dataset
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
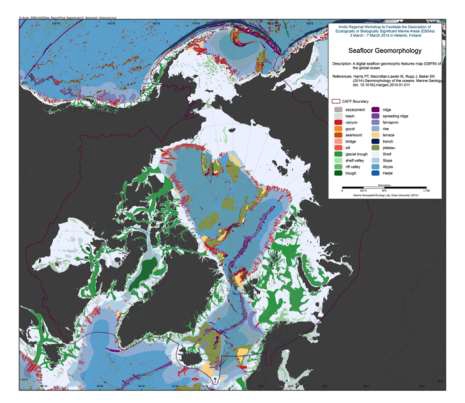
We present the first digital seafloor geomorphic features map (GSFM) of the global ocean. The GSFM includes 131,192 separate polygons in 29 geomorphic feature categories, used here to assess differences between passive and active continental margins as well as between 8 major ocean regions (the Arctic, Indian, North Atlantic, North Pacific, South Atlantic, South Pacific and the Southern Oceans and the Mediterranean and Black Seas). The GSFM provides quantitative assessments of differences between passive and active margins: continental shelf width of passive margins (88 km) is nearly three times that of active margins (31 km); the average width of active slopes (36 km) is less than the average width of passive margin slopes (46 km); active margin slopes contain an area of 3.4 million km2 where the gradient exceeds 5°, compared with 1.3 million km2 on passive margin slopes; the continental rise covers 27 million km2 adjacent to passive margins and less than 2.3 million km2 adjacent to active margins. Examples of specific applications of the GSFM are presented to show that: 1) larger rift valley segments are generally associated with slow-spreading rates and smaller rift valley segments are associated with fast spreading; 2) polar submarine canyons are twice the average size of non-polar canyons and abyssal polar regions exhibit lower seafloor roughness than non-polar regions, expressed as spatially extensive fan, rise and abyssal plain sediment deposits – all of which are attributed here to the effects of continental glaciations; and 3) recognition of seamounts as a separate category of feature from ridges results in a lower estimate of seamount number compared with estimates of previous workers. Reference: Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology.
-
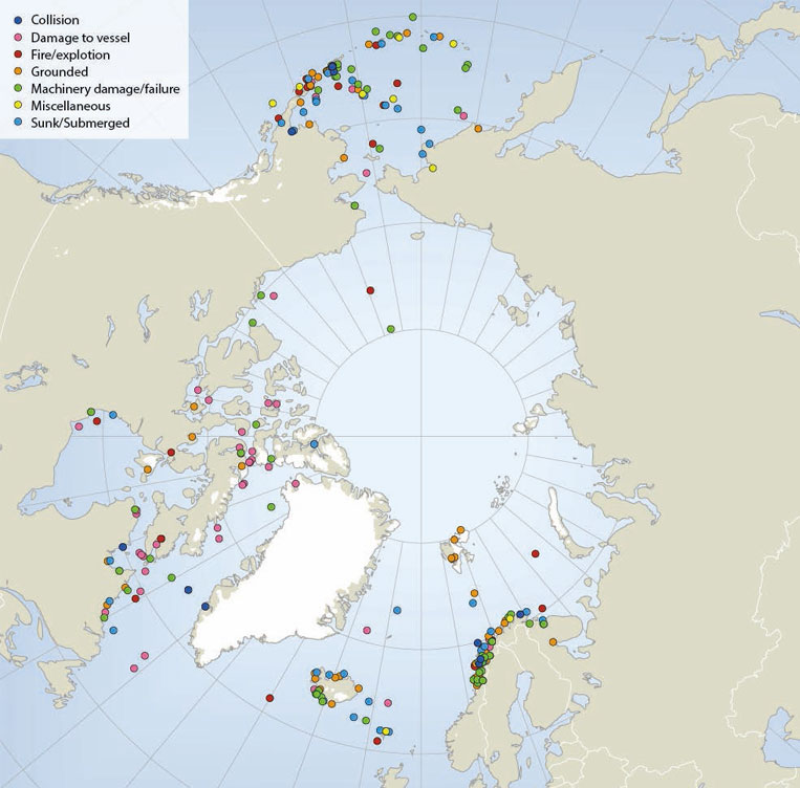
Locations of sub-Arctic and Arctic shipping accidents and incident causes, 1995-2004 (source: Arctic Marine Shipping Assessment 2009). Published in the Arctic Biodiversity Assessment (ABA) released in 2014.
