MODIS
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
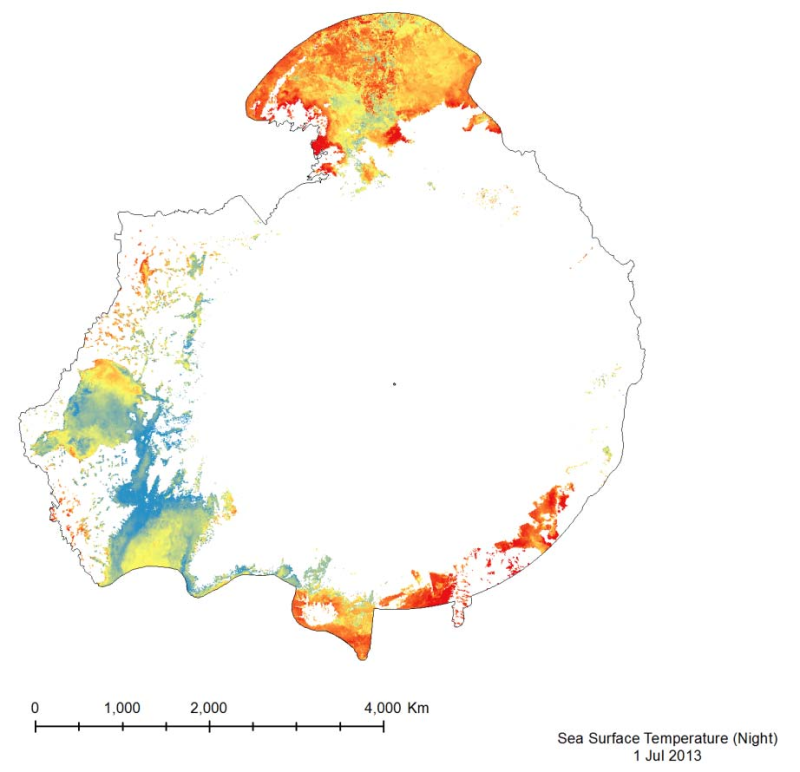
The MODIS Sea Surface Temperature (SST) product provided is a 4km spatialresolution monthly composite made from nighttime measurements from the Aqua Satellite.The nighttime measurements are used to collect a consistent temperature measurement that isunaffected by the warming of the top layer of water by the sun.
-
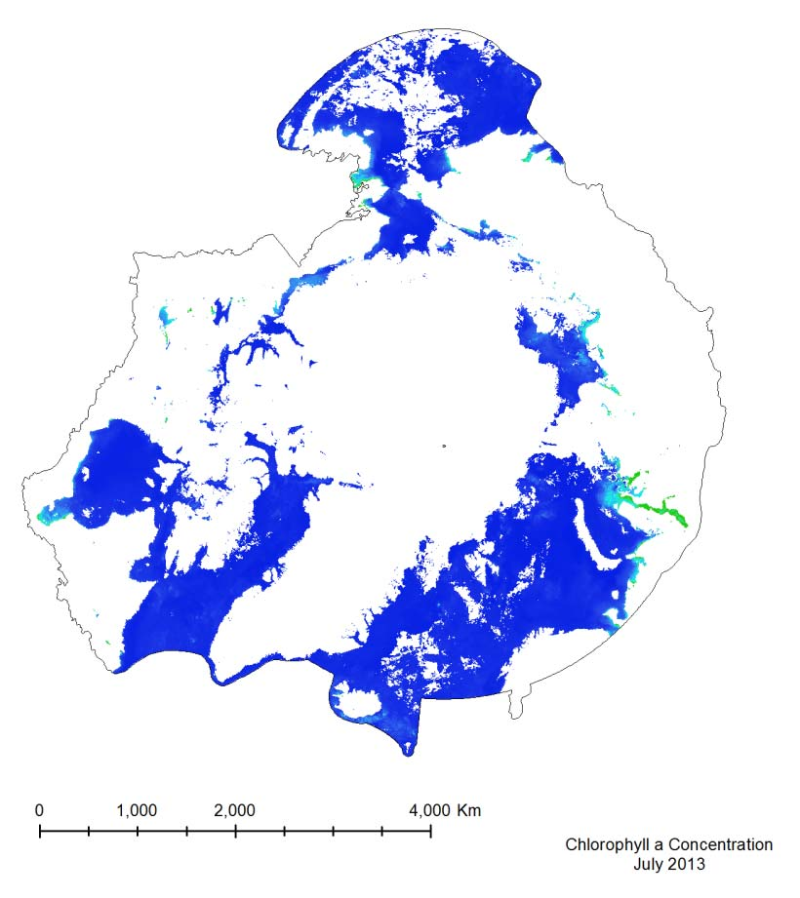
The MODIS marine chlorophyll a product provided, similar to SST, is a 4 km global monthly composite based on smaller resolution daily imagery compiled by NASA. The imagery is reliant on clear ocean (free of clouds and ice) so only months from March to October have been provided, as the chlorophyll levels in the Arctic diminish during the winter months, when sea ice is prevalent. The marine chlorophyll a is measured in mg/m3
-
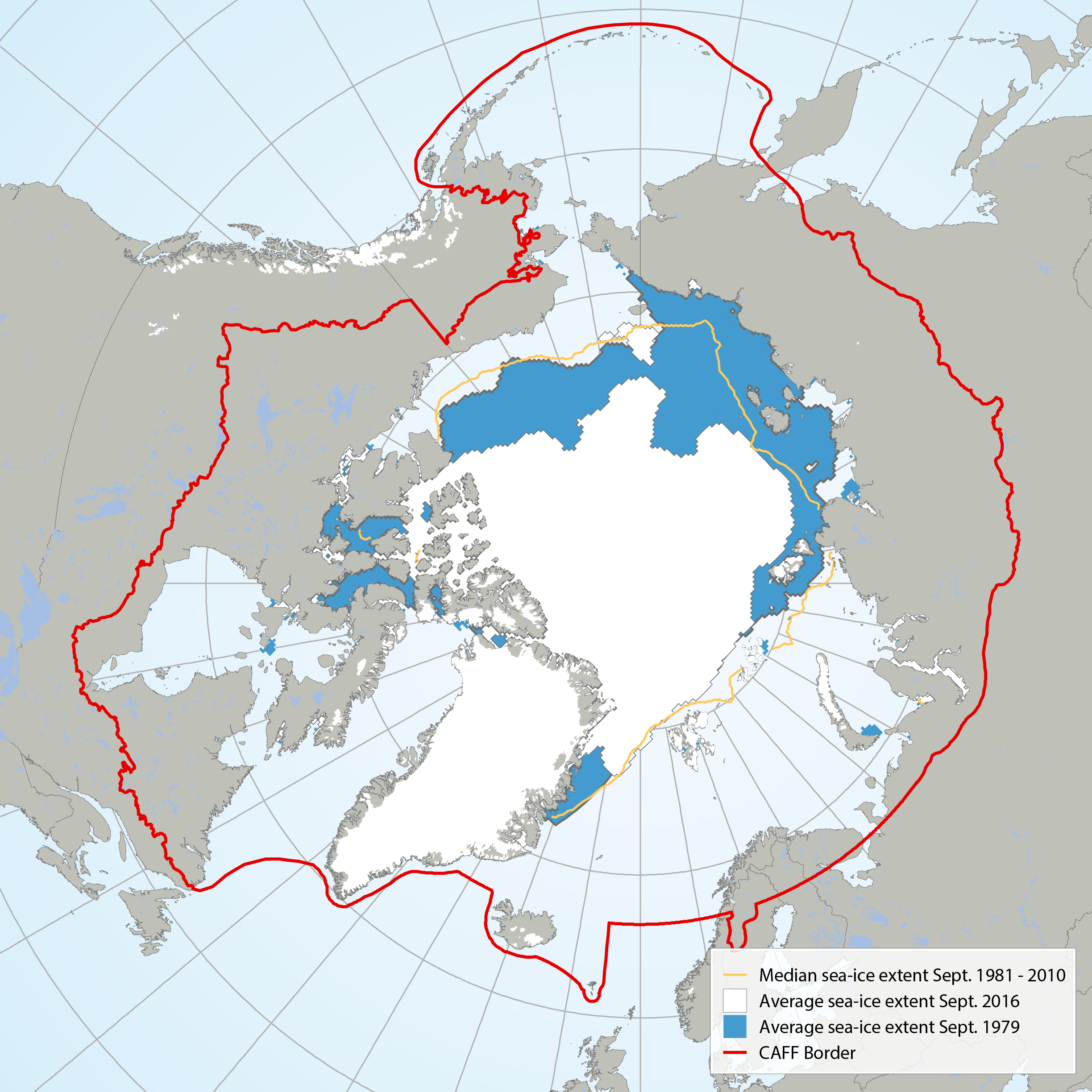
