oceans
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
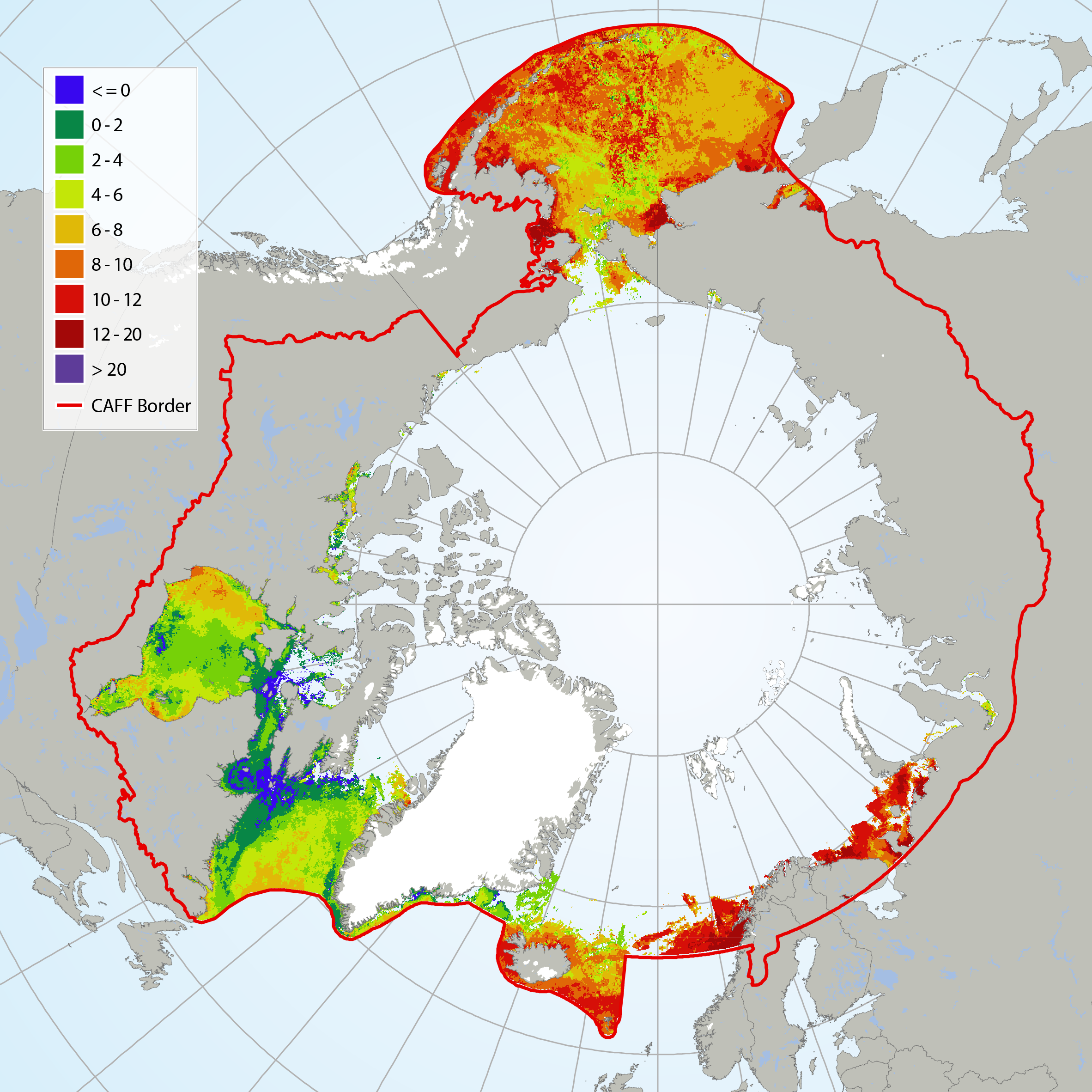
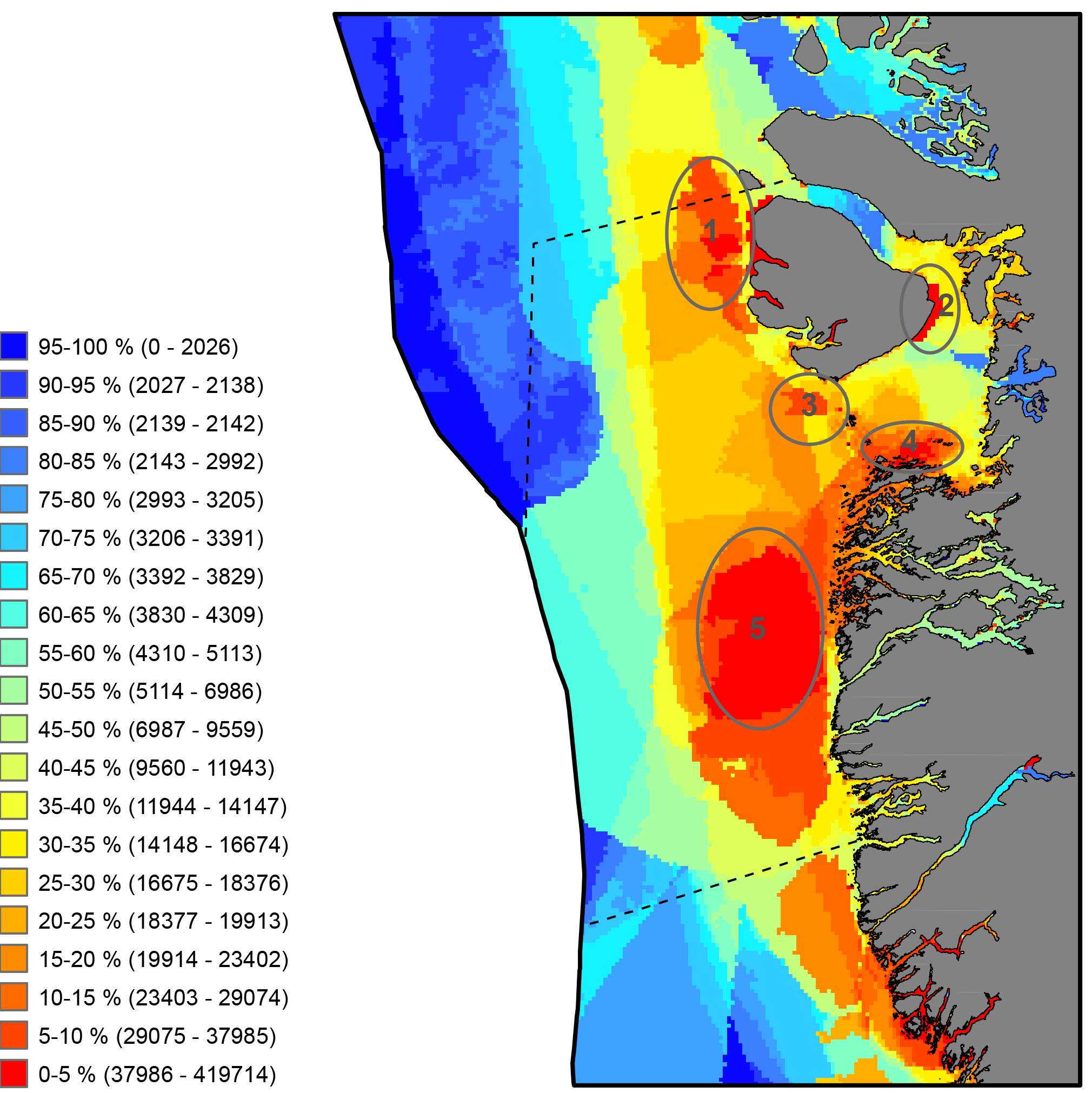
It has not been possible to identify available trend data for Arctic Ocean sea surface temperatures because there is not enough data to calculate reliable long-term trends for much of the Arctic marine environment (IPCC 2013, NOAA 2015). Here, sea surface temperature for July 2015 is shown from CAFF’s Land Cover Change Index. MODIS Sea Surface Temperature (SST) provided a four-kilometre spatial resolution monthly composite snapshot made from night-time measurements from the NASA