-
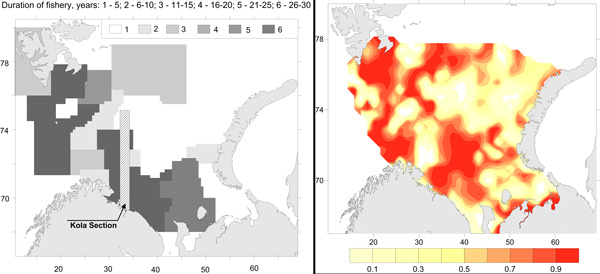
Commercial fishery impact on zoobenthos of the Barents Sea. Figure A) Intensity and duration of fishery efforts in standard commercial fishery areas in the Barents Sea. The darker the area the longer the fishery has been in operation. Figure B) Level of decline in macrobenthic biomass between 1926-1932 and 1968-1970 calculated as 1-b1968/b1930. The largest biomass decreases correspond to the darker colour, whereas lighter colour refers to no change (Denisenko 2013). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/benthos" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 97 - Figure 3.3.4
-
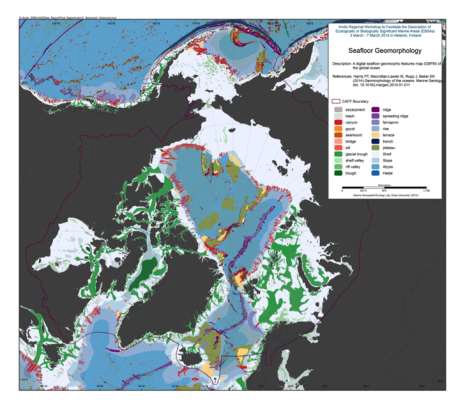
We present the first digital seafloor geomorphic features map (GSFM) of the global ocean. The GSFM includes 131,192 separate polygons in 29 geomorphic feature categories, used here to assess differences between passive and active continental margins as well as between 8 major ocean regions (the Arctic, Indian, North Atlantic, North Pacific, South Atlantic, South Pacific and the Southern Oceans and the Mediterranean and Black Seas). The GSFM provides quantitative assessments of differences between passive and active margins: continental shelf width of passive margins (88 km) is nearly three times that of active margins (31 km); the average width of active slopes (36 km) is less than the average width of passive margin slopes (46 km); active margin slopes contain an area of 3.4 million km2 where the gradient exceeds 5°, compared with 1.3 million km2 on passive margin slopes; the continental rise covers 27 million km2 adjacent to passive margins and less than 2.3 million km2 adjacent to active margins. Examples of specific applications of the GSFM are presented to show that: 1) larger rift valley segments are generally associated with slow-spreading rates and smaller rift valley segments are associated with fast spreading; 2) polar submarine canyons are twice the average size of non-polar canyons and abyssal polar regions exhibit lower seafloor roughness than non-polar regions, expressed as spatially extensive fan, rise and abyssal plain sediment deposits – all of which are attributed here to the effects of continental glaciations; and 3) recognition of seamounts as a separate category of feature from ridges results in a lower estimate of seamount number compared with estimates of previous workers. Reference: Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology.
