unknown
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Appendix 11. Taxa of hetorotrophic protists reported from Foxe Basin, Canada (FB), Disko Bay, W Greenland (DB; Vors 1993), the Greenland Sea (GLS; Ikävalko & Gradinger 1997) and Northern Baffin Bay, Canada (NBB; Lovejoy et al. 2002).
-
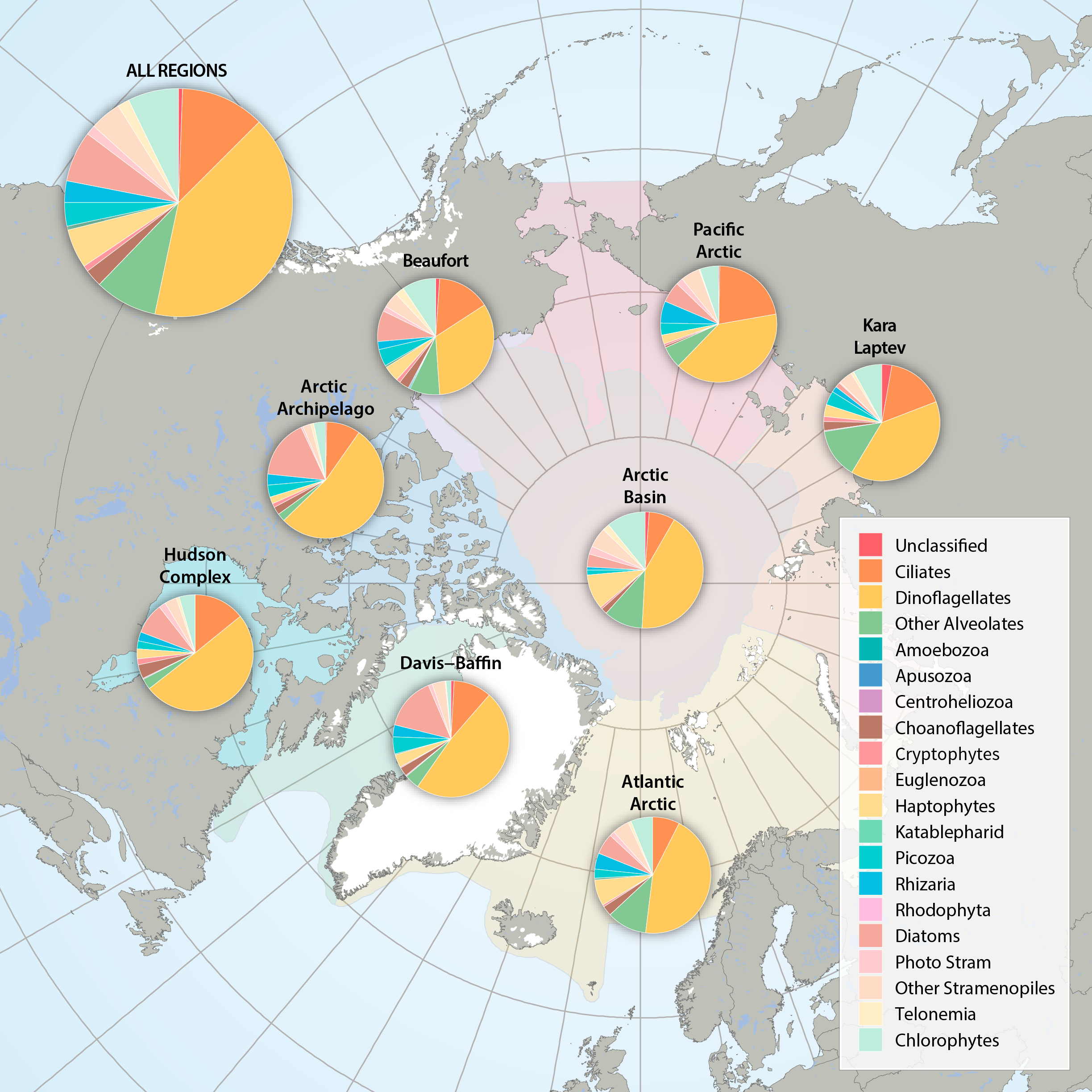
Figure 3.2.2a: Relative abundance of major eukaryote taxonomic groups found by high throughput sequencing of the small-subunit (18S) rRNA gene across Arctic Marine Areas. Figure 3.2.2b: Relative abundance of major eukaryote functional groups found by microscopy in the Arctic Marine Areas. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/plankton" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 70 - Figures 3.2.2a and 3.2.2b
-
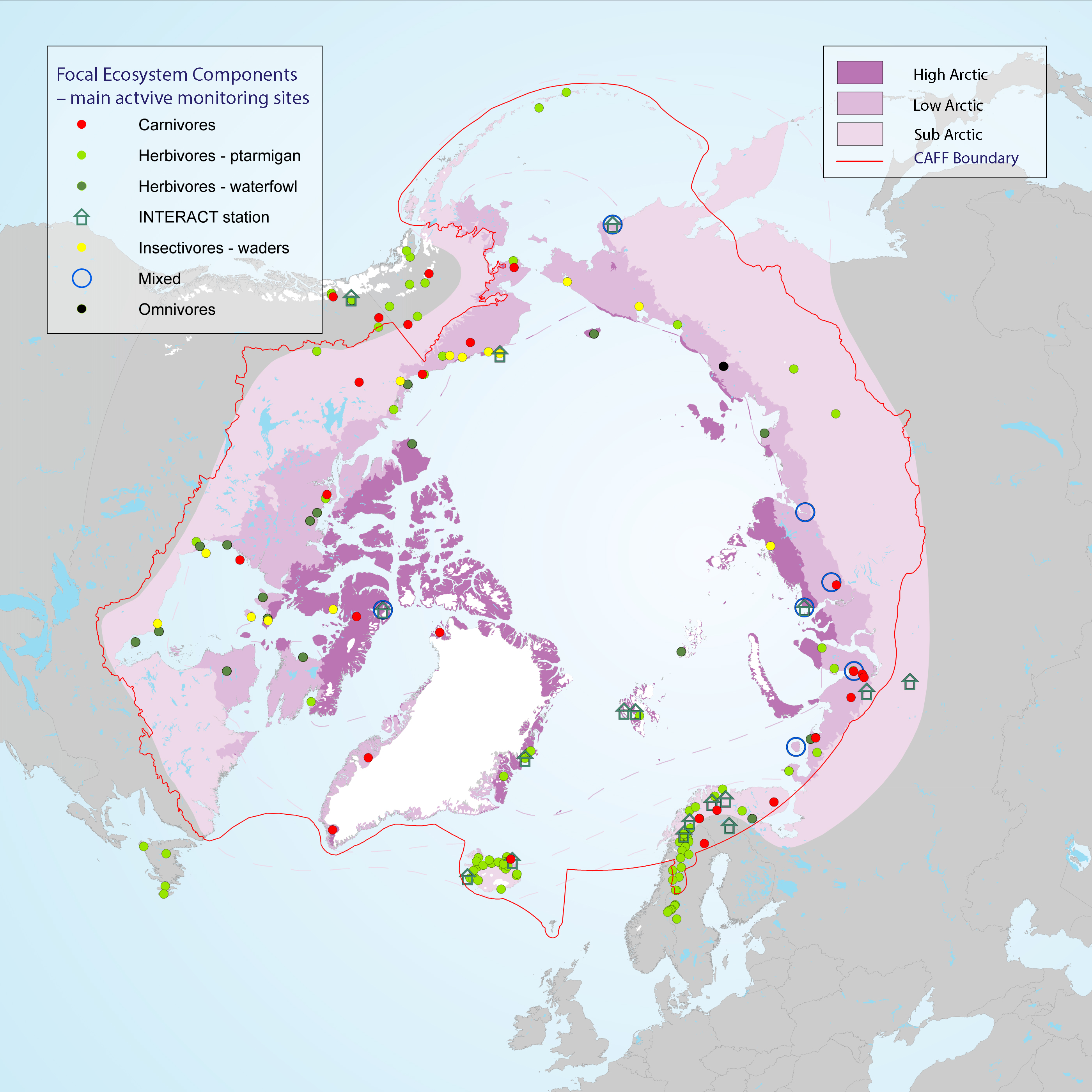
Many population counts of gregarious migrant species, such as waders and geese, take place along the flyways and at wintering grounds outside the Arctic which stresses the importance of continued development of movement ecology studies. Monitoring of FEC attributes related to breeding success and links to environmental drivers within the Arctic takes place in a wide network of research sites across the Arctic, although