unknown
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
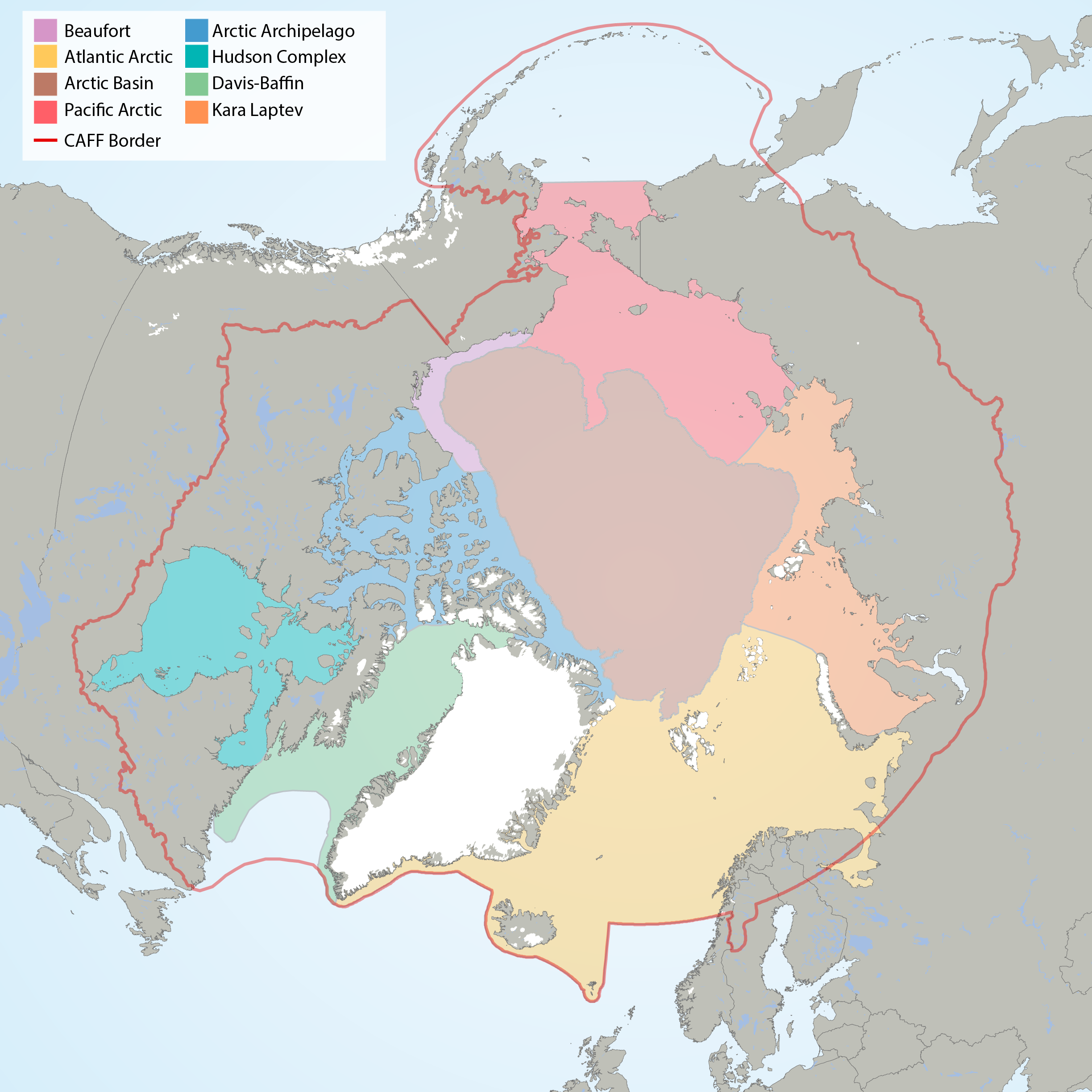
Arctic Marine Areas (AMAs) as defined in the CBMP Marine Plan. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 1</a> - Page 15 - Figure 1.2
-
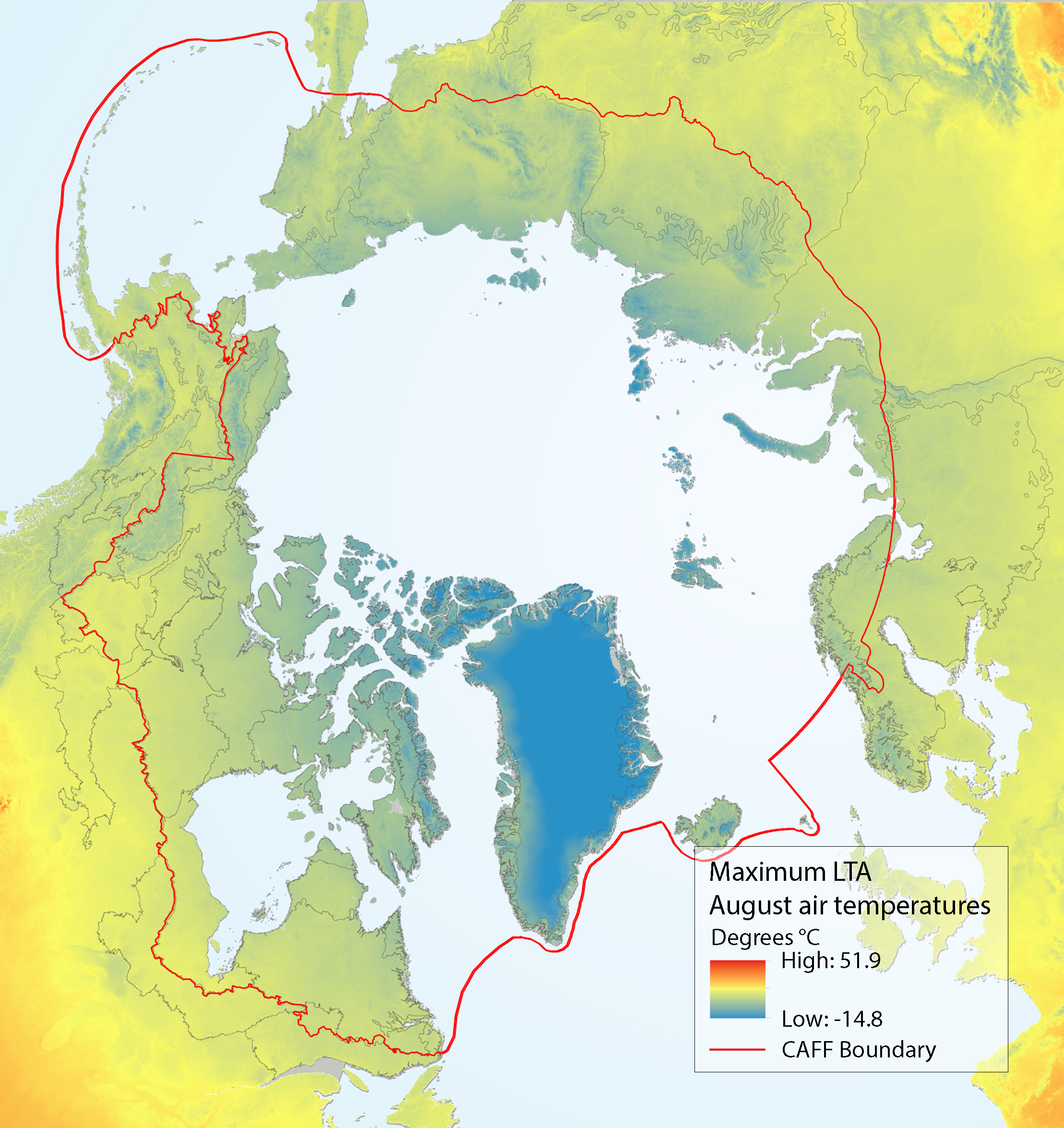
Maximum LTA (long-term average) August air temperatures for the circumpolar region, with ecoregions used in the analysis of the SAFBR outlined in black. Source for temperature layer: Fick and Hijmans (2017). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 5 - Page 89 - Figure 5-5
-
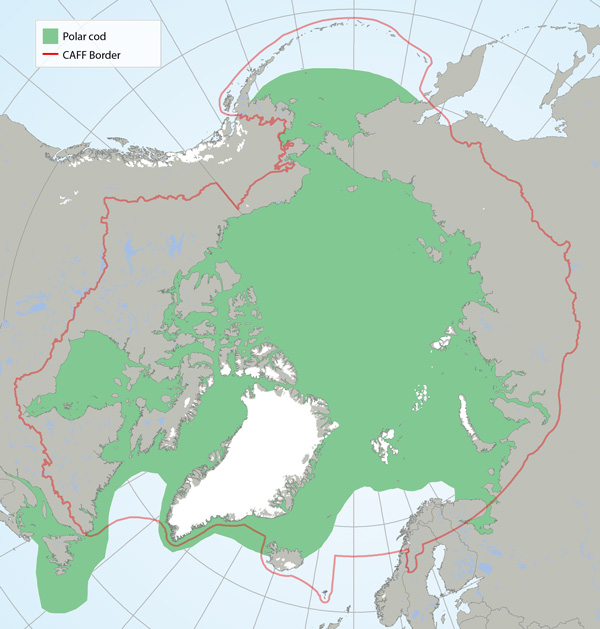
Distribution of polar cod (Boreogadus saida) based on participation in research sampling, examination of museum voucher collections and the literature (Mecklenburg et al. 2011, 2014, 2016; Mecklenburg and Steinke 2015). Map shows the maximum distribution observed from point data and includes both common and rare locations. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-fishes" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 114 - Figure 3.4.2
-
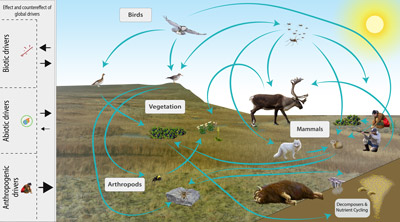
The Arctic terrestrial food web includes the exchange of energy and nutrients. Arrows to and from the driver boxes indicate the relative effect and counter effect of different types of drivers on the ecosystem. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 26- Figure 2.4
-
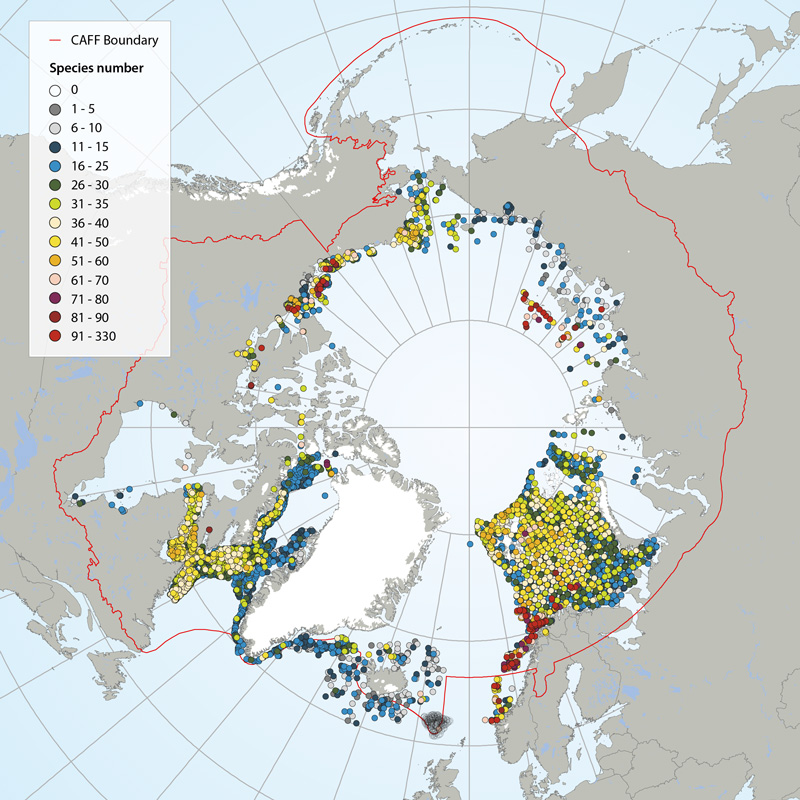
Number of megafauna species/taxa in the Arctic (7,322 stations in total), based on recent trawl investigations. Stations with highest species/taxon number are sorted to the top, meaning that dense concentrations of stations (e.g. Eastern Canada, Barents Sea), with low species numbers are hidden behind stations with higher species numbers. Also note that species numbers are somewhat biased by differing taxonomic resolution between studies. Data from: Icelandic Institute of Natural History, Iceland; Marine Research Institute, Iceland; University of Alaska, Fairbanks, U.S.; Greenland Institute of Natural Resources, Greenland; Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia; Université du Québec à Rimouski, Canada; Fisheries and Oceans Canada; Institute of Marine Research, Norway; and Polar Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography, Murmansk, Russia. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/benthos" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 91 - Box figure 3.3.2 Several regions of the Pan Arctic have been sampled with trawl. Even though the trawl configurations and the taxonomic level are different from area to area, we choose to consider the taxonomic richness as relatively comparative.