-
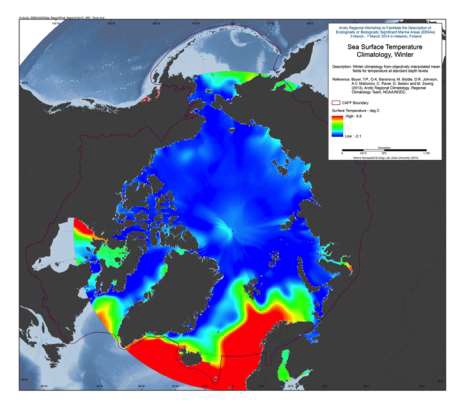
A set of mean fields for temperature and salinity for the Arctic Seas and environs are available for viewing and downloading. Area: The area encompassed is all longitudes from 60°N to 90°N latitudes. Horizontal resolution: Temperature and salinity are available on a 1°x1° and a 1/4°x1/4° latitude/longitude grid. Time resolution: All climatologies for all variables use all available data regardless of year of measurement. Climatologies were calculated for annual (all-data), seasonal, and monthly time periods. Seasons are as follows: Winter (Jan.-Mar.), Spring (Apr.-Jun.), Summer (Jul.-Aug.), Fall (Oct.-Dec.). Vertical resolution: Temperature and salinity are available on 87 standard levels with higher vertical resolution than the World Ocean Atlas 2009 (WOA09), but levels extend from the surface to 4000 m. Units: Temperature units are °C. Salinity is unitless on the Practical Salinity Scale-1978 [PSS]. Data used: All data from the area found in the World Ocean Database (WOD) as of the end of 2011. For a description of this dataset, please see World Ocean Database 2009 IntroductionMethod: The method followed for calculation of the mean climatological fields is detailed in the following publications: Temperature: Locarnini et al., 2010, Salinity: Antonov et al., 2010. Additional details on the 1/4° climatological calculation are found in Boyer et al., 2005, from: <a href="http://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/regional_climate/arctic/" target="_blank">NOAA</a> Reference: Boyer, T.P., O.K. Baranova, M. Biddle, D.R. Johnson, A.V. Mishonov, C. Paver, D. Seidov and M. Zweng (2012), Arctic Regional Climatology, Regional Climatology Team, NOAA/NODC, source: <a href="www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/regional_climate/arctic" target="_blank">NOAA</a>
-
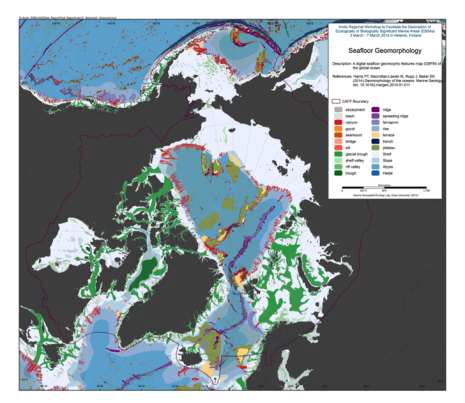
We present the first digital seafloor geomorphic features map (GSFM) of the global ocean. The GSFM includes 131,192 separate polygons in 29 geomorphic feature categories, used here to assess differences between passive and active continental margins as well as between 8 major ocean regions (the Arctic, Indian, North Atlantic, North Pacific, South Atlantic, South Pacific and the Southern Oceans and the Mediterranean and Black Seas). The GSFM provides quantitative assessments of differences between passive and active margins: continental shelf width of passive margins (88 km) is nearly three times that of active margins (31 km); the average width of active slopes (36 km) is less than the average width of passive margin slopes (46 km); active margin slopes contain an area of 3.4 million km2 where the gradient exceeds 5°, compared with 1.3 million km2 on passive margin slopes; the continental rise covers 27 million km2 adjacent to passive margins and less than 2.3 million km2 adjacent to active margins. Examples of specific applications of the GSFM are presented to show that: 1) larger rift valley segments are generally associated with slow-spreading rates and smaller rift valley segments are associated with fast spreading; 2) polar submarine canyons are twice the average size of non-polar canyons and abyssal polar regions exhibit lower seafloor roughness than non-polar regions, expressed as spatially extensive fan, rise and abyssal plain sediment deposits – all of which are attributed here to the effects of continental glaciations; and 3) recognition of seamounts as a separate category of feature from ridges results in a lower estimate of seamount number compared with estimates of previous workers. Reference: Harris PT, Macmillan-Lawler M, Rupp J, Baker EK Geomorphology of the oceans. Marine Geology.