Average September sea ice extent in 1979 (blue) compared with 2016 (white) and the median sea ice extent (yellow line) from 1981 to 2010 (Data: NSDIC 2016). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 27 - Figure 2.4
-
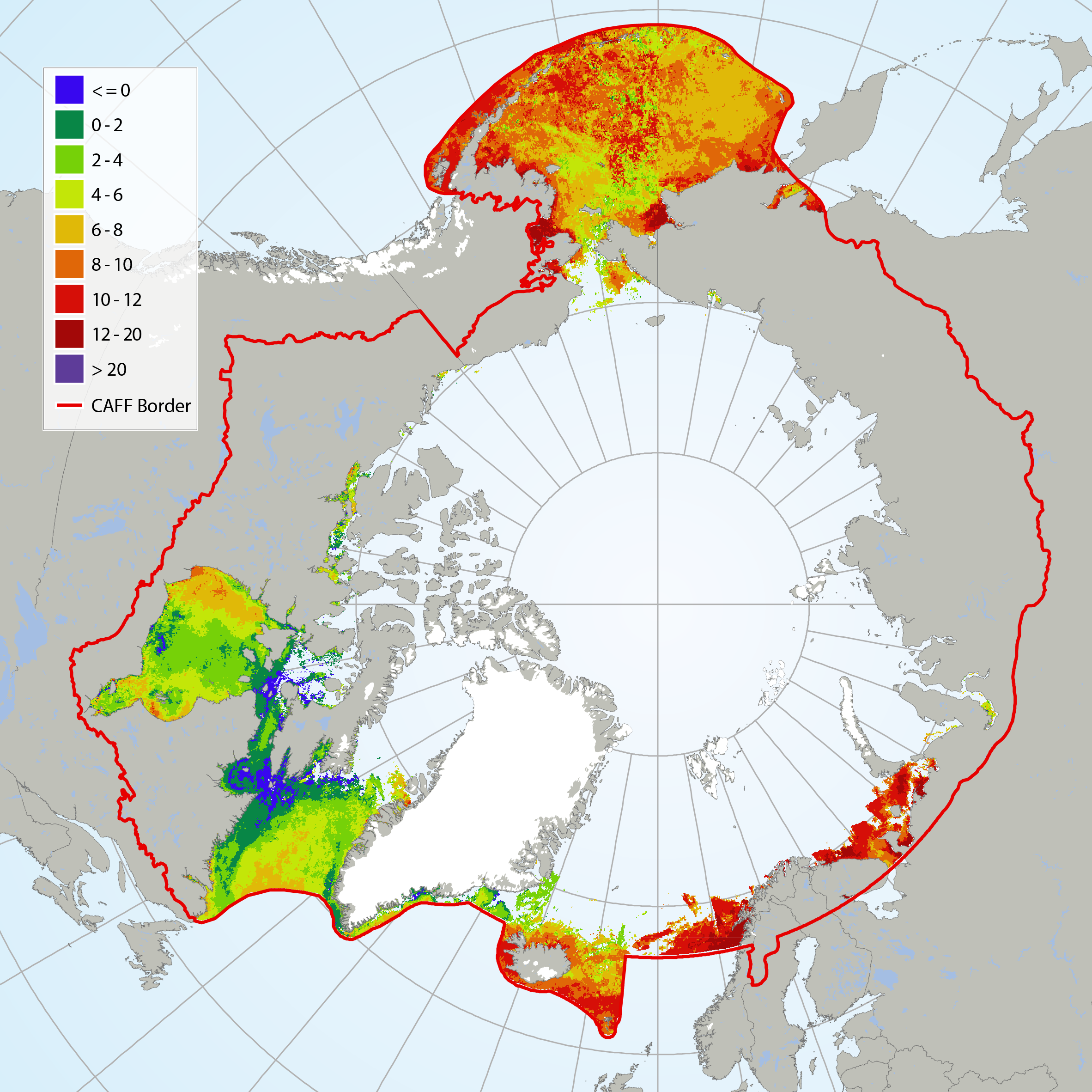
It has not been possible to identify available trend data for Arctic Ocean sea surface temperatures because there is not enough data to calculate reliable long-term trends for much of the Arctic marine environment (IPCC 2013, NOAA 2015). Here, sea surface temperature for July 2015 is shown from CAFF’s Land Cover Change Index. MODIS Sea Surface Temperature (SST) provided a four-kilometre spatial resolution monthly composite snapshot made from night-time measurements from the NASA Aqua Satellite. The night-time measurements are used to collect a consistent temperature measurement that is unaffected by the warming of the top layer of water by the sun. STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 25 - Figure 2.3
-
