START
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
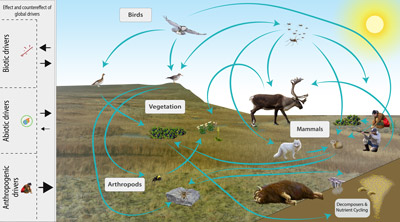
The Arctic terrestrial food web includes the exchange of energy and nutrients. Arrows to and from the driver boxes indicate the relative effect and counter effect of different types of drivers on the ecosystem. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 26- Figure 2.4
-
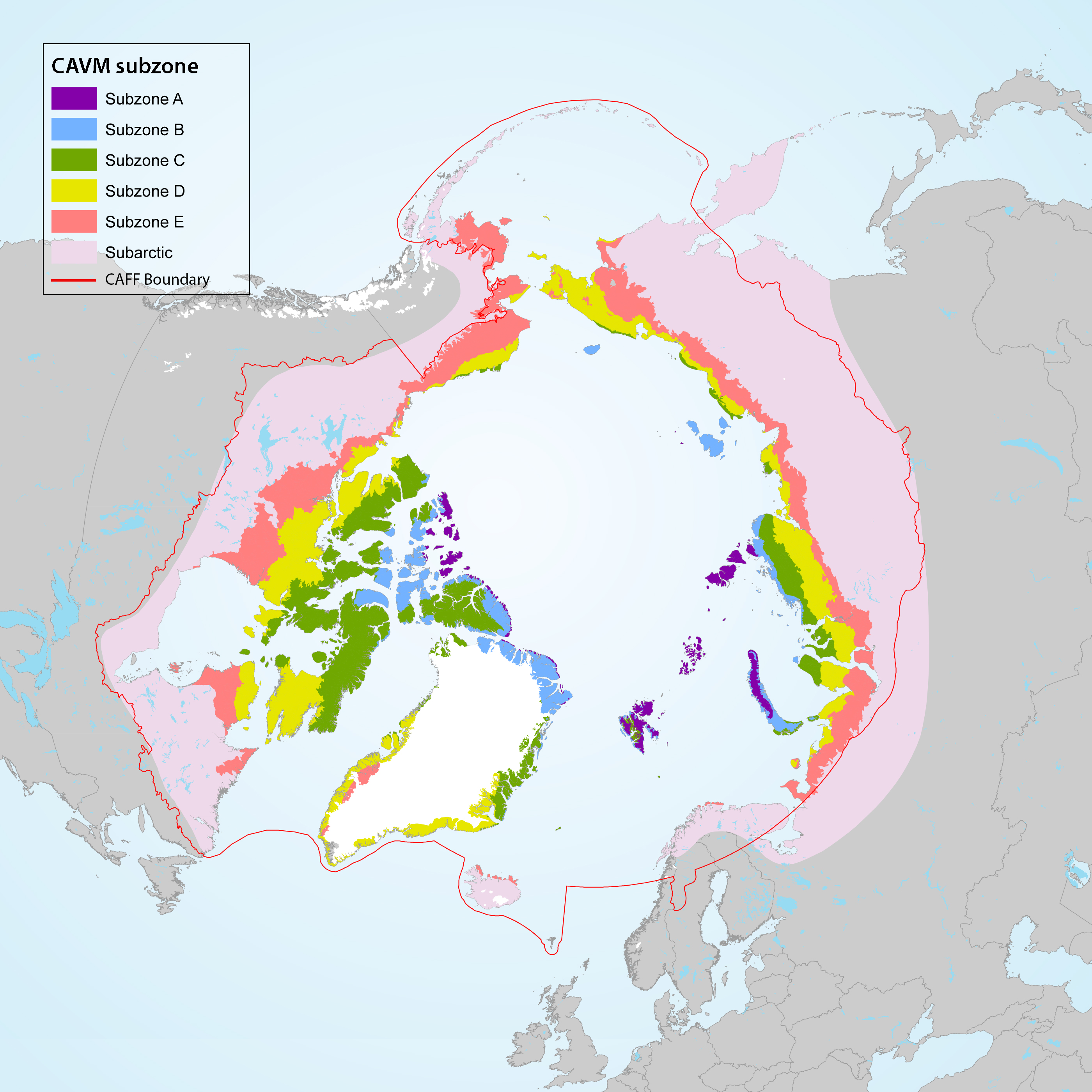
Geographic area covered by the Arctic Biodiversity Assessment and the CBMP–Terrestrial Plan. Subzones A to E are depicted as defined in the Circumpolar Arctic Vegetation Map (CAVM Team 2003). Subzones