with low coverage of the high Arctic zone (Figure 3-25) STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 58 - Figure 3.25
-
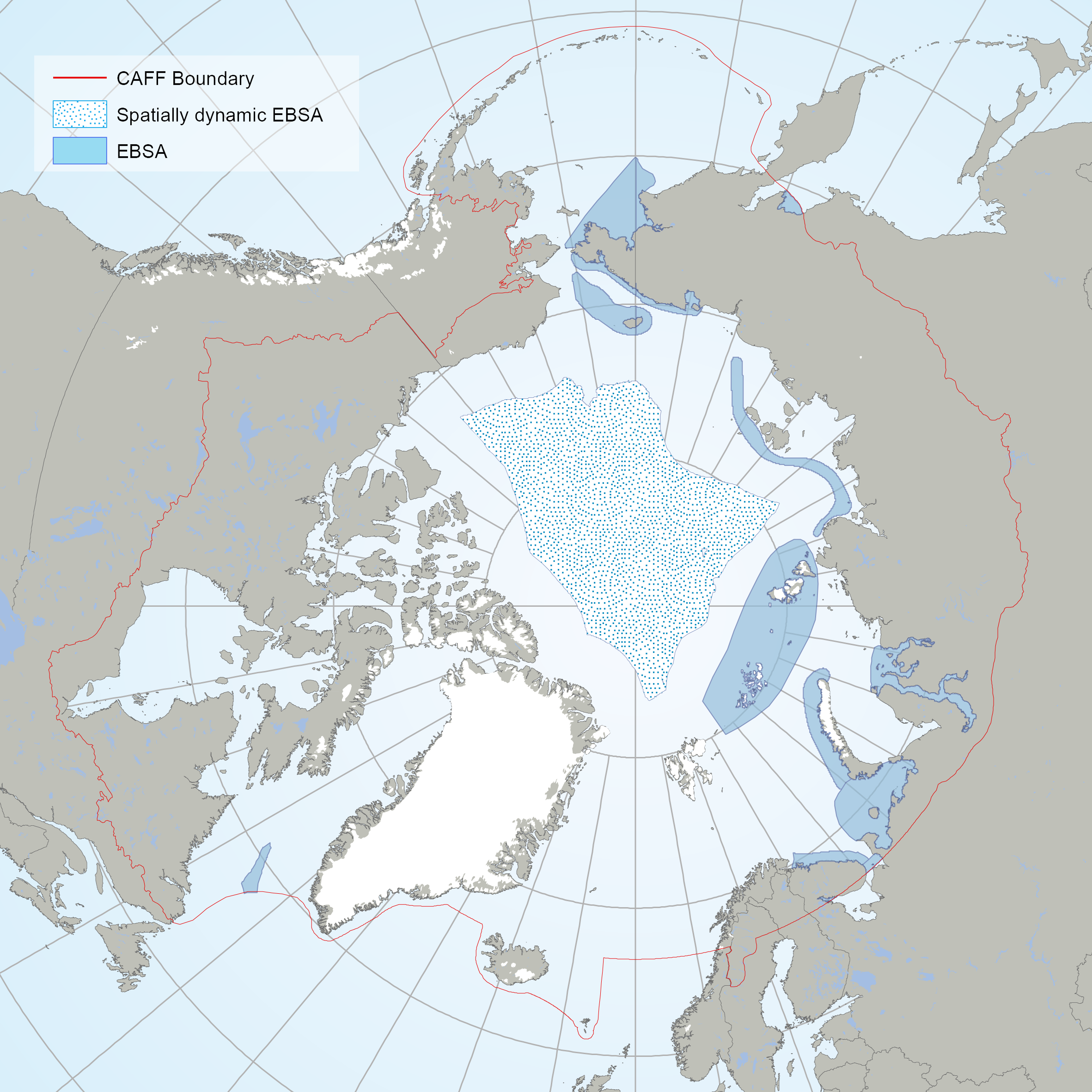
The EBSAs are special areas in the ocean that serve important purposes, in one way or another, to support the healthy functioning of oceans and the many services that it provides. The EBSAs contained din this dataset are the result of an Arctic Regional Workshop to Facilitate the Description of Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (EBSAs) held in Finland on 3-7 march, 2014. <a href="https://www.cbd.int/ebsa/ebsas" target="_blank">Resource</a>
