inlandWaters
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-

Figure 2-1 The CBMP takes an adaptive Integrated Ecosystem based Approach to monitoring and data creation. This figure illustrates how management questions, conceptual ecosystem models based on science and Traditional Knowledge (TK), and existing monitoring networks are designed to guide the four CBMP Steering Groups (marine, freshwater, terrestrial, and coastal) in their development. Monitoring outputs (data) are designed to feed into the assessment and decision-making processes (data, communication and reporting). The findings are then intended to feed back into the monitoring program. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 2 - Page 15 - Figure 2-1
-
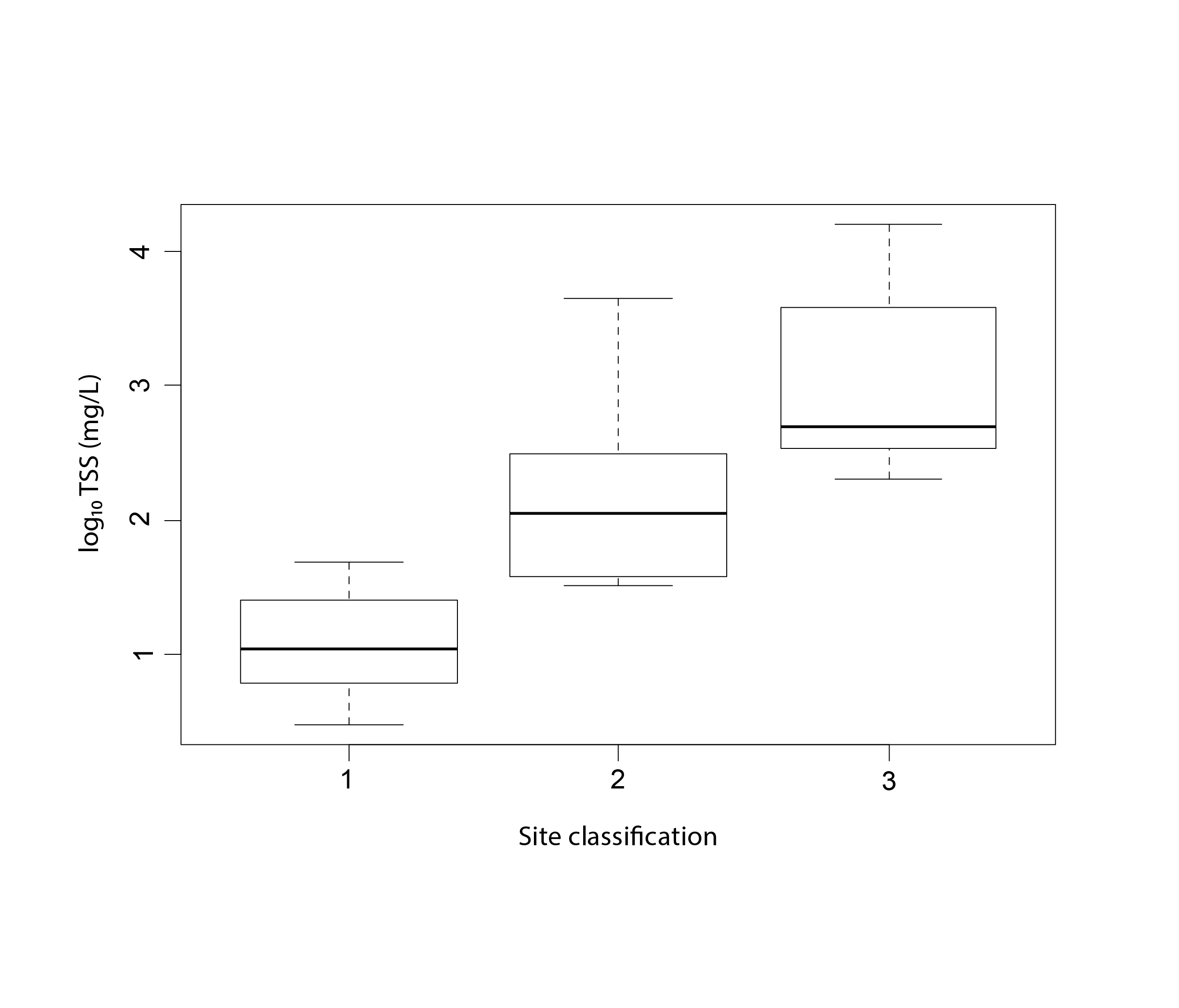
Figure 3-4 Effects of permafrost thaw slumping on Arctic rivers, including (upper) a photo of thaw slump outflow entering a stream on the Peel Plateau, Northwest Territories, Canada, and (lower) log10-transformed total suspended solids (TSS) in (1) undisturbed, (2) 1-2 disturbance, and (3) > 2 disturbance stream sites, with letters indicating significant differences in mean TSS among disturbance classifications Plot reproduced from Chin et al. (2016). State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter3 - Page 21 - Figure 3-4
-
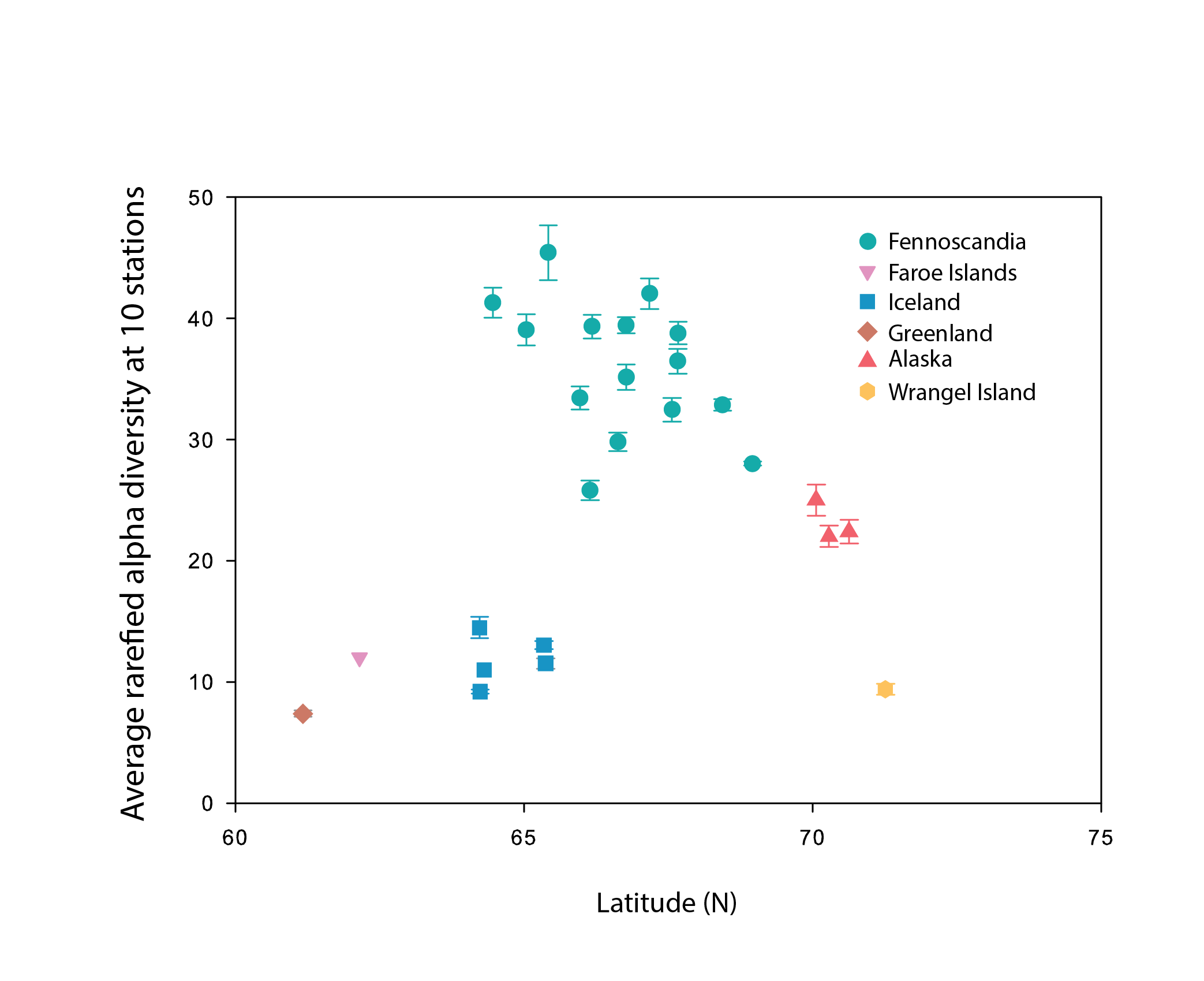
Alpha diversity (rarefied to 10 stations, with error bars indicating standard error) of littoral lake benthic macroinvertebrates plotted as a function of the average latitude of stations in each hydrobasin. Hydrobasins are coloured by country/region. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4- Page 68 - Figure 4-31
-
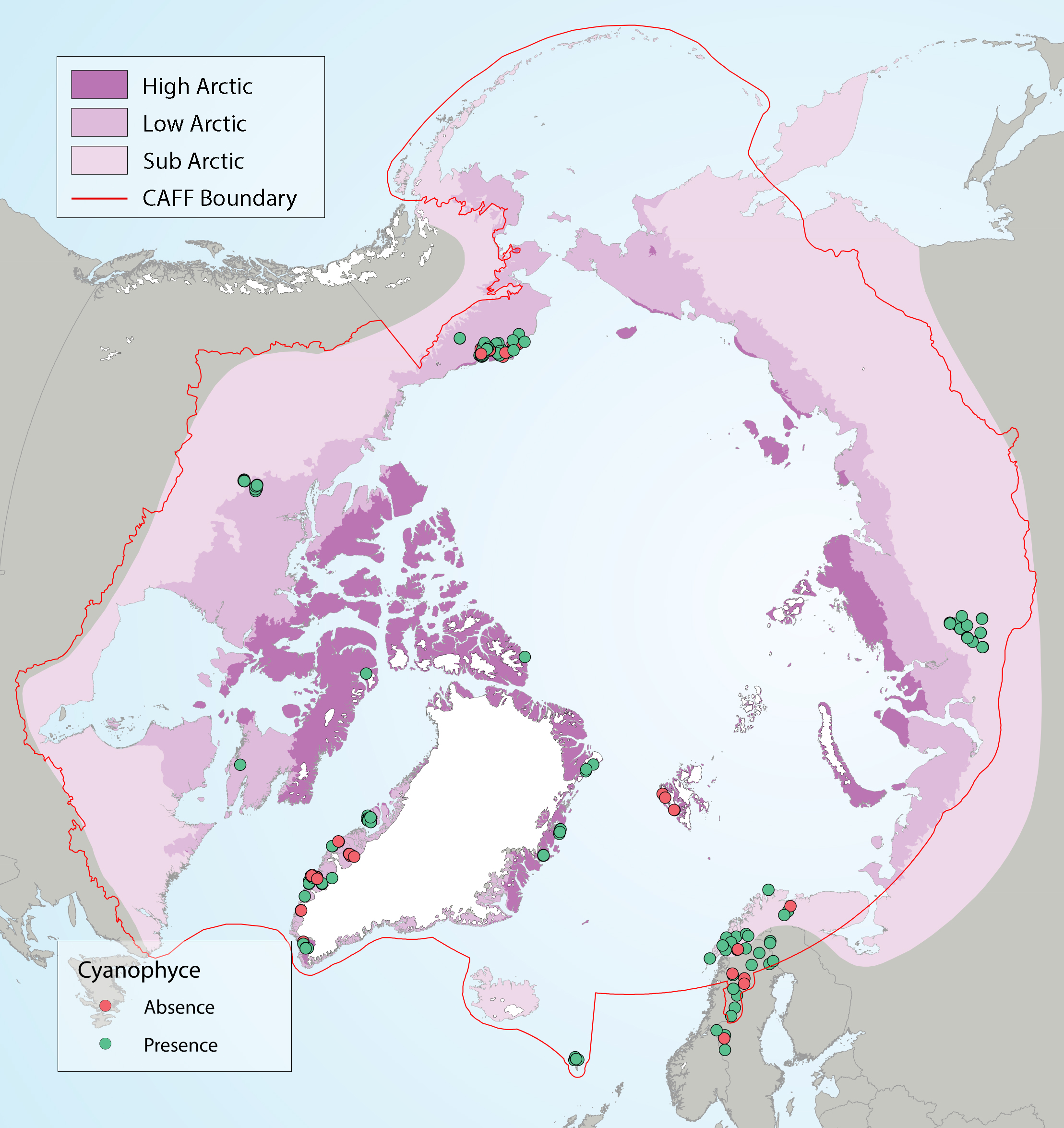
Circumpolar Arctic distribution of Cyanophyceae using presence- absence data from all sites sampled between 1980-2015. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 50 - Figure 4-21
-
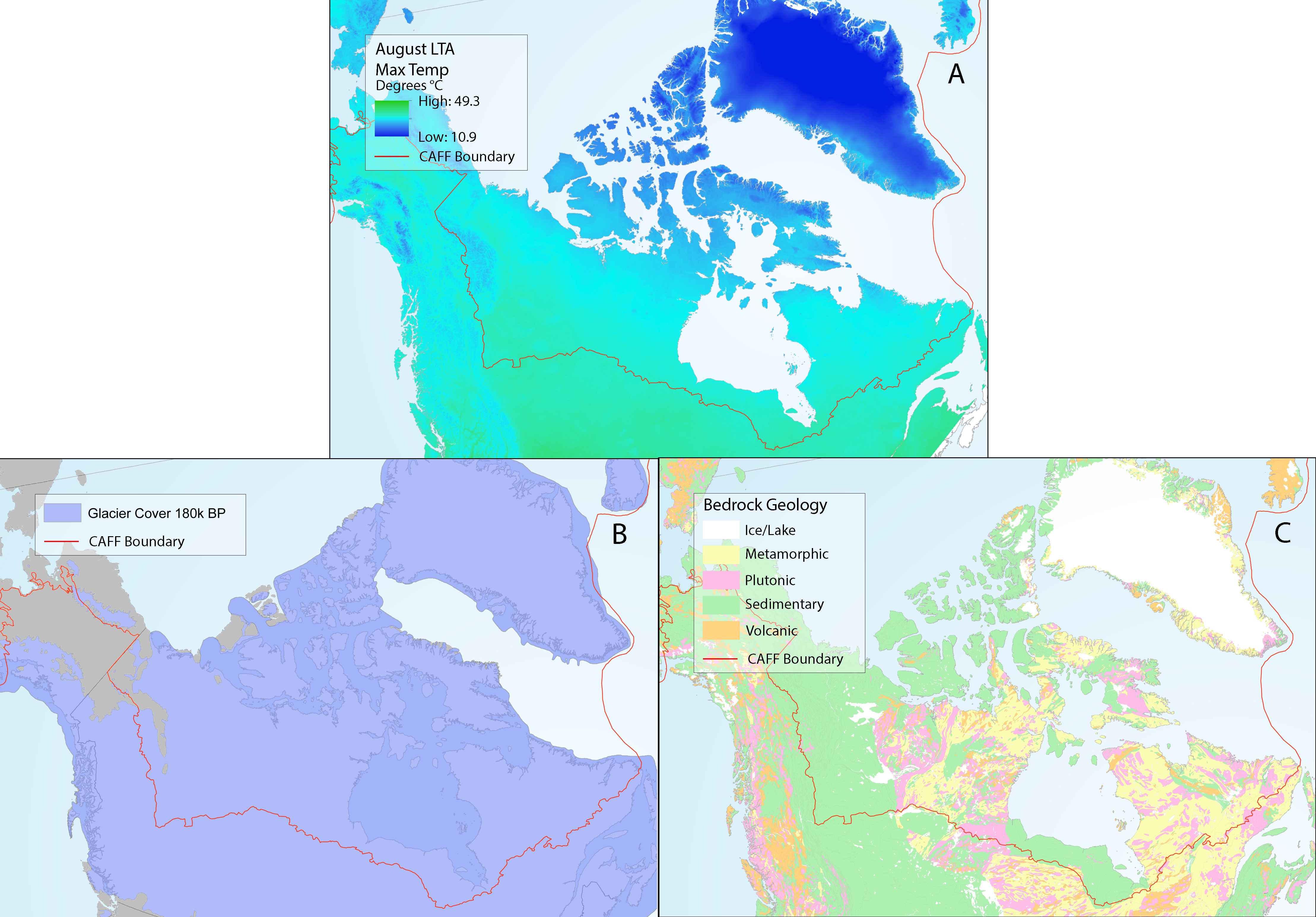
Abiotic drivers in North America, including (a) long-term average maximum August air temperature, (b) spatial distribution of ice sheets in the last glaciation