A, B and C are the high Arctic while subzones D and E are the low Arctic. Definition of high Arctic, low Arctic, and sub-Arctic follow Hohn & Jaakkola 2010. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 1 - Page 14 - Figure 1.2
-
Several smaller populations of caribou inhabit sub-Arctic portions of Alaska, including five populations along the Aleutian Archipelago and west coast. These populations are considered part of the migratory tundra ecotype based on genetics, although in some instances their ecology and habitat are similar to the mountain caribou ecotype found in western Canada. Population dynamics and trends for these populations are variable (Figure 3-29). They are managed by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game through hunting quotas. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 72 - Figure 3.29
-
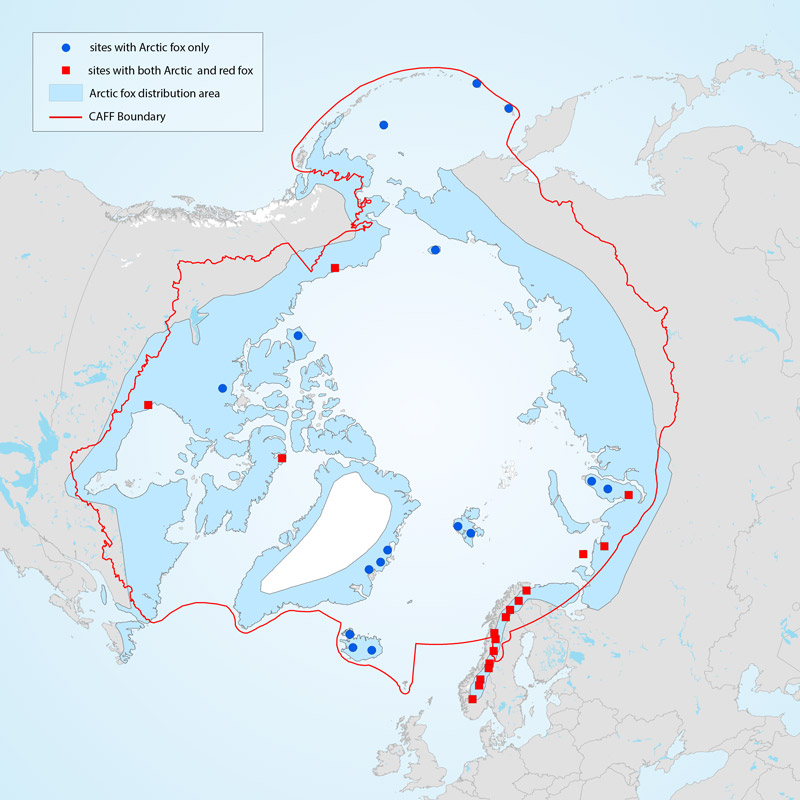
Arctic foxes are currently monitored at 34 sites throughout the North, with most monitoring efforts concentrated in Fennoscandia (Figure 3-32). The duration of monitoring across all sites is variable at between 2 and 56 years and was ongoing at 27 of the 34 sites (79%) as of 2015. Monitoring projects cover almost equally the four climate zones of the species’ distribution—high Arctic, low Arctic, sub-Arctic, and montane/alpine. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 82 - Figure 3.32
-
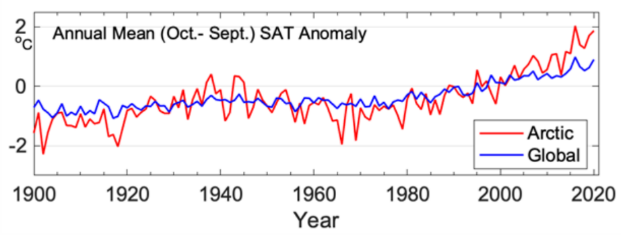
Warming in the Arctic has been significantly faster than anywhere else on Earth (Ballinger et al. 2020). Trends in land surface temperature are shown on Figure 2-2. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 2 - Page 23 - Figure 2.2
-
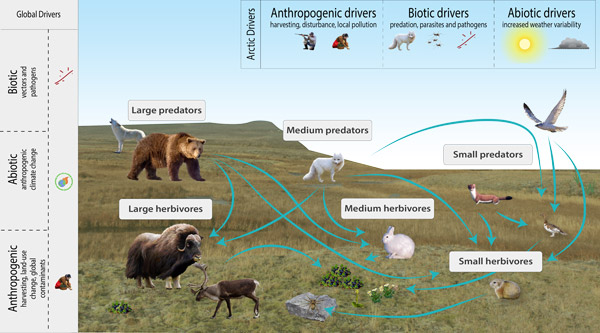
Conceptual model of Arctic terrestrial mammals, showing FECs, interactions with other biotic groups and examples of drivers and attributes relevant at various spatial scales. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 67 - Figure 3.28
-
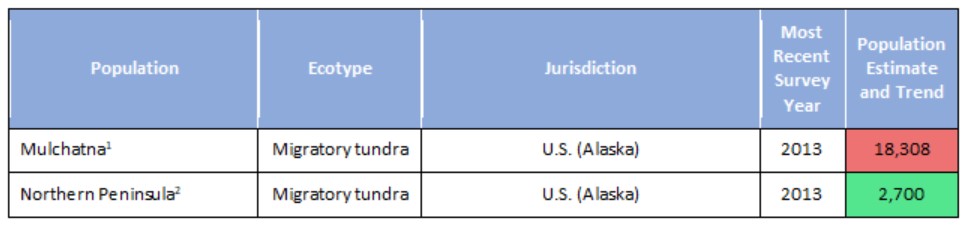
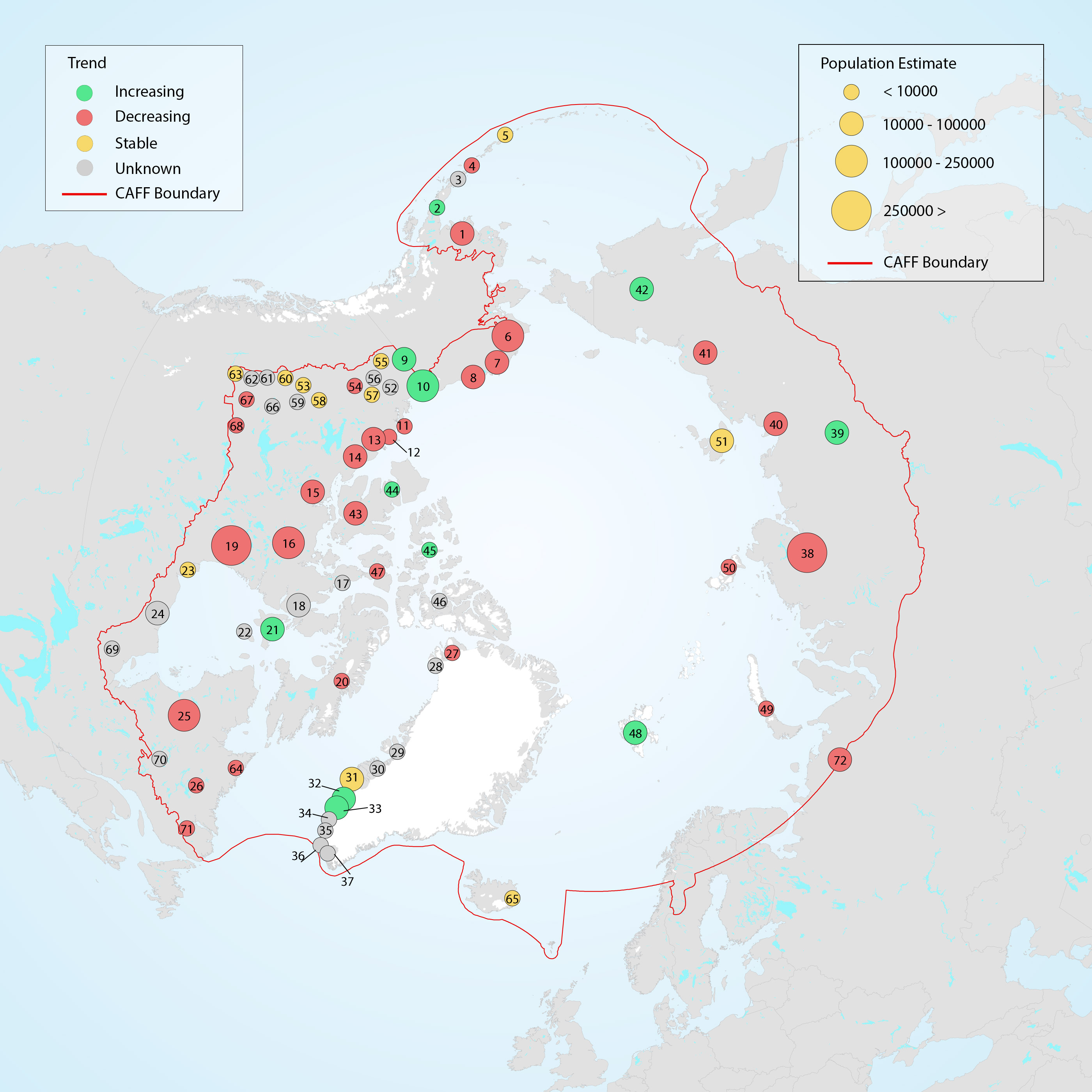
Population estimates and trends for Rangifer populations of the migratory tundra, Arctic island, mountain, and forest ecotypes where their circumpolar distribution intersects the CAFF boundary. Population trends (Increasing, Stable, Decreasing, or Unknown) are indicated by shading. Data sources for each population are indicated as footnotes. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 70 - Table 3.4
-