-
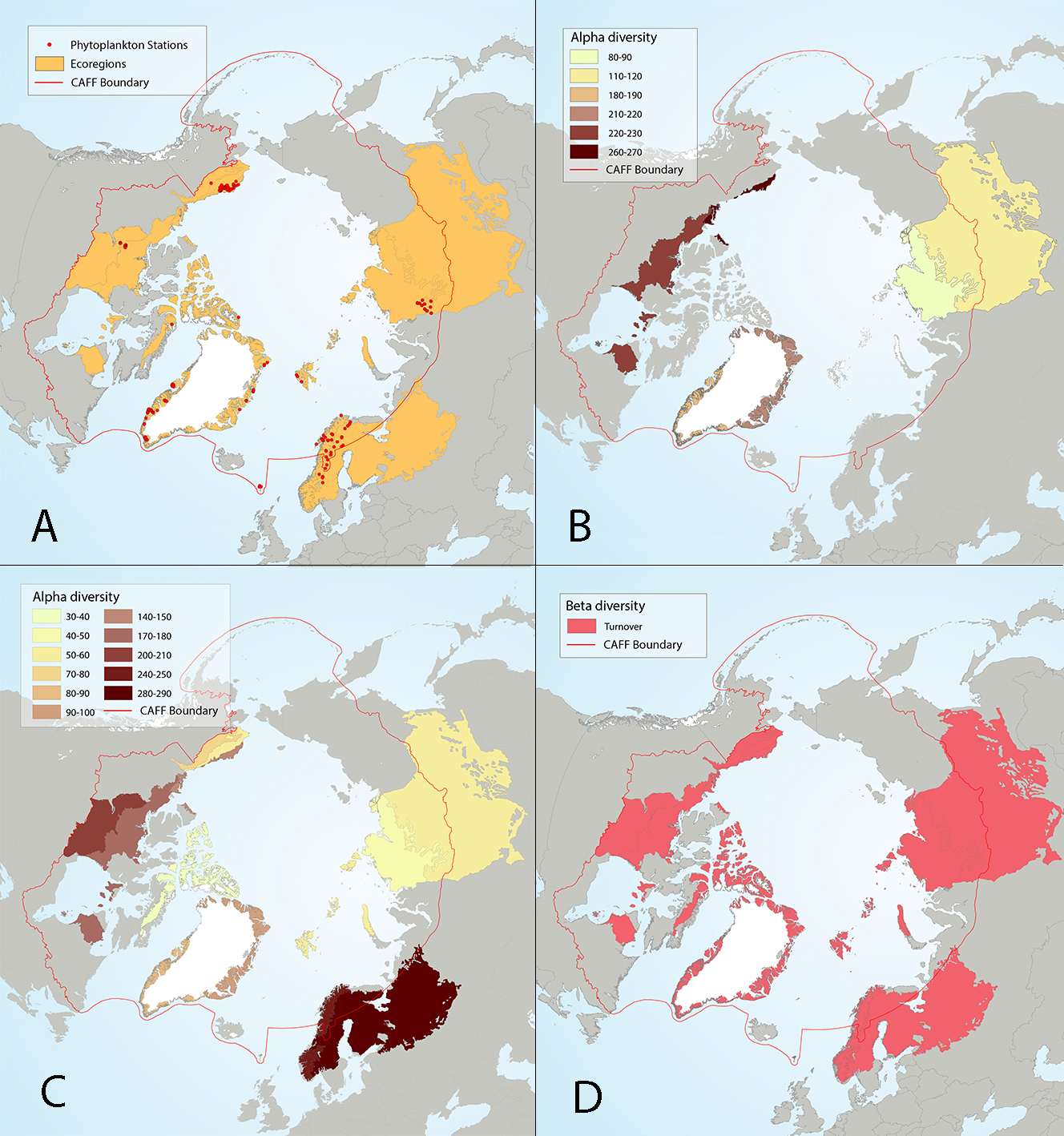
Figure 4 17 Results of circumpolar assessment of lake phytoplankton,(a) the location of phytoplankton stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 35 stations; (c) all ecoregions with phytoplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 56 - Figure 4-17
-
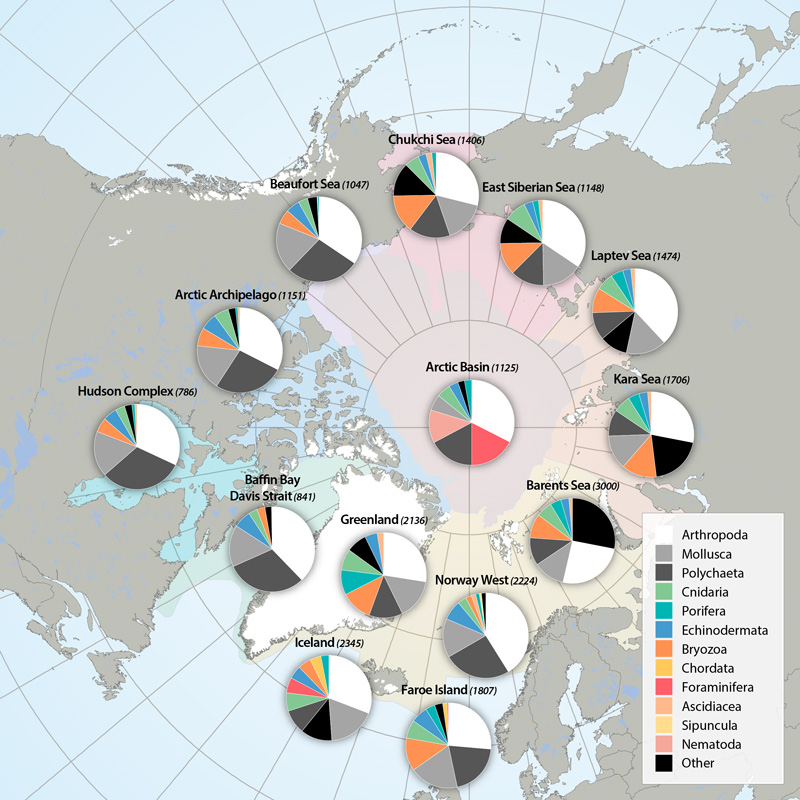
Arthropods (e.g., shrimps, crabs, sea spiders, amphipods, isopods) dominate taxon numbers in all Arctic regions, followed by polychaetes (e.g., bristle worms) and mollusks (e.g., gastropods, bivalves). Other taxon groups are diverse in some regions, such as bryozoans in the Kara Sea, cnidarians in the Atlantic Arctic, and foraminiferans in the Arctic deep-sea basins. This pattern is biased, however, by the meiofauna inclusion for the Arctic Basin (macro- and meiofauna size ranges overlap substantially in deep-sea fauna, so nematodes and foraminiferans are included) and the influence of a lack of specialists for some difficult taxonomic groups. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/benthos" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 89 - Box figure 3.3.1 Each region of the Pan Arctic has been sampled with a set of different sampling gears, including grab, sledge and trawl, while other areas has only been sampled with grab. Here is the complete species/taxa number and the % distribution of species/taxa in main phyla, per region of the Pan Arctic.
-
Appendix 20. Arctic indigenous languages status and trends. Data used to compile the information for the table was collected from both census records and academic sources, each of the CAFF countries and indigenous peoples organizations (Permanent Participants to the Arctic Council) where possible also provided statistical information.
