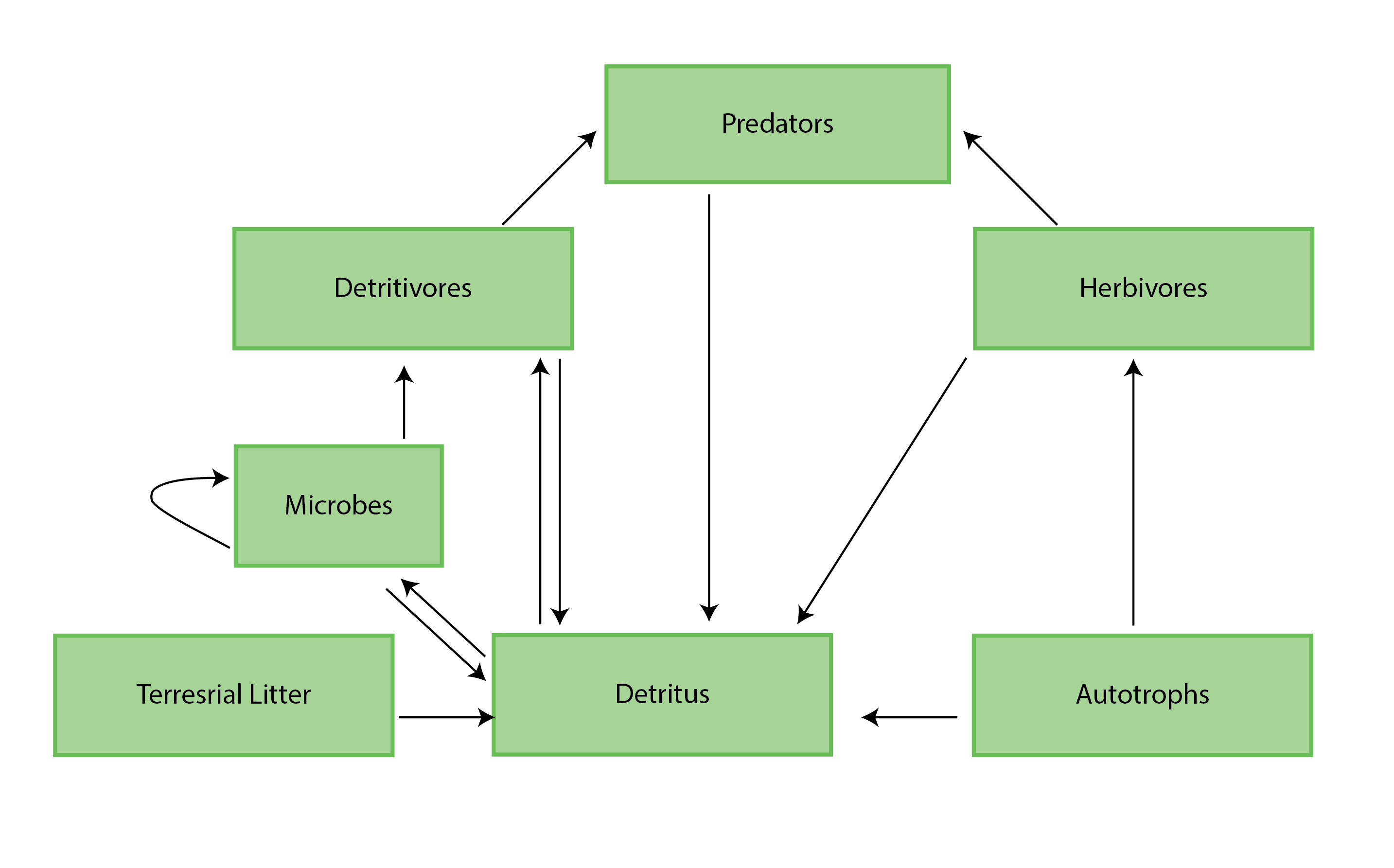
Figure 4-1 A generic food web diagram for a lake or river, indicating the basic trophic levels (boxes) and energy flow (arrows) between those levels. Reproduced from Culp et al. (2012a). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 25 - Figure 4-1
-
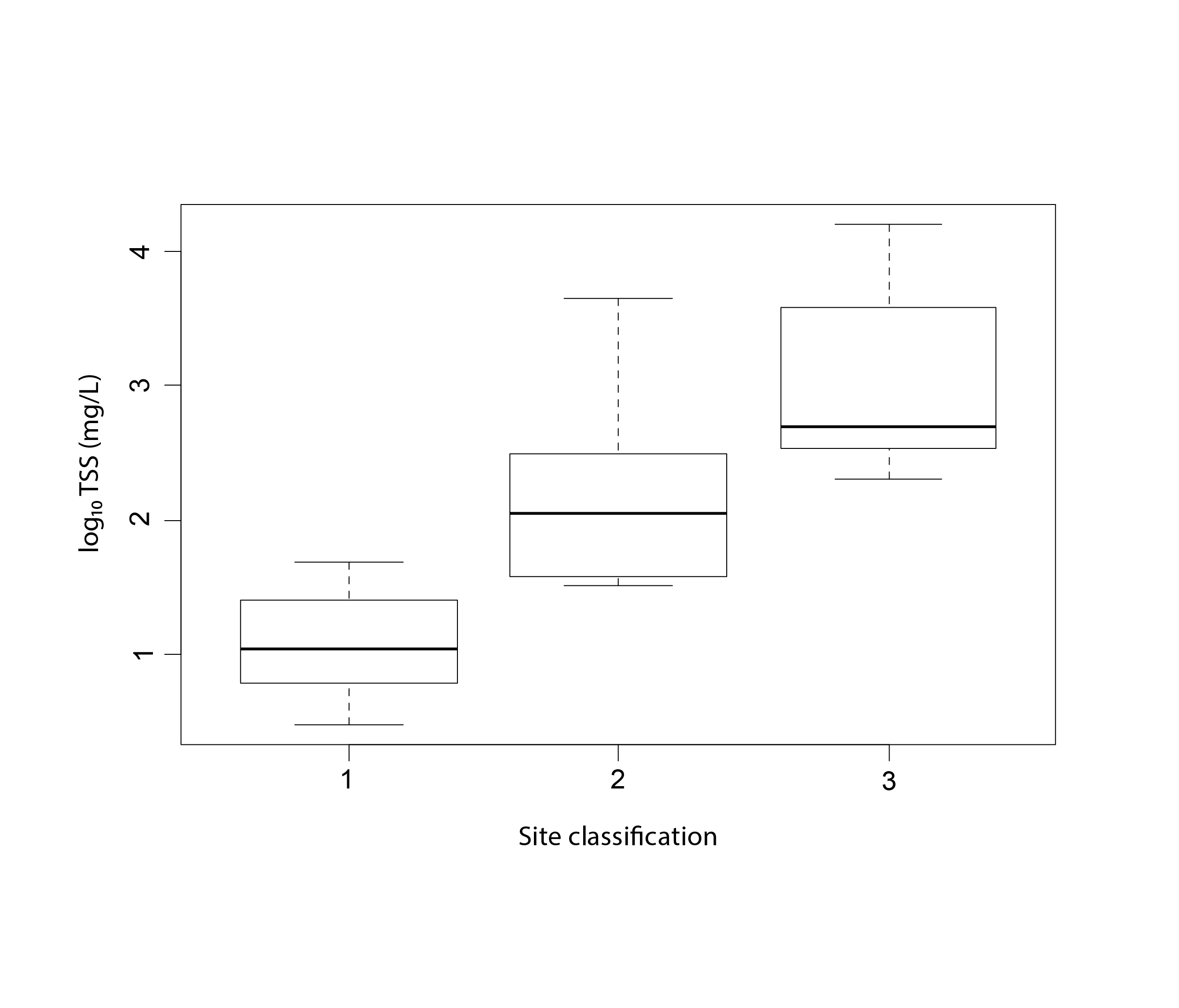
Figure 3-4 Effects of permafrost thaw slumping on Arctic rivers, including (upper) a