-
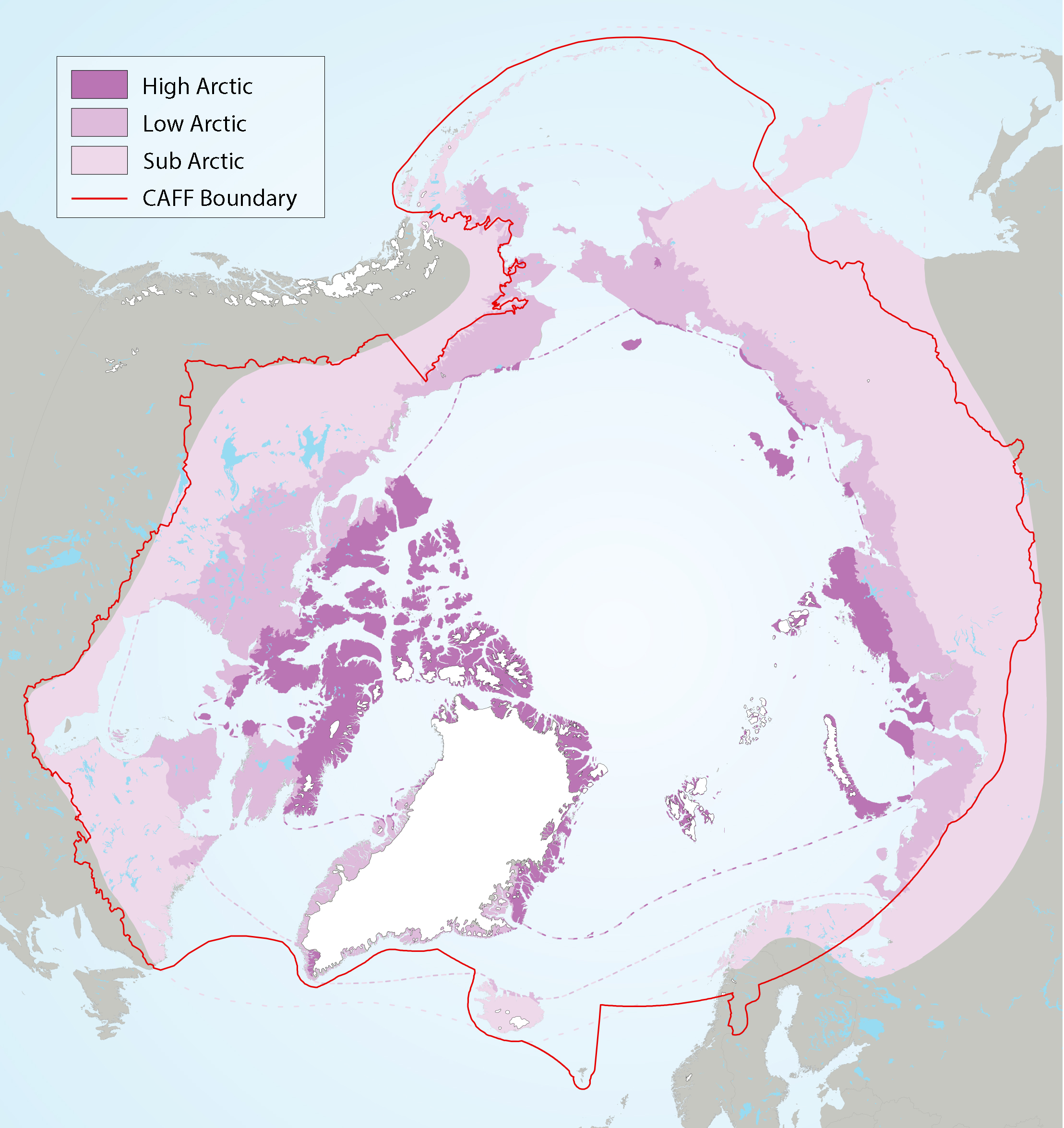
Figure 2-2 Arctic freshwater boundaries from the Arctic Council’s Arctic Biodiversity Assessment developed by CAFF, showing the three sub-regions of the Arctic, namely the high (dark purple), low (purple) and sub-Arctic (light purple)
-
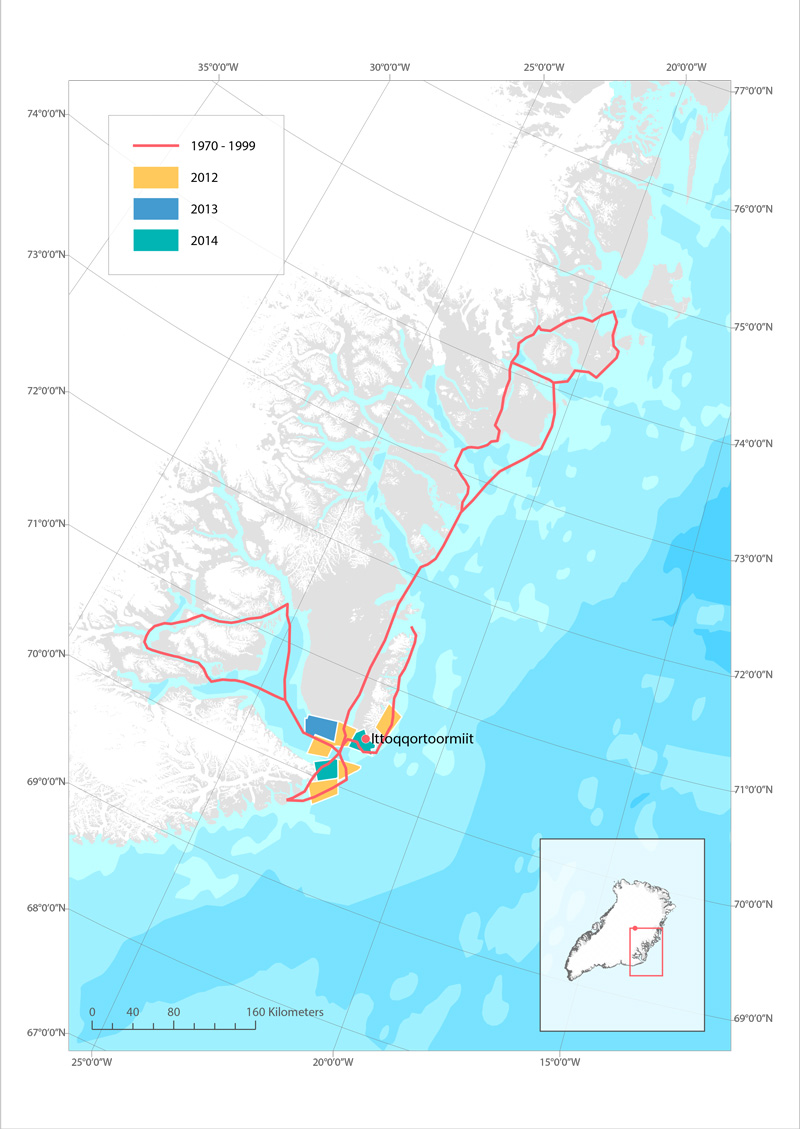
Routes used for hunting polar bear in Ittoqqoortoormiit, East Greenland before 1999 (red line), and in 2012 (yellow), 2013 (blue) and 2014 (green). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 159 - Box figure 3.6.1
-
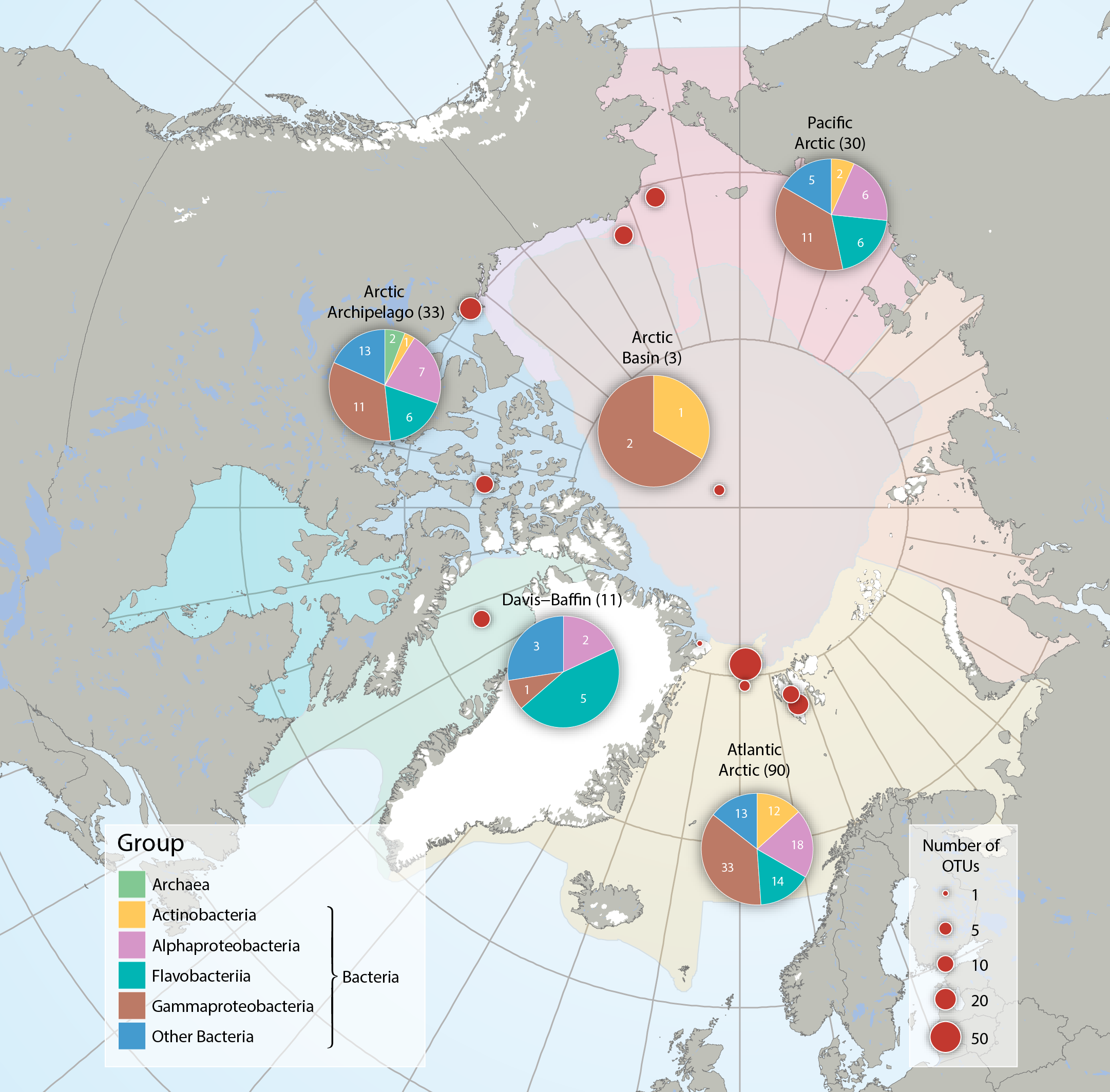
Bacteria and Archaea across five Arctic Marine Areas based on number of operational taxonomic units (OTUs), or