of the North American Arctic region, and (c) geological setting of bedrock geology underlying North America. Panel (a) source Fick and Hijmans (2017). Panel (b) adapted from: Physical Geology by Steve Earle, freely available at http://open.bccampus.ca. Panel (c) source: Geogratis. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 5 - Page 86 - Figure 5-3
-
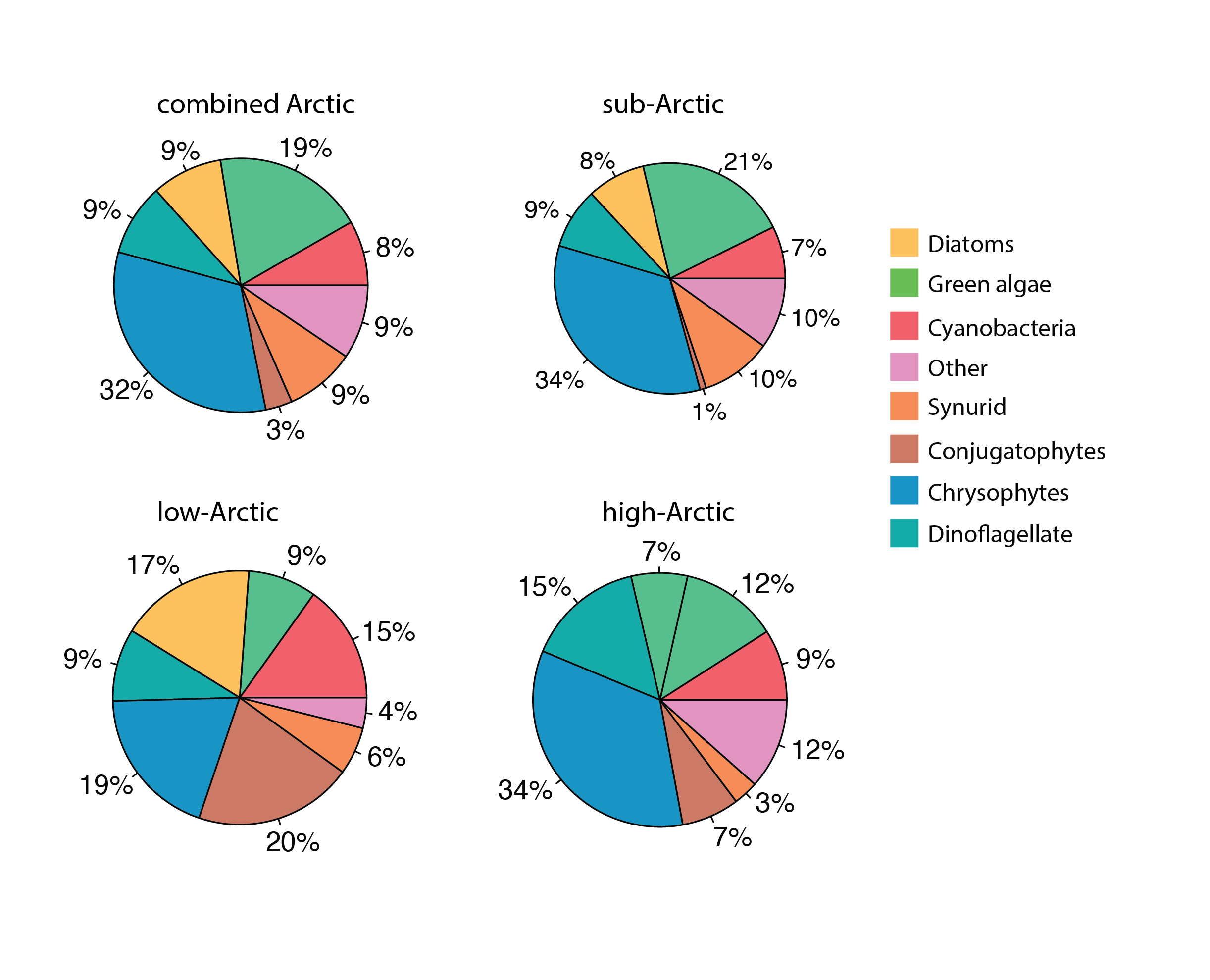
Phytoplankton percent composition by dominant classes across the three Arctic regions, using relative presence across stations calculated from from presence – absence data. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 48 - Figure 4-19
-
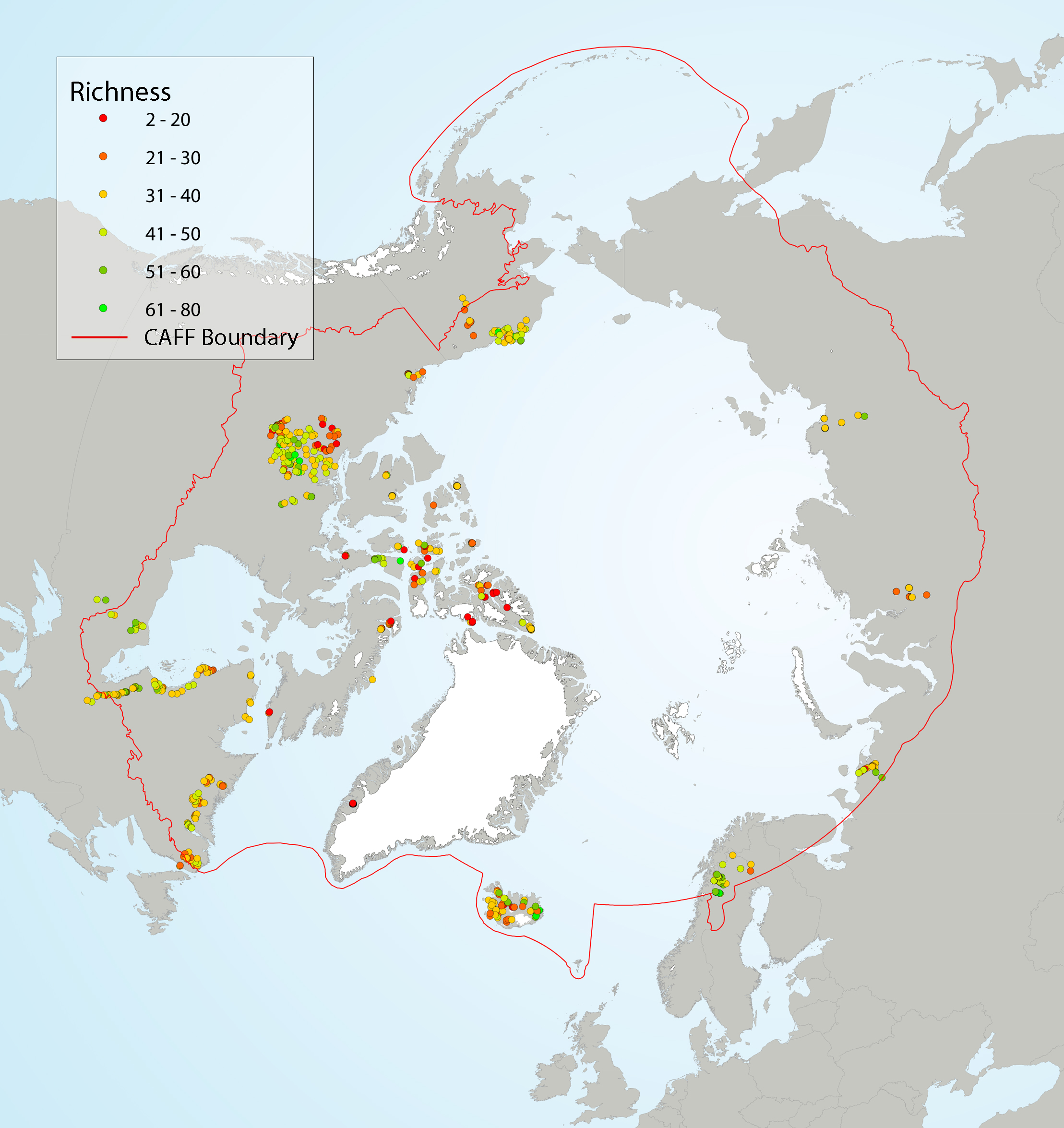
Figure 4 9 Local diatom species richness of Arctic lake surface sediments, showing (left) richness as a function of latitude, and (right) site-specific richness. A LOESS smoother (blue line) with a span of 0.75 and a 95% confidence interval (grey shading) was applied to the data (left) to better highlight the general trend. Coloured circles on the map indicate the species richness at the sampling sites. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 37 - Figure 4-9
-
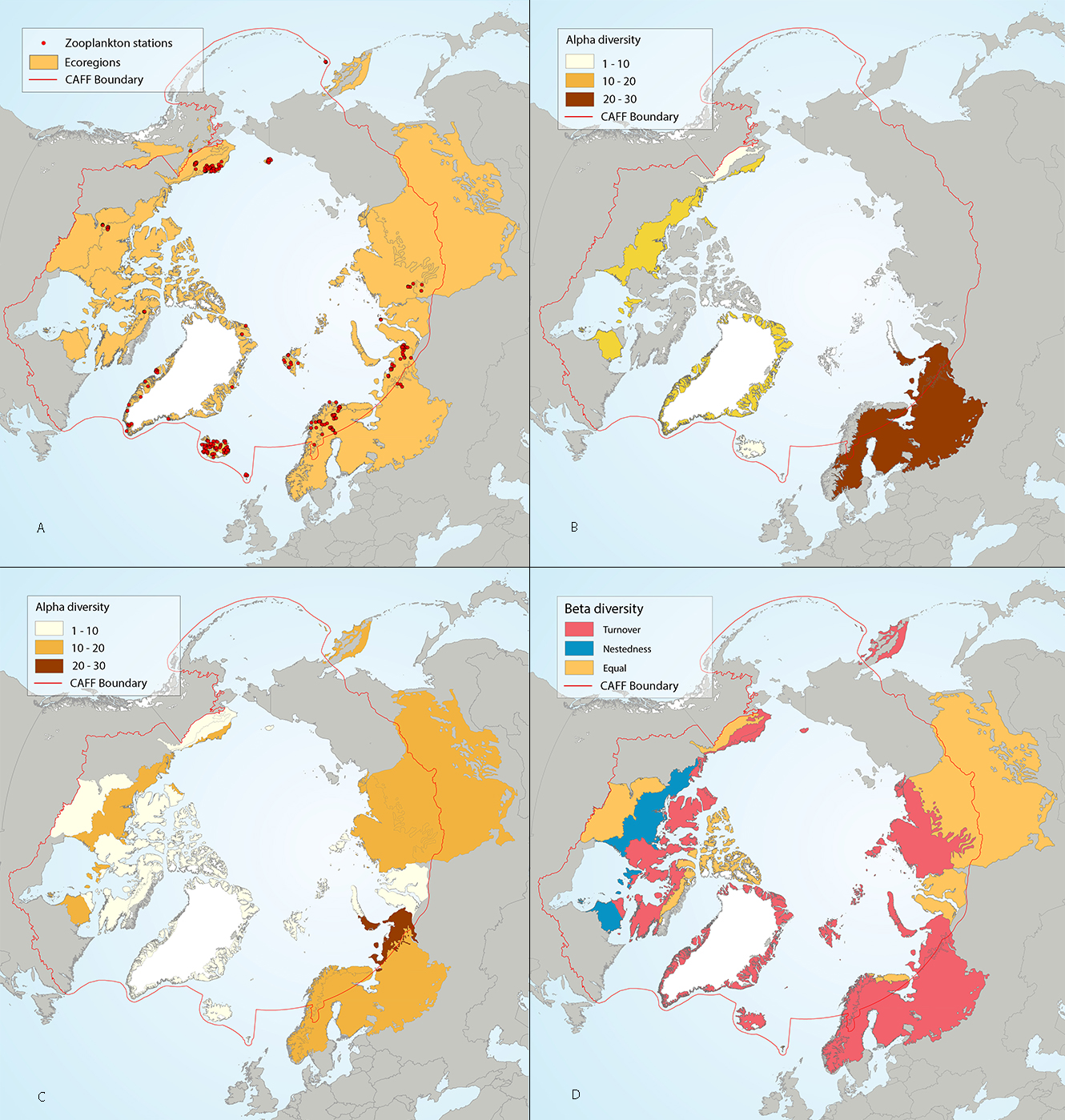
Results of circumpolar assessment of lake zooplankton, focused just on crustaceans, and indicating (a) the location of crustacean zooplankton stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many crustacean zooplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 25 stations; (c) all ecoregions with crustacean zooplankton stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 58 - Figure 4-25