-
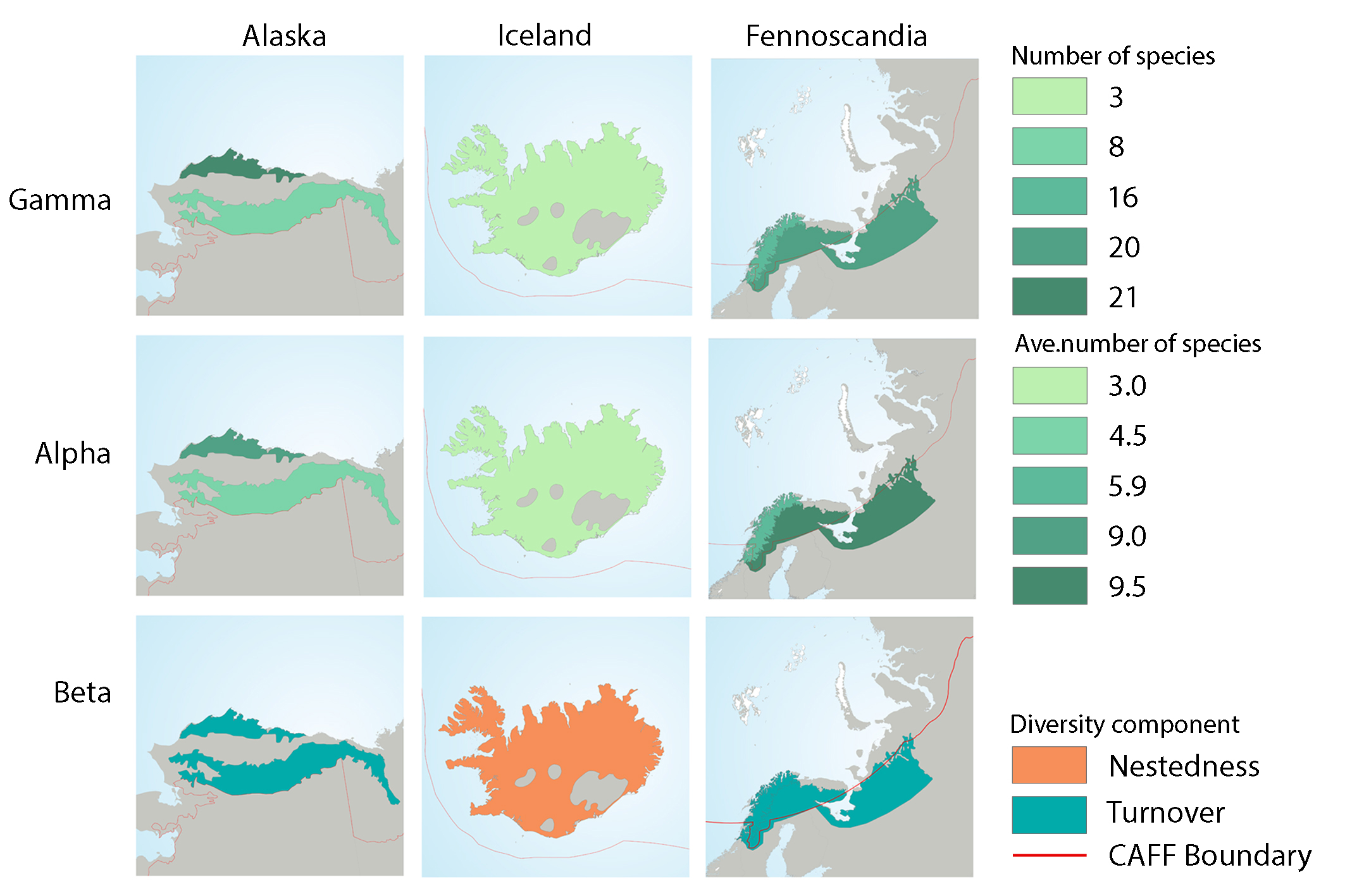
Fish diversity characteristics in three geographical regions: Alaska, Iceland, and Fennoscandia. Gamma diversity is based the total number of species sampled in hydrobasins of each ecoregion. Alpha diversity shows the mean basin species richness (95% confidence interval) and beta diversity shows the component of beta diversity, nestedness or turnover, that dominated within each of the ecoregions; gamma, alpha, and beta diversity estimates were based on a subset of basins where a minimum of 10 stations were sampled. All maps are drawn to the same scale. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 77 - Figure 4-39