photo of thaw slump outflow entering a stream on the Peel Plateau, Northwest Territories, Canada, and (lower) log10-transformed total suspended solids (TSS) in (1) undisturbed, (2) 1-2 disturbance, and (3) > 2 disturbance stream sites, with letters indicating significant differences in mean TSS among disturbance classifications Plot reproduced from Chin et al. (2016). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter3 - Page 21 - Figure 3-4
-
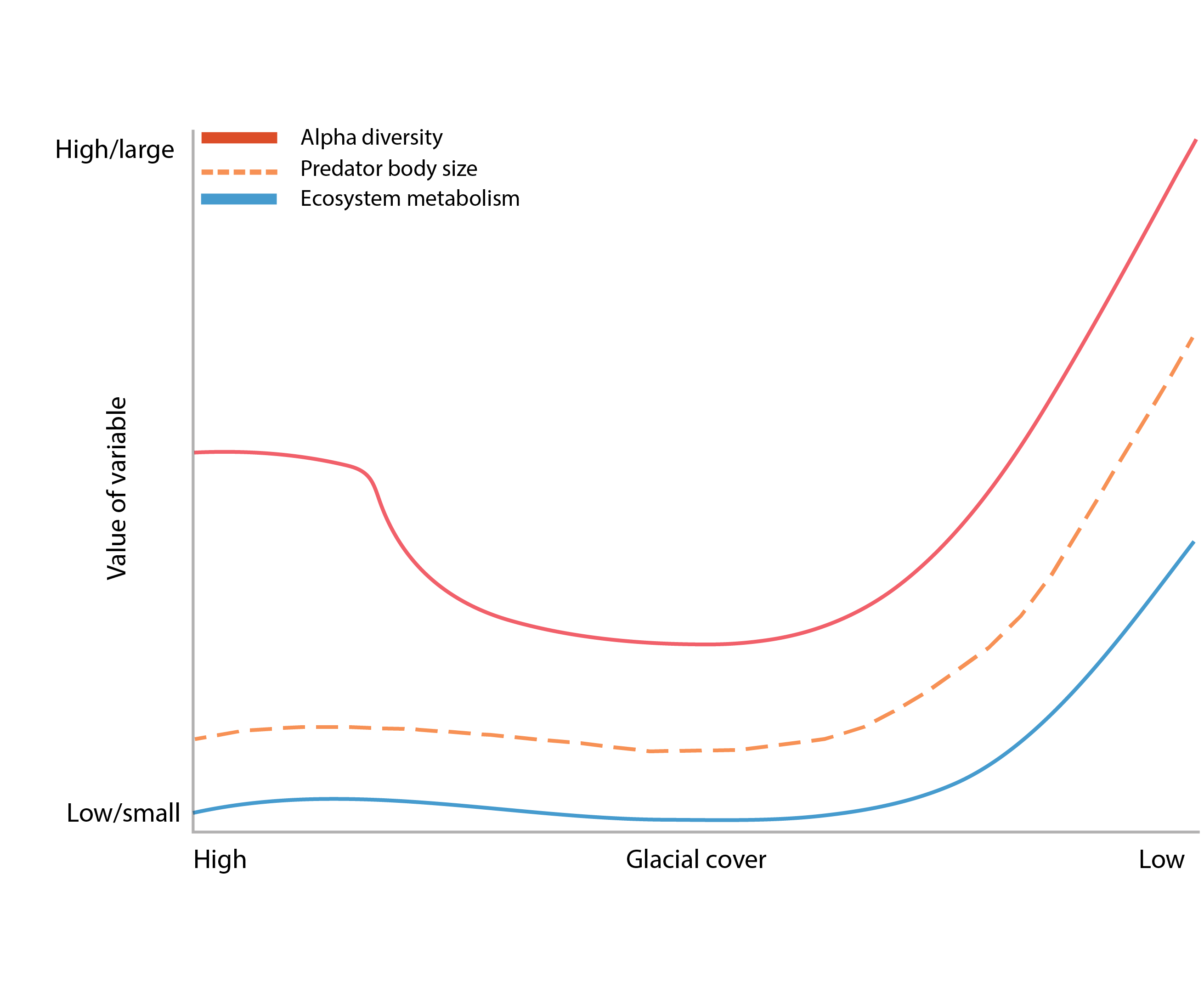
Figure 3-5 Changes in alpha diversity (red line), predator body size (blue dashed line), and ecosystem metabolism (blue solid line) with a shift in glacial cover from high (left) to low (right). Redrawn from Milner et al. (2017). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 3 - Page 22 - Figure 3-5
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)