Aqua Satellite. The night-time measurements are used to collect a consistent temperature measurement that is unaffected by the warming of the top layer of water by the sun. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 25 - Figure 2.3
-
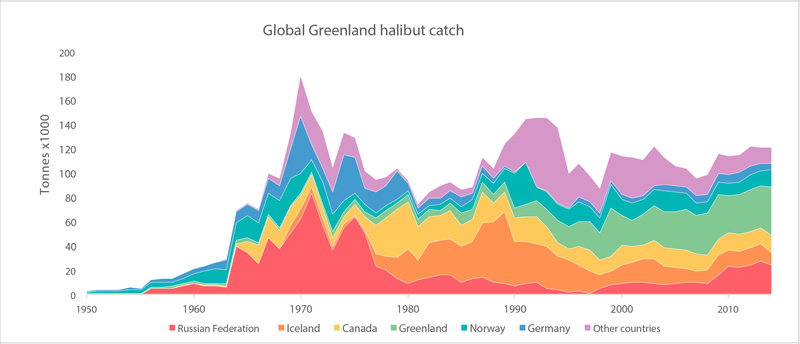
Global catches of Greenland halibut (FAO 2015). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-fishes" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 121 - Figure 3.4.8
-
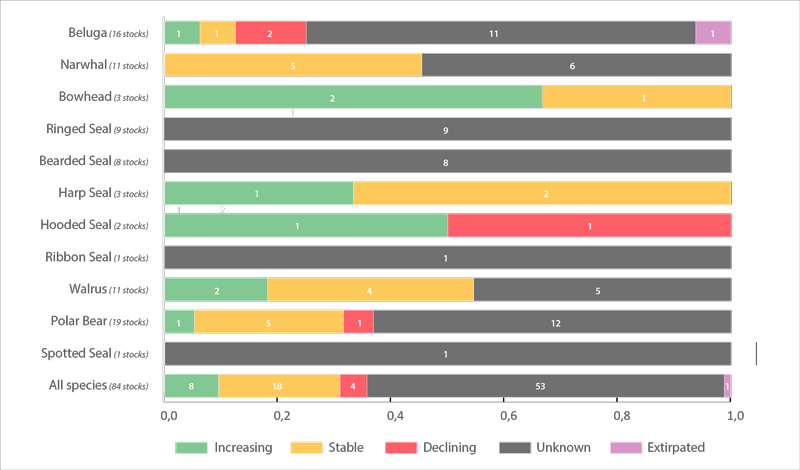
Trends in abundance of Arctic marine mammal Focal Ecosystem Components based on the most recent assessment for