-
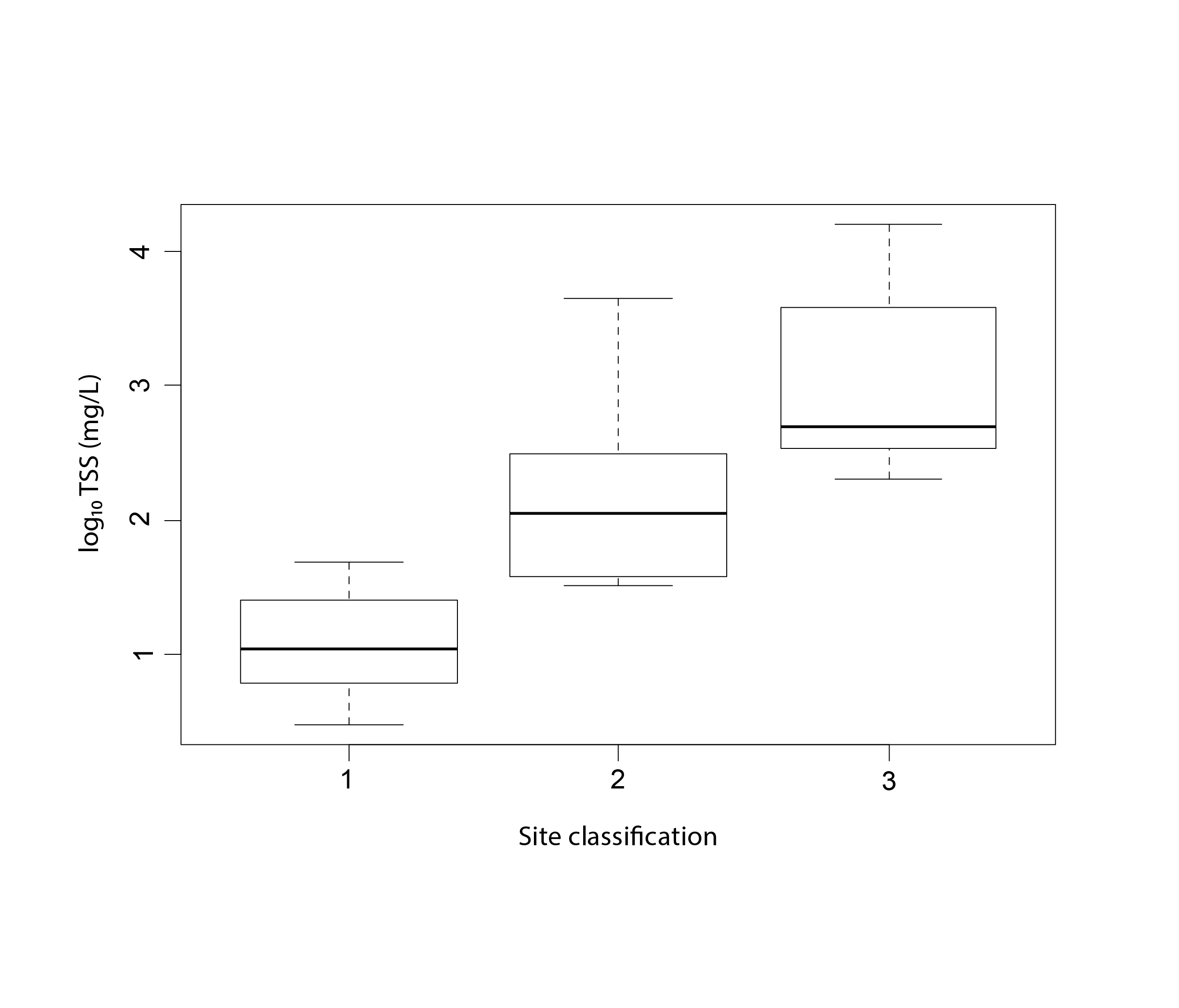
Figure 3-4 Effects of permafrost thaw slumping on Arctic rivers, including (upper) a photo of thaw slump outflow entering a stream on the Peel Plateau, Northwest Territories, Canada, and (lower) log10-transformed total suspended solids (TSS) in (1) undisturbed, (2) 1-2 disturbance, and (3) > 2 disturbance stream sites, with letters indicating significant differences in mean TSS among disturbance classifications Plot reproduced from Chin et al. (2016). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter3 - Page 21 - Figure 3-4