molecular species. Composition of microbial groups, with respective numbers of OTUs (pie charts) and number of OTUs at sampling locations (red dots). Data aggregated by the CBMP Sea Ice Biota Expert Network. Data source: National Center for Biotechnology Information’s (NCBI 2017) Nucleotide and PubMed databases. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/sea-ice-biota" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 38 - Figure 3.1.2 From the report draft: "Synthesis of available data was performed by using searches conducted in the National Center for Biotechnology Information’s “Nucleotide” (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/guide/data-software/) and “PubMed” (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed) databases. Aligned DNA sequences were downloaded and clustered into OTUs by maximum likelihood phylogenetic placement."
-
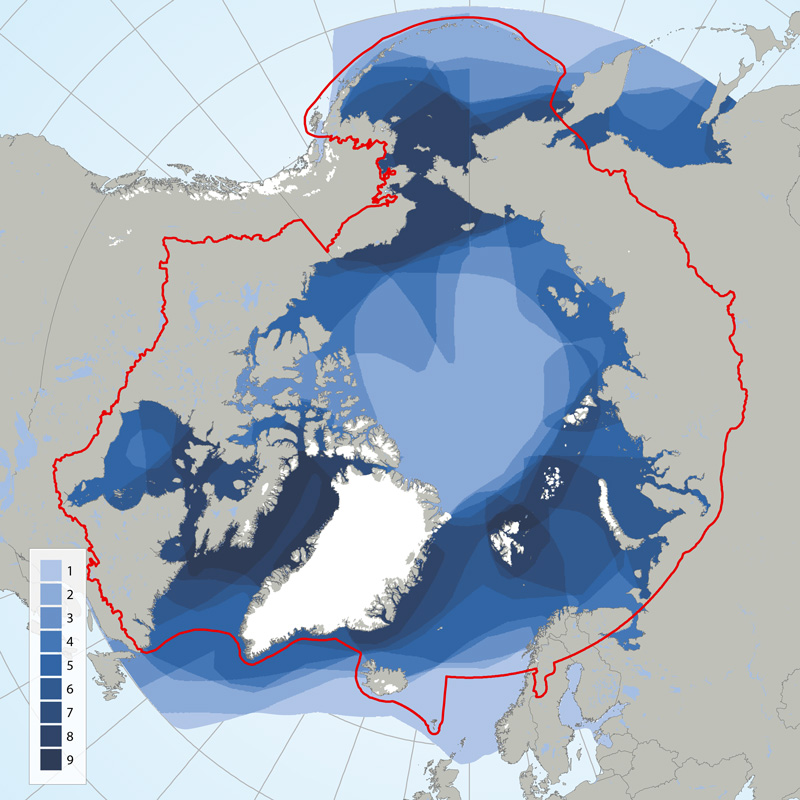
Circumpolar depiction of species richness based on the distributions of the 11 ice-associated Focal Ecosystem Components (according to the distributions reported in IUCN Red List species accounts). A maximum of nine species occur in any one geographic location. The Arctic gateways in both the Atlantic and Pacific regions have the highest species diversity. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 152 - Figure 3.6.1
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)