each recognized subpopulation of a species (red, declining trend; yellow, stable trend; green, increasing trend; grey, unknown trend). Number of subpopulations is given after species name. Each column is divided into equal segments, the sizes of which are not proportional to the size of the subpopulation. Ringed seal and bearded seal segments represent subspecies. Walrus segments represent subpopulations within subspecies. See Table 3.6.1 for details on abundance. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 156 - Figure 3.6.2
-
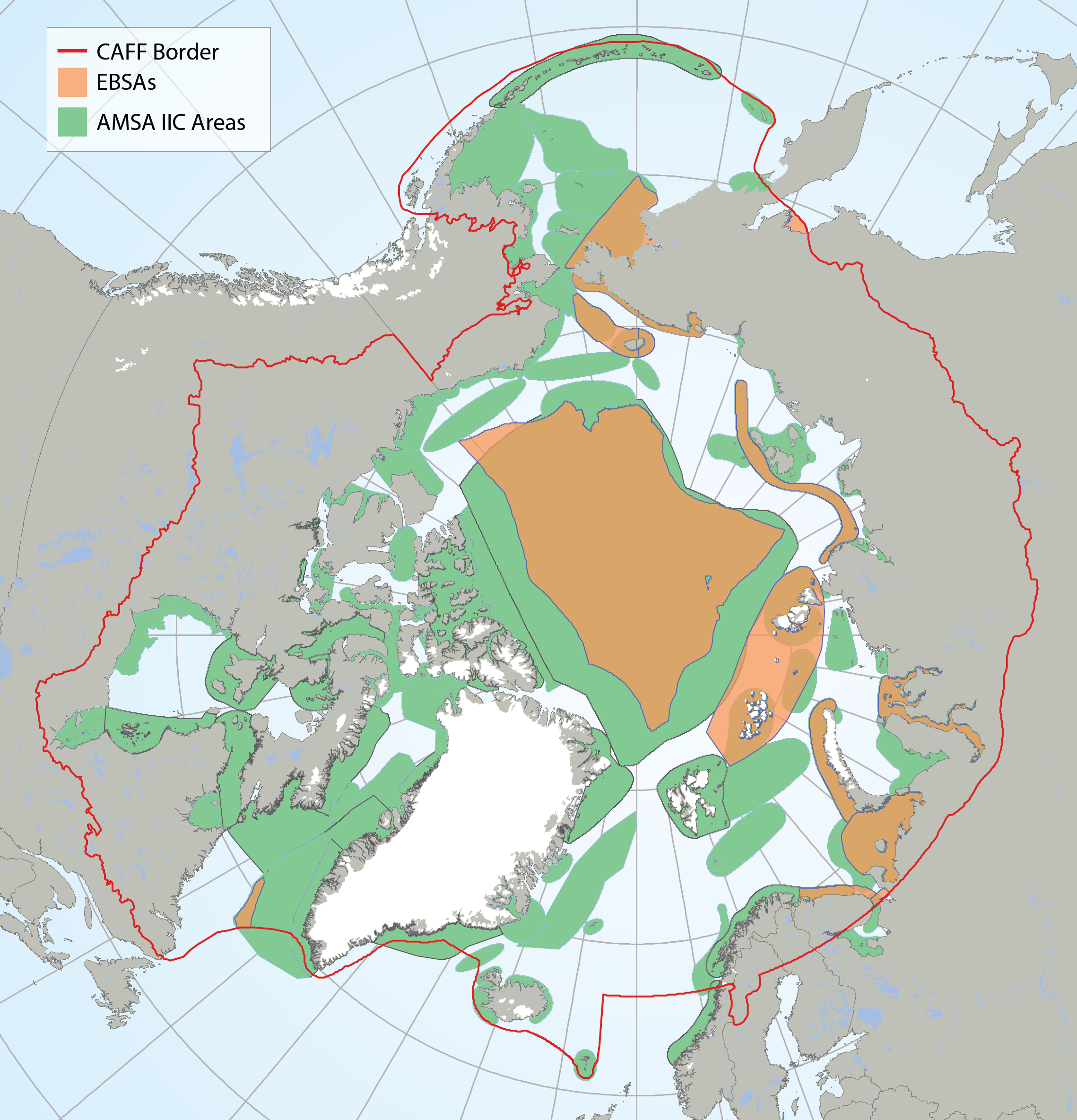