-
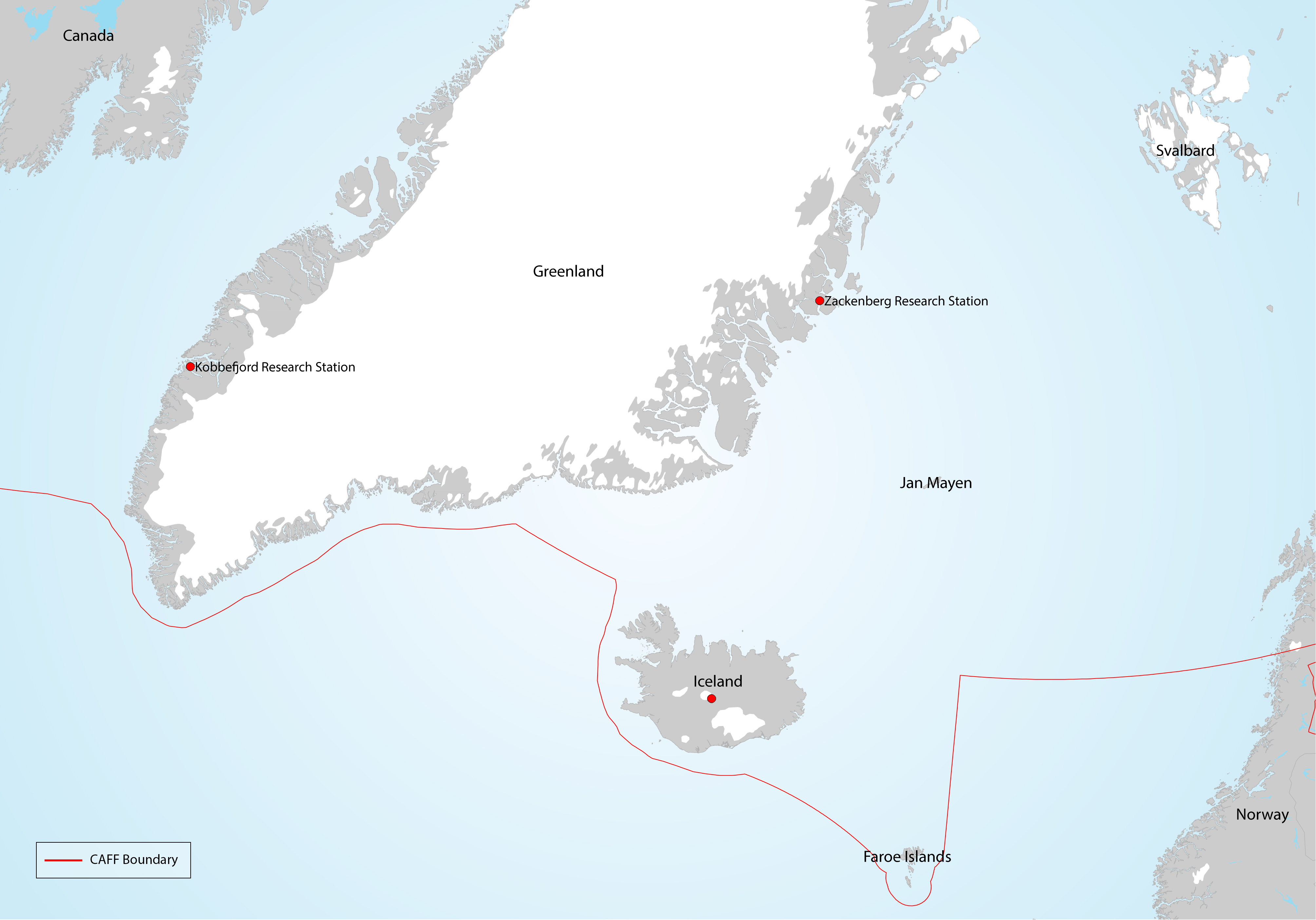
The baseline survey and ongoing monitoring required to adequately describe Arctic arthropod biodiversity and to identify trends is largely lacking. Although some existing publications reporting long-term and extensive sampling exist, they are limited in species level information, taxonomic coverage and/or geographic location/extent (Figure 3-19) STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 44 - Figure 3.19
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)