-
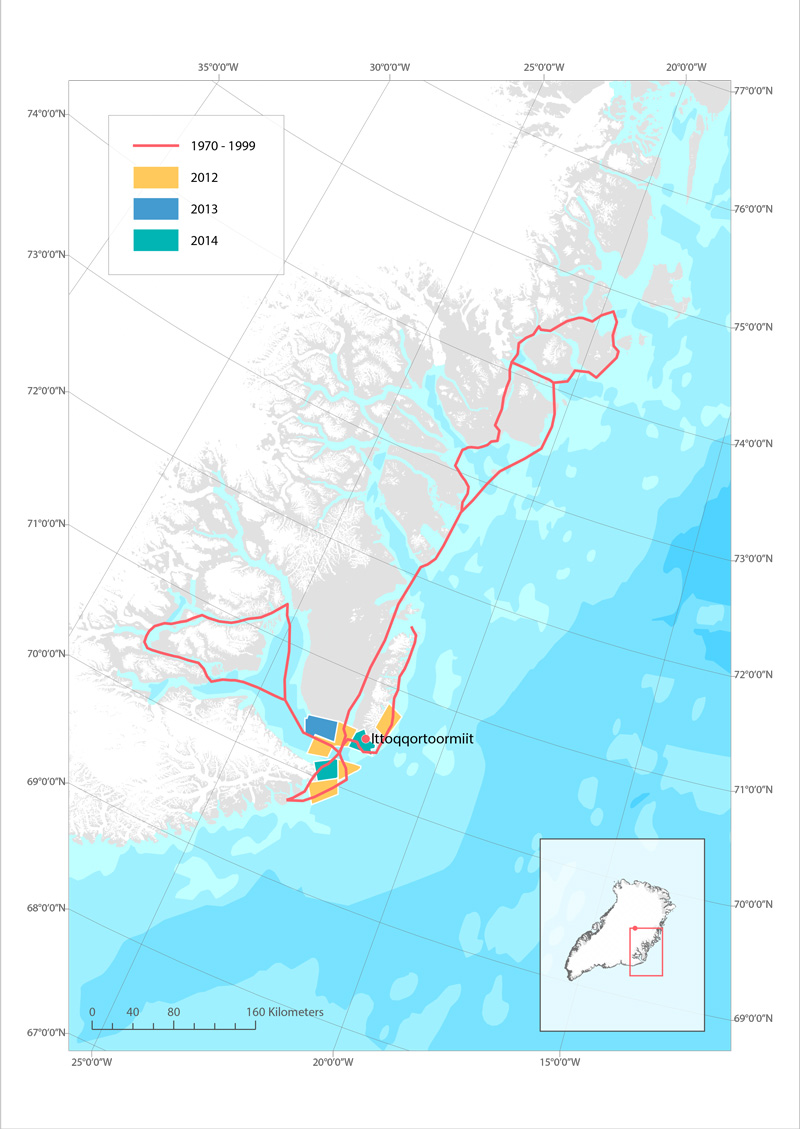
Routes used for hunting polar bear in Ittoqqoortoormiit, East Greenland before 1999 (red line), and in 2012 (yellow), 2013 (blue) and 2014 (green). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 159 - Box figure 3.6.1
-
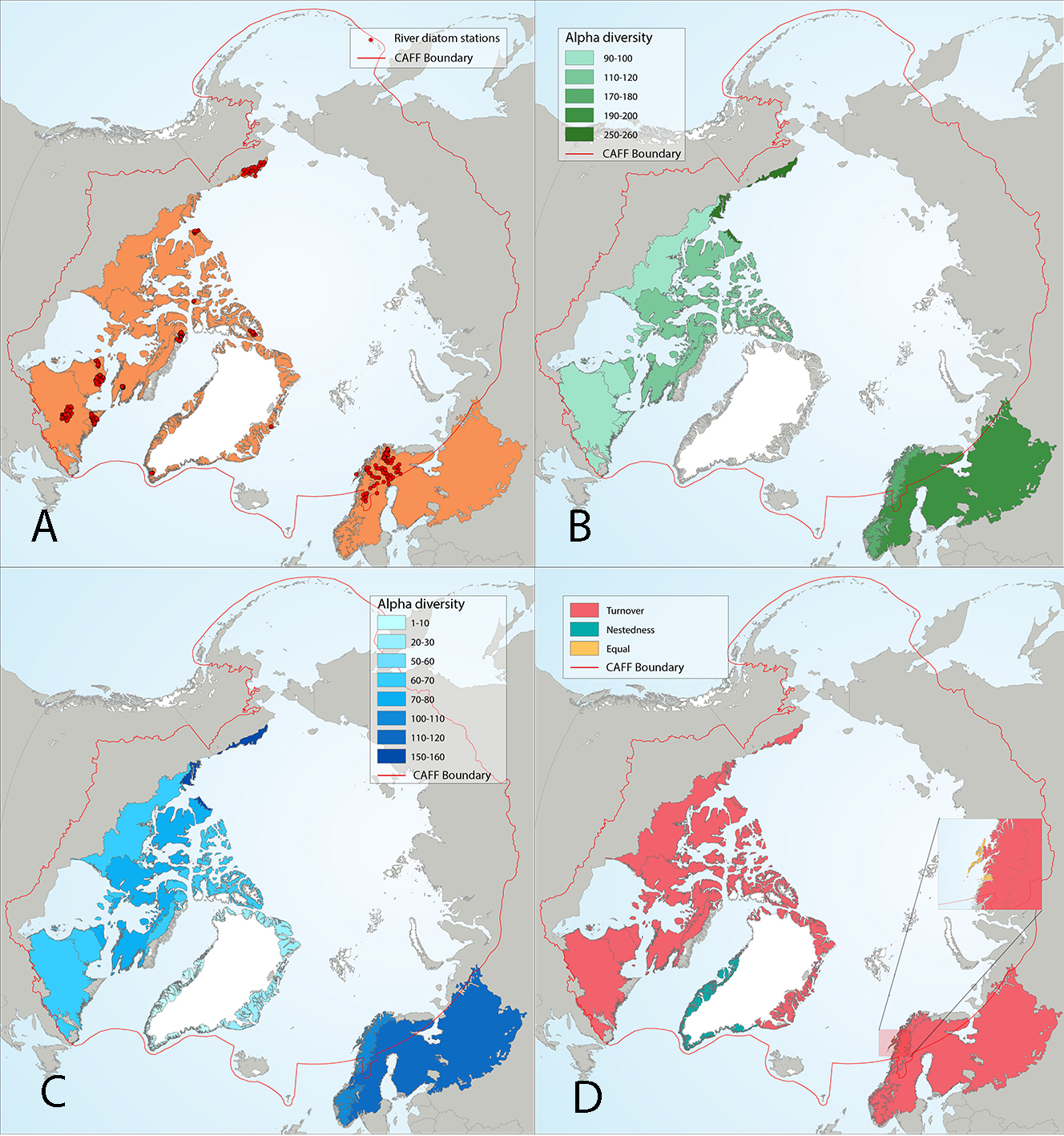
Results of circumpolar assessment of river diatoms, indicating (a) the location of river diatom stations, underlain by circumpolar ecoregions; (b) ecoregions with many river diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 40 stations; (c) all