Arctic Ecologically and Biologically Significant Areas (EBSAs) and Arctic Marine Areas of Heightened Ecological and Cultural Significance as identified in the Arctic Marine Shipping Assessment (AMSA) IIC report. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 1</a> - Page 16 - Box Figure 1.1
-
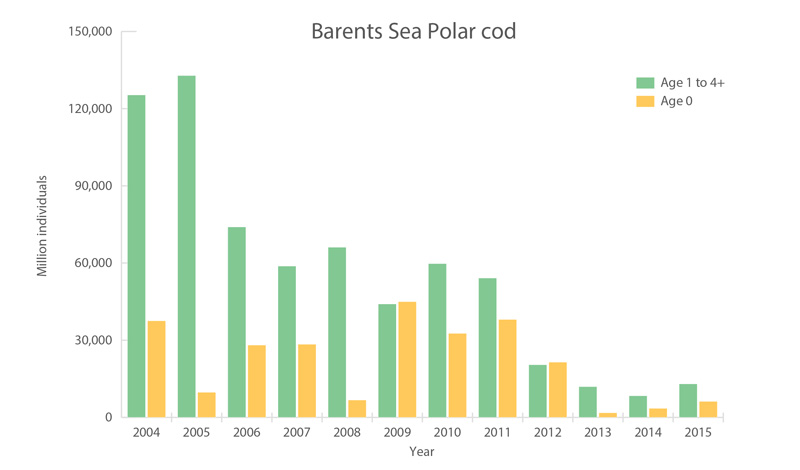
Polar cod in the Barents Sea. Acoustic estimate of polar cod 1-year-old and older (green) and pelagic trawl index of age 0-group abundance (yellow). Source: Joint IMR-PINRO ecosystem survey (Prozorkevich 2016). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-fishes" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 116 - Figure 3.4.3