-
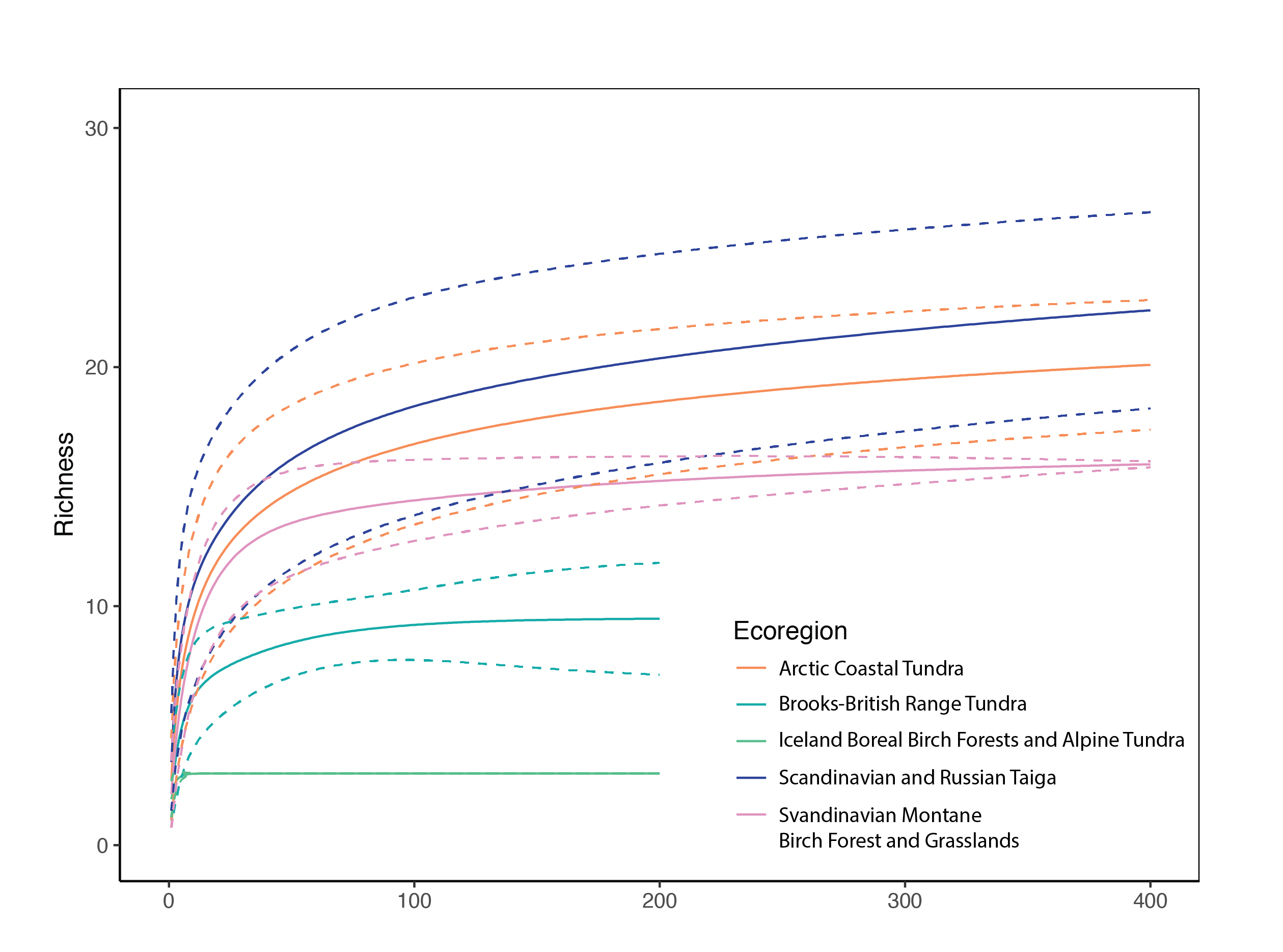
Provides richness estimates and 95% confidence bounds for five ecoregions. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 77 - Figure 4-38
-
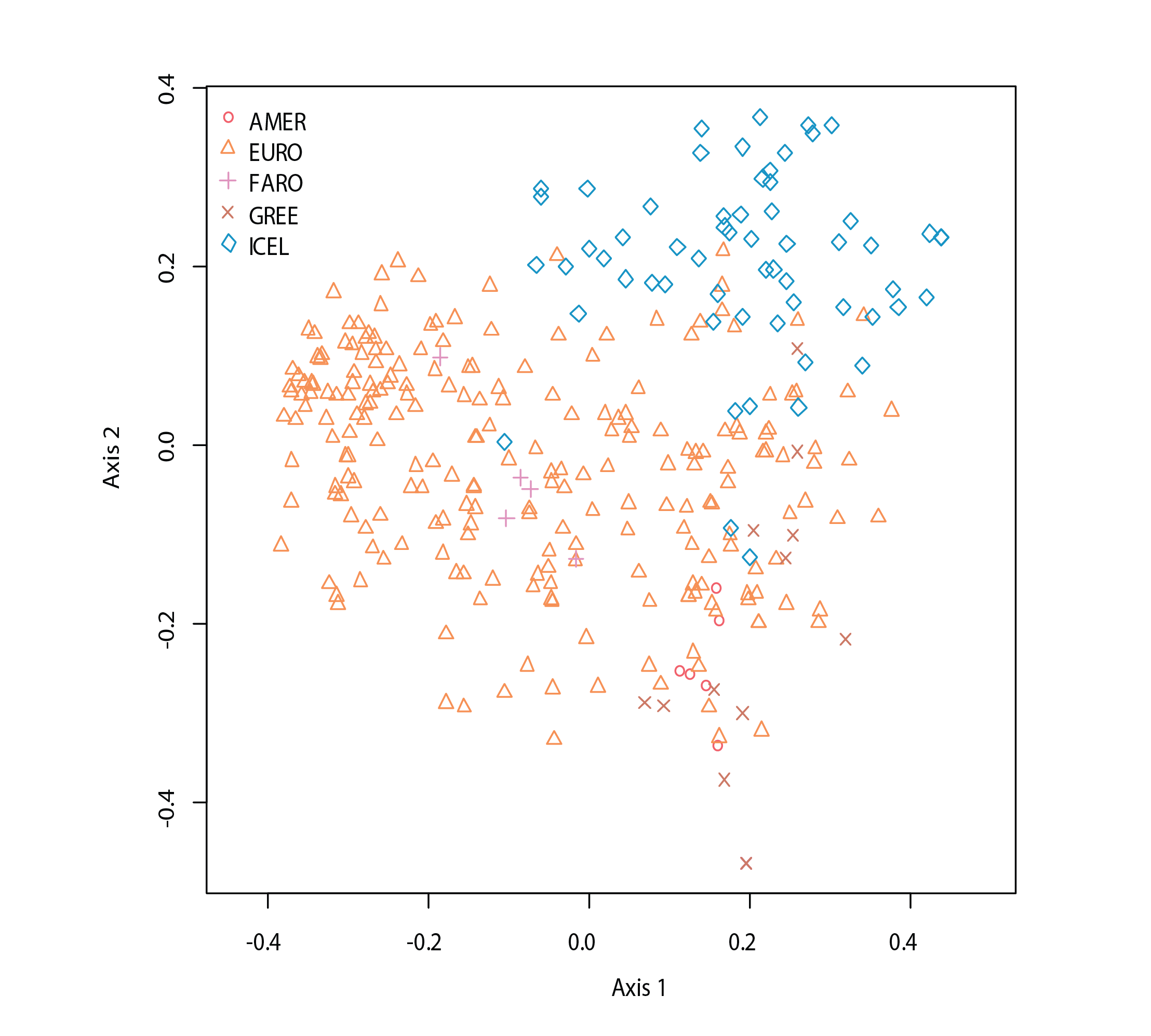
Orgination of macrophyte data (axis labels should be changed from Dim1 to Axis I and from Dim2 to Axis II), with symbols/colours differing by region. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 3 - Page 55 - Figure 4-24
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)