ecoregions with river diatom stations, colored on the basis of alpha diversity rarefied to 10 stations; (d) ecoregions with at least two stations in a hydrobasin, colored on the basis of the dominant component of beta diversity (species turnover, nestedness, approximately equal contribution, or no diversity) when averaged across hydrobasins in each ecoregion. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 36 - Figure 4-8
-
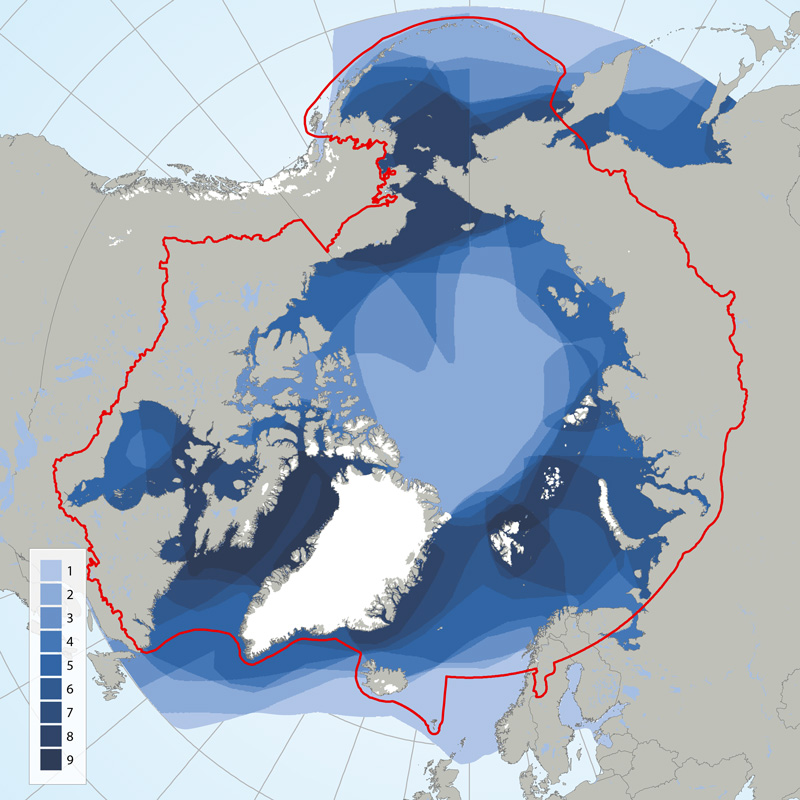
Circumpolar depiction of species richness based on the distributions of the 11 ice-associated Focal Ecosystem Components (according to the distributions