-
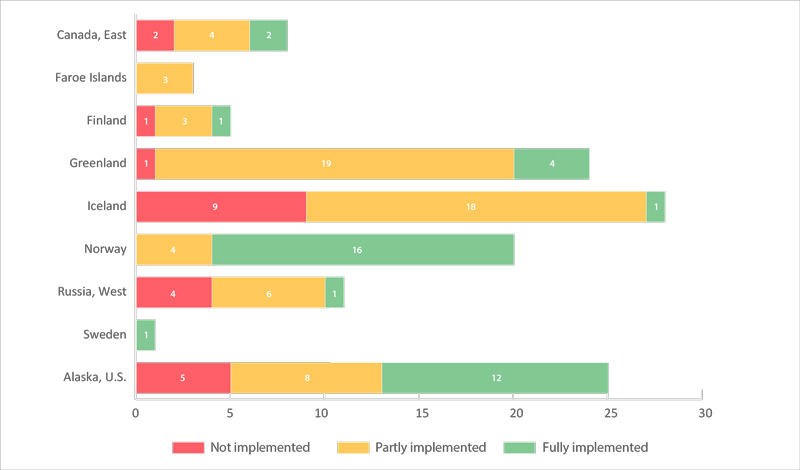
The number of key sites (monitored colonies) for seabirds (in 22 CSMP ecoregions) by country (a total of 125 sites). Sites are categorized as having fully, partially, or not met the CSMP criteria for parameters monitored (see 2.6.2). Data were from Appendix 3 of the CSMP (Irons et al. 2015); the degree of implementation may have changed at some sites since this summary was compiled. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/seabirds" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 134 - Figure 3.5.2
-
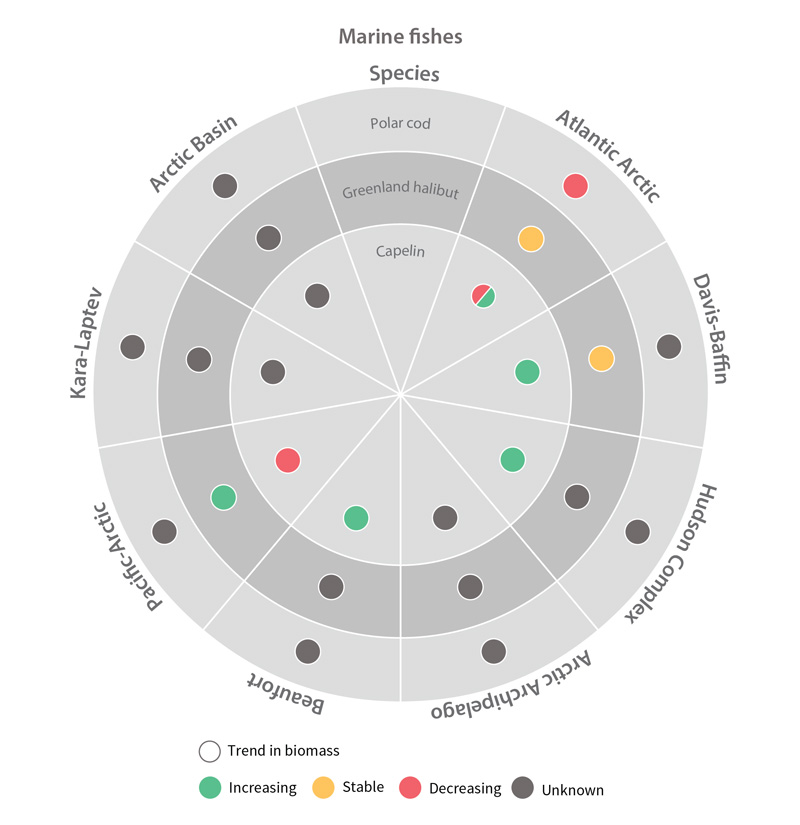