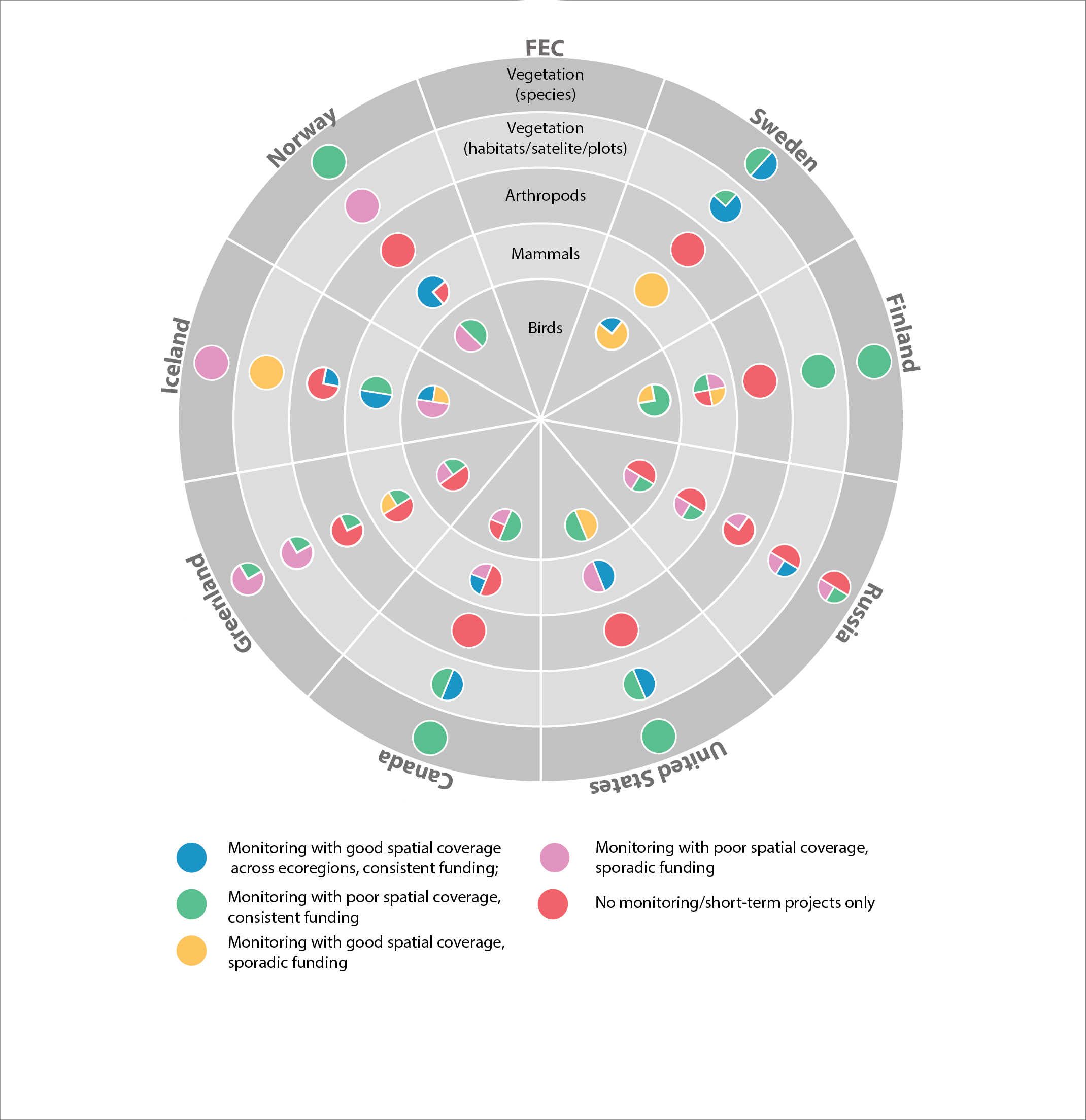
Current state of monitoring for Arctic terrestrial biodiversity FECs in each Arctic state. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 4 - Page 102 - Figure 4.1
-
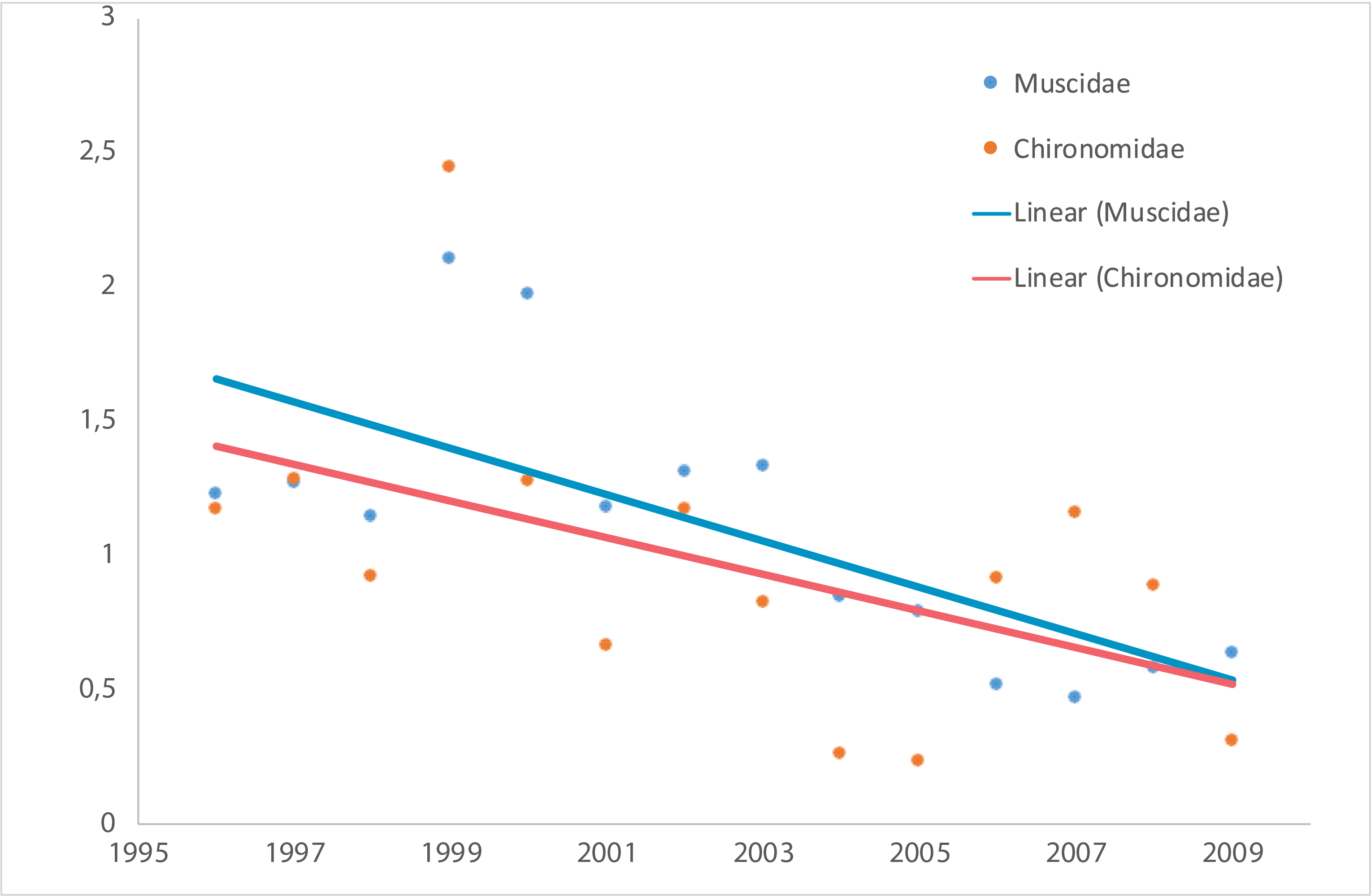
Temporal trends of arthropod abundance, 1996–2009. Estimated by the number of individuals caught per trap per day during the season from four different pitfall trap plots, each consisting of eight (1996–2006) or four (2007–2009) traps. Modified from Høye et al. 2013. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 41 - Figure 3.16
-
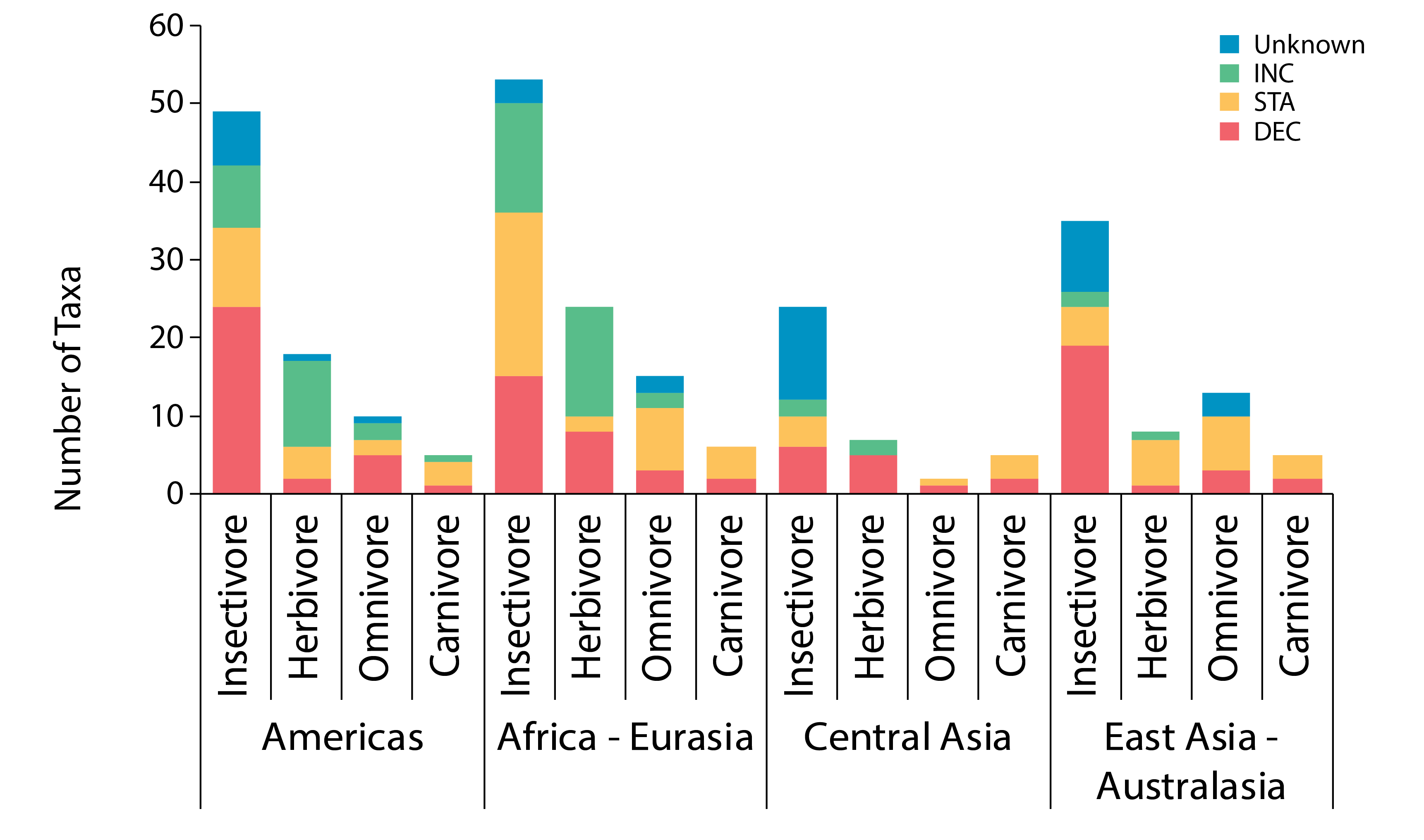
Regional differences are more pronounced in the insectivore guild (Figure 3-24). Although diversity of waders was moderate in the East Asian–Australasian Flyway, 88% (15 of 17) of taxa with known trends were declining—the largest proportion of any group. Both short-term (the last 15 years) and long-term (more than 30 years) trends were available for 157 taxa. Trends were unchanged over the two time periods for 80% of taxa, improved for 11% and worsened for 9%.. STATE OF THE ARCTIC TERRESTRIAL BIODIVERSITY REPORT - Chapter 3 - Page 56 - Figure 3.24
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)