reported in IUCN Red List species accounts). A maximum of nine species occur in any one geographic location. The Arctic gateways in both the Atlantic and Pacific regions have the highest species diversity. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 152 - Figure 3.6.1
-
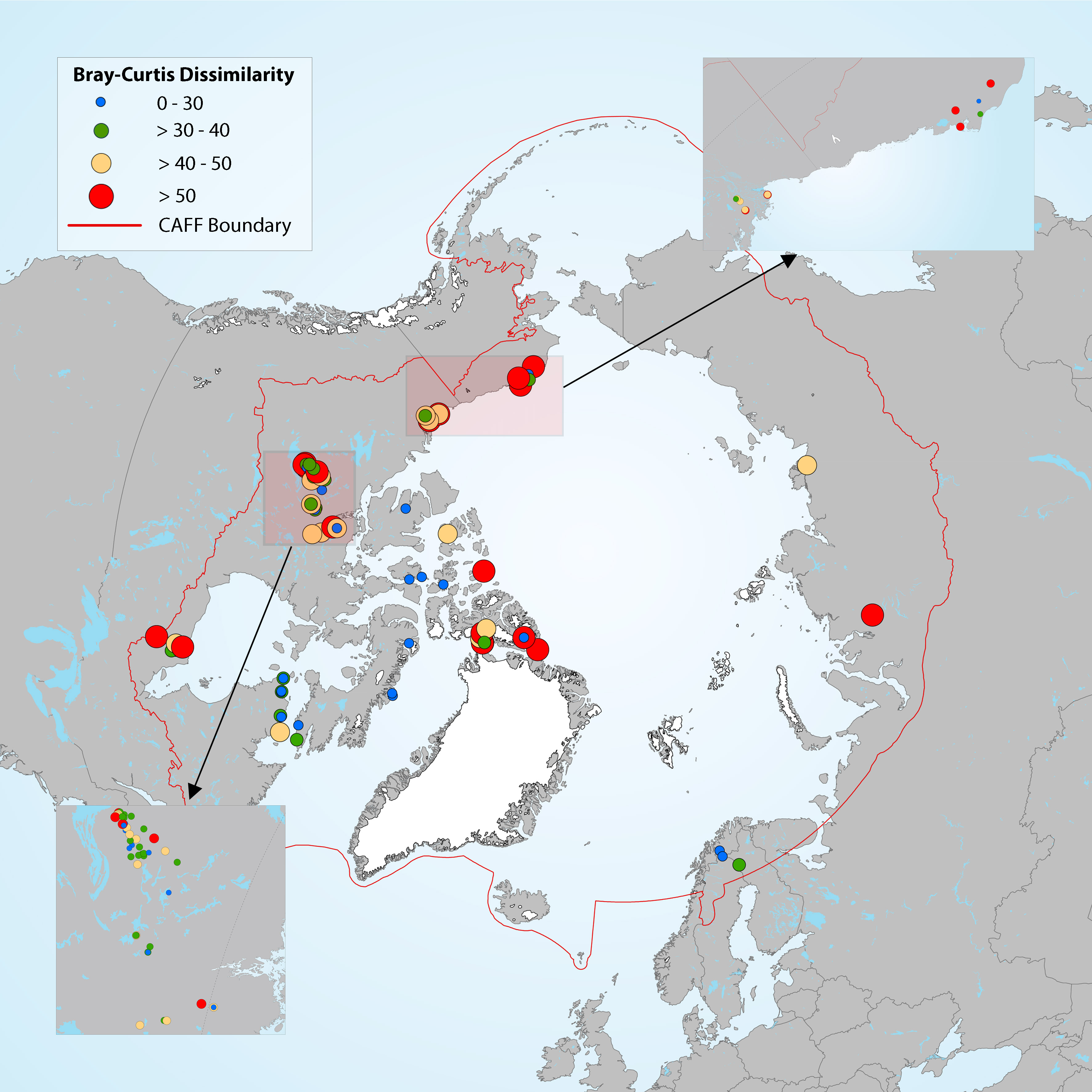
Estimation of diatom assemblage changes over a period of about 200 years (top versus bottom sediment cores). Figure 4-14 Map showing the magnitude of change in diatom assemblages between bottom (pre-industrial) and top (modern) section of the cores, estimated by Bray-Curtis (B-C) dissimilarity. Boundaries