Trends in biomass of marine fish Focal Ecosystem Components across each Arctic Marine Area STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 4 - Page 180 - Figure 4.4
-
Critical to the successful implementation of EBM in the Arctic is the existence of a cohesive circumpolar approach to the collection and management of data and the application of compatible frameworks, standards and protocols that this entails. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 29 - Box Figure 2.2
-
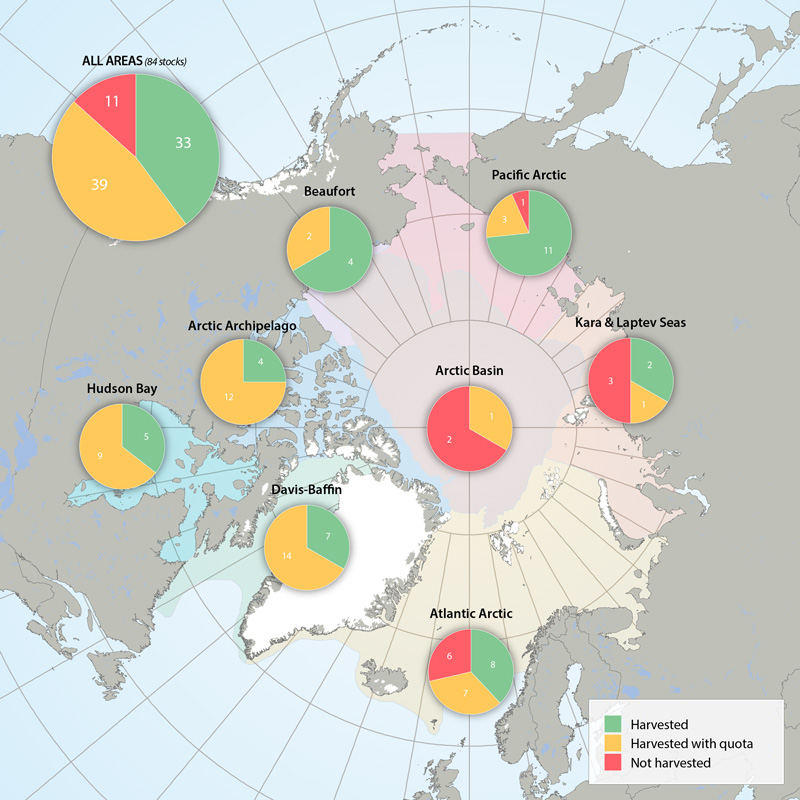