The Land Cover Dynamics MODIS product is a yearly product that represents thetiming of vegetation phenology globally. Sub-datasets include vegetation growth, maturity,senescence, and dormancy. This product also includes the NBAR-(Nadir Bidirectionalreflectance distribution function (BRDF) adjusted Reflectance) based EVI, in part becausethe EVI is used to create the Land Cover Dynamics. The Land Cover Dynamics product uses both Terra and Aqua MODIS data. Version005 (provided) has a 500 m spatial resolution, which is an improvement from the 1,000 mversion 004 product. This product is only available in MODIS tiles, so the tiles needed tocover the CAFF pan-Arctic region has been downloaded but not clipped to the pan-Arcticextent at this time.
-
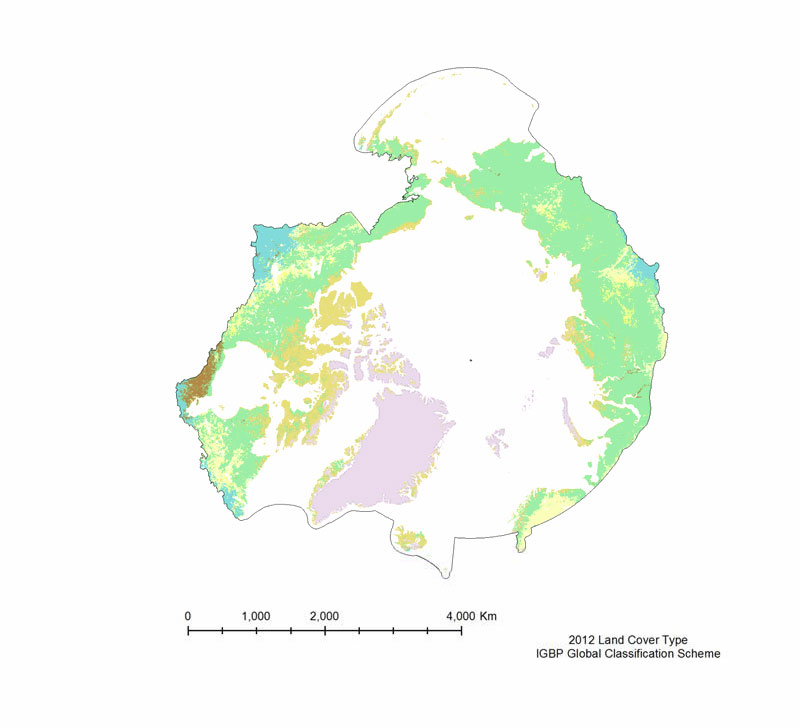
The MODIS Land Cover Type product is created yearly using three landclassification schemes; the International Geosphere Biosphere Programme (IGBP)classification scheme, the Univertiy of Maryland (UMD) classification scheme, and aMODIS-derived Leaf Area Index /Fraction of Photosynthetically Active Radiation(LAI/fPAR) classification scheme (Table 3). The International Geosphere Biosphere Programme (IGBP) identifies seventeenland cover classes, including eleven natural vegetation classes, three non-vegetated landclasses, and three developed land classes. The product provided is derived using the samealgorithm as the 500 m Land Cover Type (MOD12Q1), but is on a 0.05° Climate Model Grid(CMG), that has been clipped to the pan-Arctic extent. The UMD classification scheme issimilar to the IGBP classification scheme, but it excludes the Permanent wetlands,Cropland/Natural vegetation mosaic, and the Snow and ice classes. The LAI/fPARclassification scheme is the smallest of the three, and focuses on forest structure; it only haseleven classes. All three land cover classification schemes are provided, but the IGBPclassification scheme is the most amenable to the Pan-Arctic region.