for the B-C dissimilarity categories are based on distribution quartiles (0-30%, 30-40%, 40- 50% and >50%), where the lowest values (blue dots) represent the lowest degree of change in diatom assemblage composition between top and bottom sediment core samples in each lake. State of the Arctic Freshwater Biodiversity Report - Chapter 4 - Page 41 - Figure 4-14
-
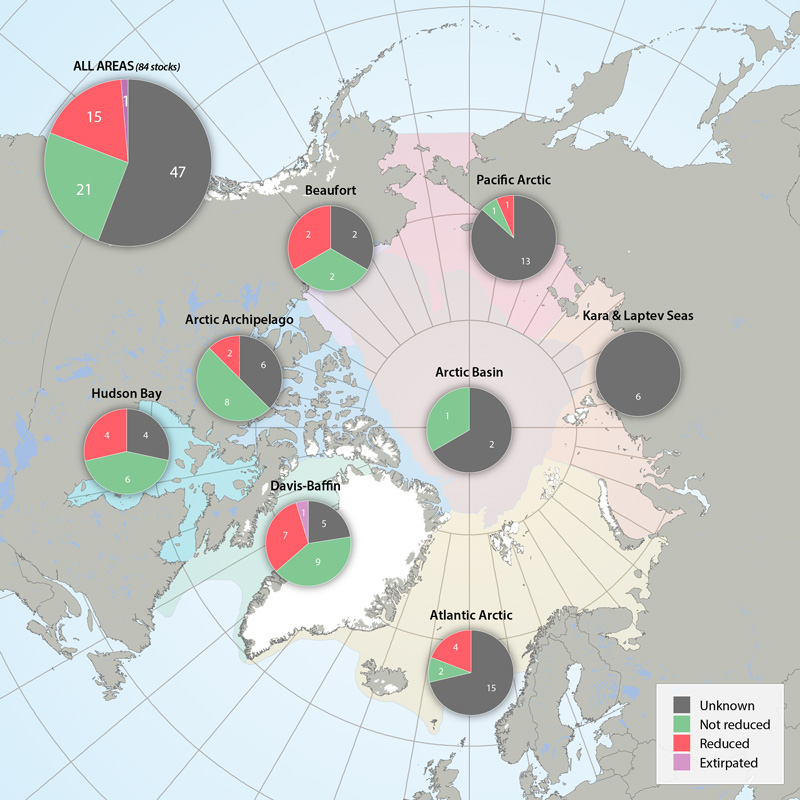
Status of marine mammal Focal Ecosystem Component stocks by Arctic Marine Area. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 157 - Figure 3.6.3
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)