Harvest marine mammal Focal Ecosystem Component stocks in Arctic Marine Areas. Harvested without quotas, with quotas or not harvested. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/findings/marine-mammals" target="_blank">Chapter 3</a> - Page 158 - Figure 3.6.4
-
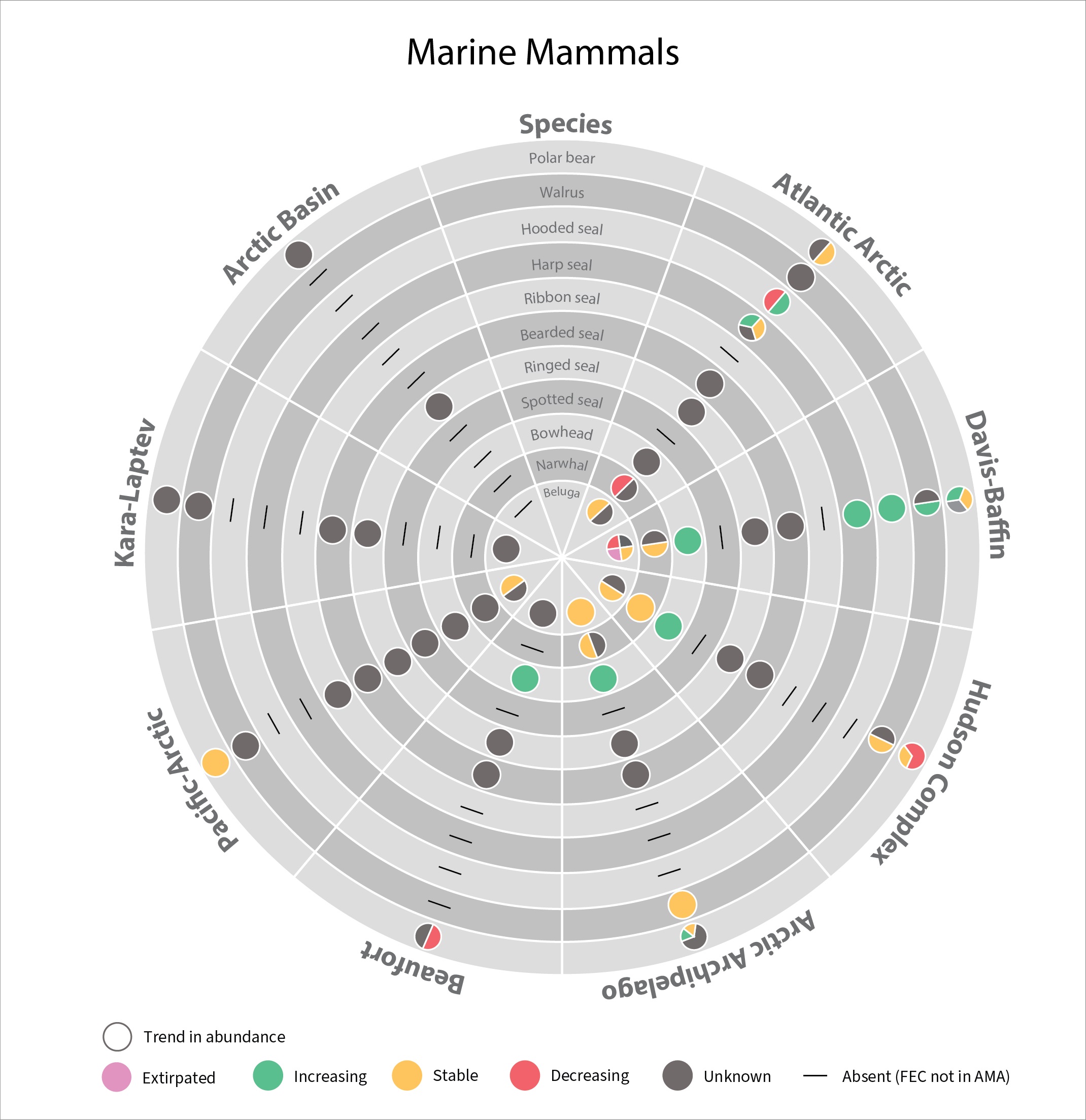
In 2017 the SAMBR synthesized data about biodiversity in Arctic marine ecosystems around the circumpolar Arctic.. SAMBR highlighted observed changes and relevant monitoring gaps. This 2021 update provides information on the status of marine mammals in the Arctic from 2015–2020: More detail can be found in the Marine Mammals 2021 Technical report. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)