-
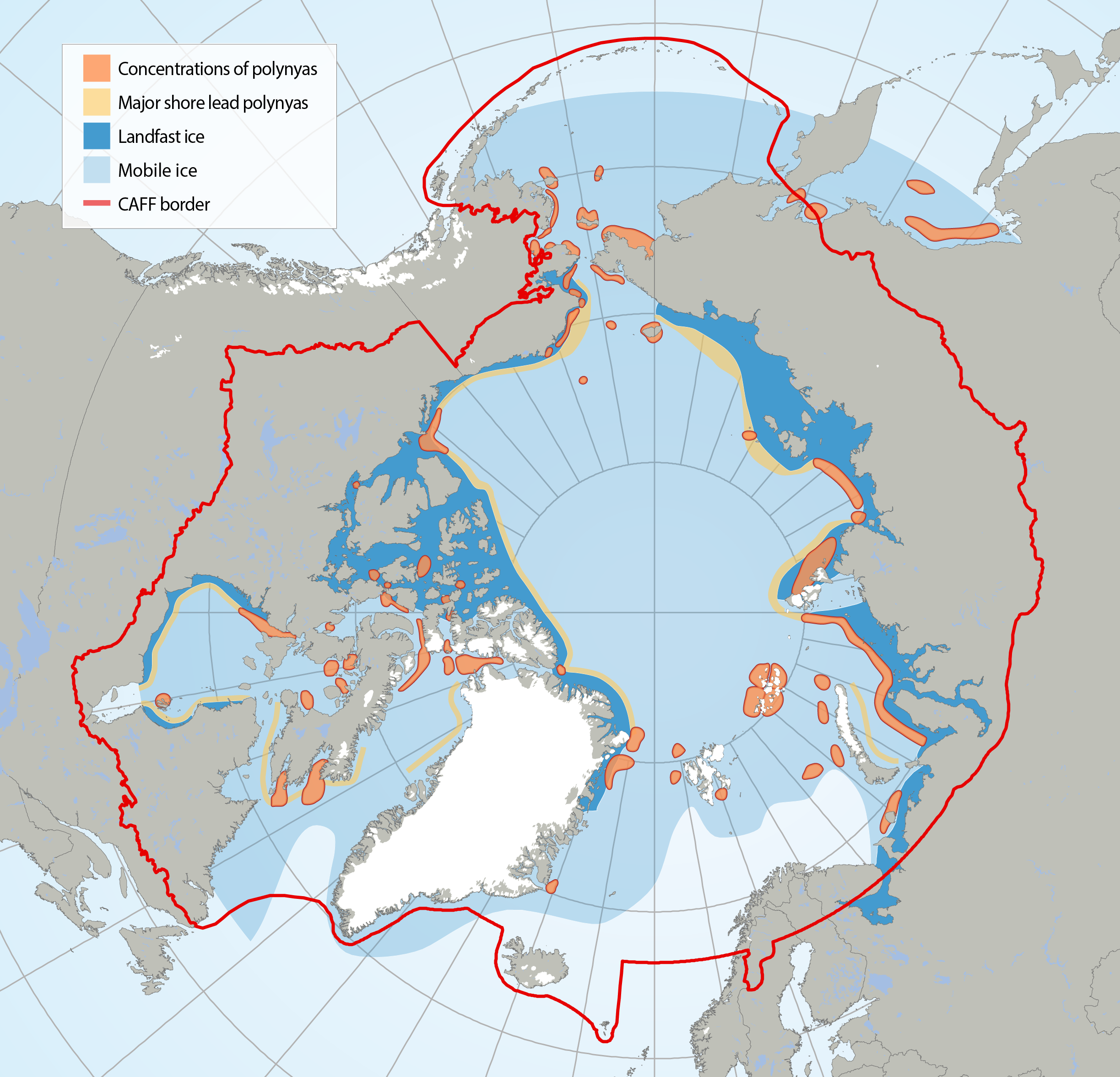
Circumpolar map of known polynyas. Note that polynyas are dynamic systems and some may no longer exist in the form known from their recent history. Adapted from Meltofte (2013) and based on Barber and Massom (2007). STATE OF THE ARCTIC MARINE BIODIVERSITY REPORT - <a href="https://arcticbiodiversity.is/marine" target="_blank">Chapter 2</a> - Page 28 - Figure 2.5
-
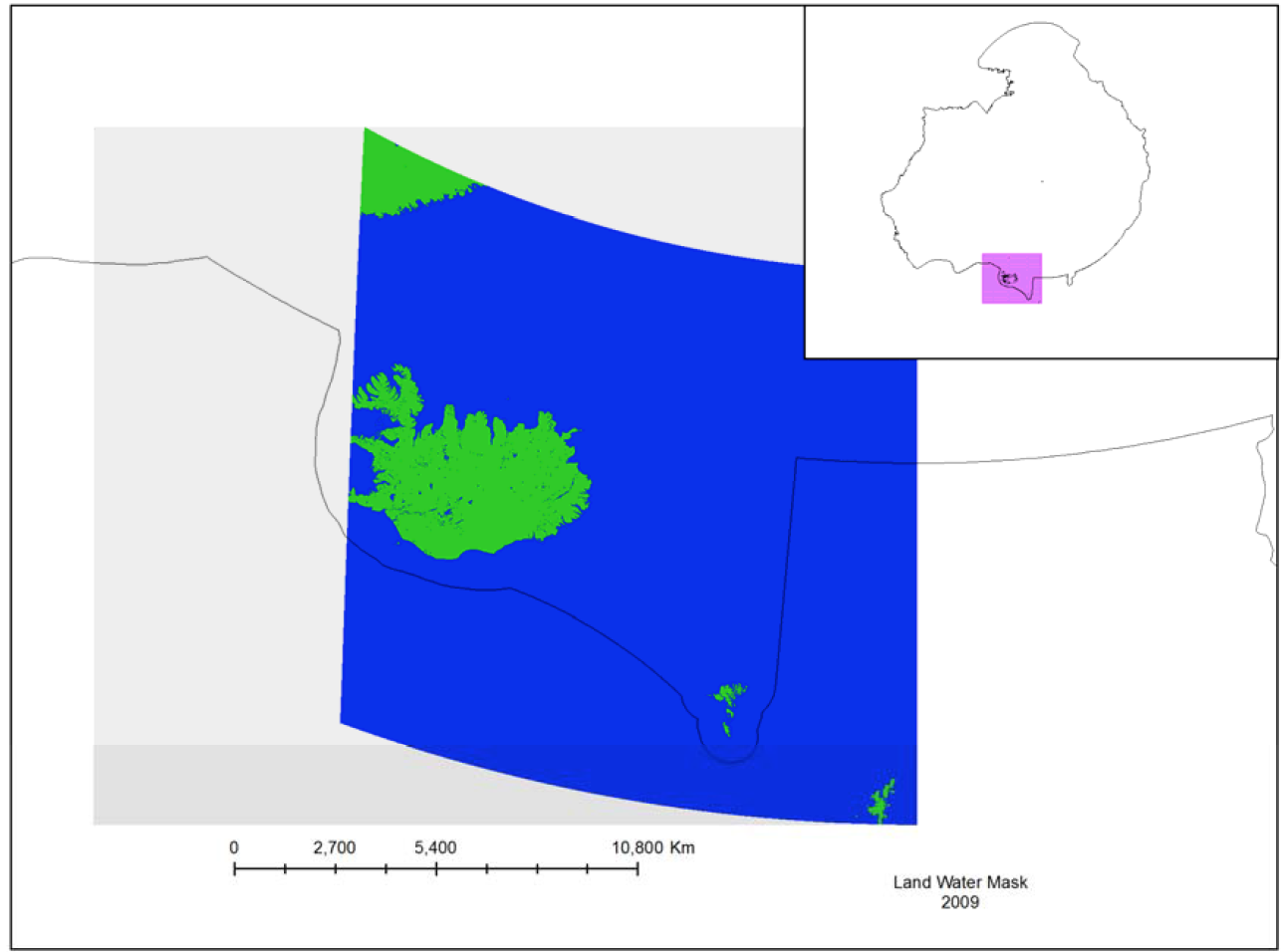
The MODIS Land Water Mask is created from MODIS 250 m imagery incombination with Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) Water Body Data (SWBD) tocreate a global map of surface water at 250 m spatial resolution. Currently, only one mapexists, created in 2009 by Carroll et al. (2009). Because only one MODIS-based map exists,an analysis of surface water change is not possible at this time.
 CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)
CAFF - Arctic Biodiversity Data Service (ABDS)